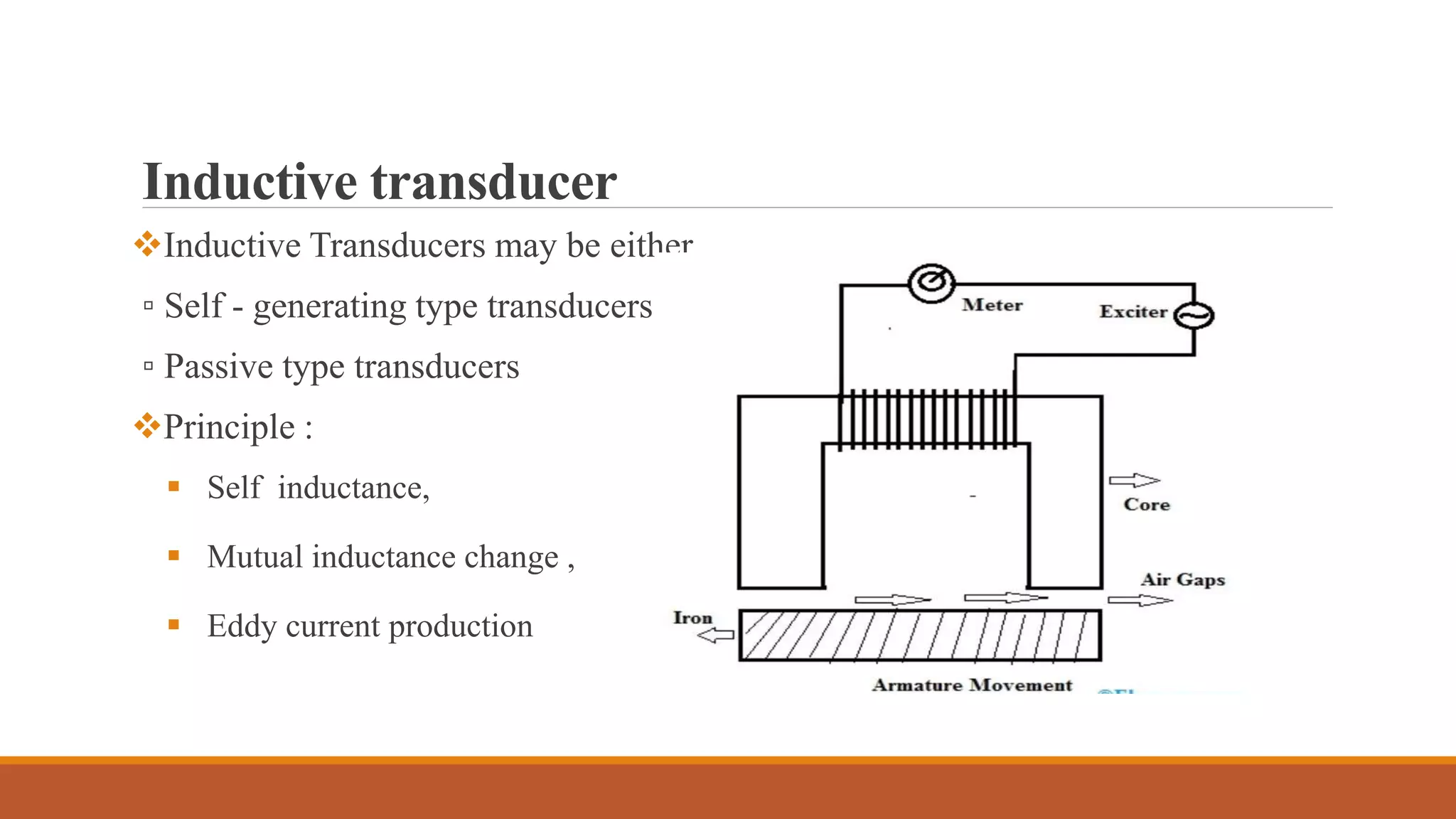
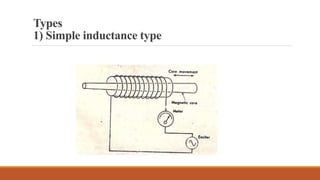
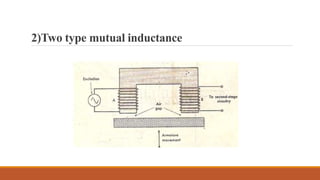
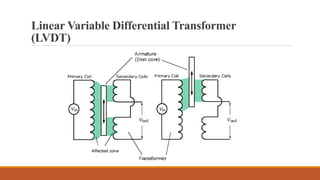
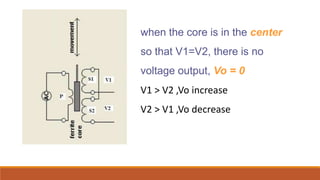
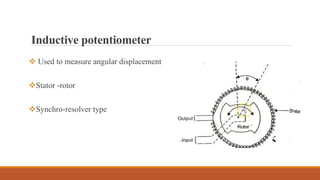
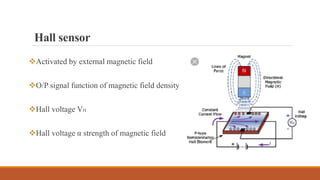
Inductive transducers can be either self-generating or passive types that use principles of self-inductance, mutual inductance change, or eddy current production to measure displacement, position, motion, or presence of metals. They have advantages of high responsivity and insensitivity to load effects but disadvantages of reduced operating range due to side effects and sensitivity to temperature and magnetic fields. Common applications include detection of metals, touch pads, position and motion measurement.