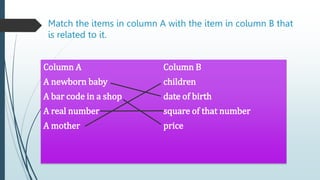
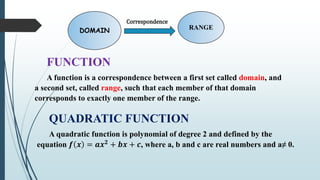
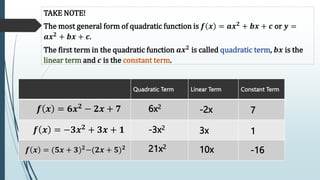
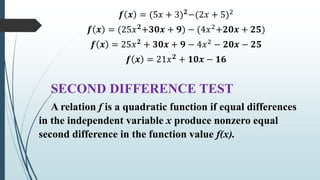
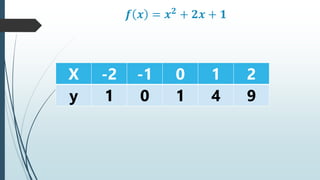
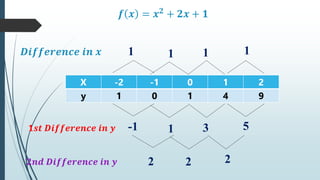
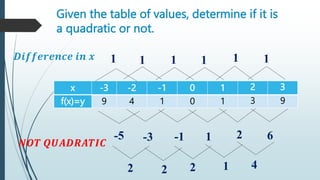
This document provides information about quadratic functions including:
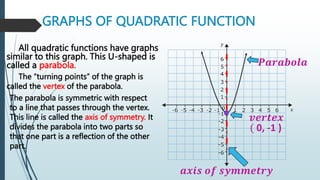
1. Quadratic functions have graphs that form a U-shaped curve called a parabola with a single turning point called the vertex.
2. The axis of symmetry of the parabola passes through the vertex and divides the graph into two symmetrical parts.
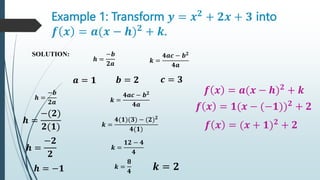
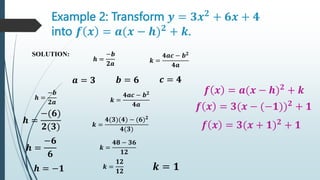
3. Quadratic functions can be transformed between the standard form f(x)=ax^2 + bx + c and the vertex form f(x)=a(x-h)^2 + k using completing the square. This allows finding the vertex (h,k) of the parabola.
4. Examples show how to transform quadratic functions between the standard and vertex