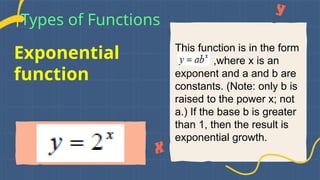
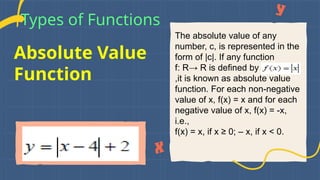
This document covers evaluating functions and types of mathematical functions including constant, identity, polynomial, quadratic, cubic, power, rational, exponential, logarithmic, absolute value, and greatest integer functions. It explains the evaluation process through substitution and the operations involved. Each function type is defined with its general form and examples provided for better understanding.




![Greatest Integer
Function
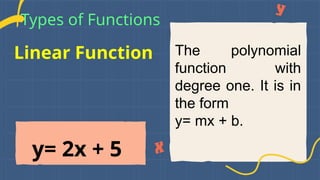
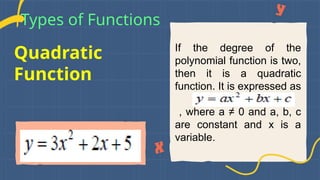
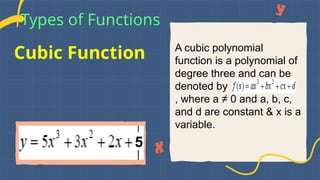
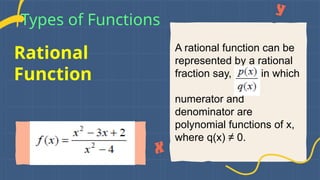
Types of Functions
If a function f: R→ R is
defined by f(x) = [x], x ∈
X, round-off it to the
integer less than the
number. Suppose that the
given interval is in the
form of
(x, x+1), the value of
greatest integer function is
x which is an integer.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/module2evaluatingfunctions-241214060748-10ca11a9/85/MODULE-2-Evaluating-Functions-and-Word-Problems-pptx-15-320.jpg)











