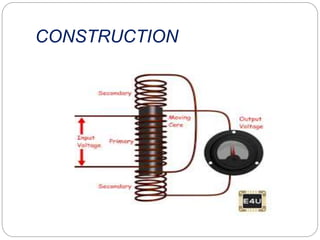
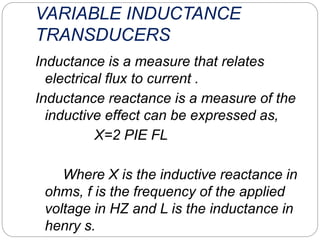
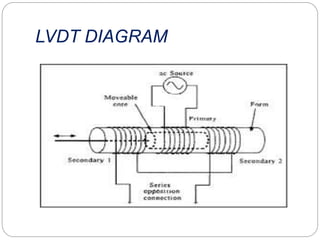
This document discusses inductive transducers, specifically Linear Variable Differential Transformers (LVDTs). LVDTs are inductive transducers that measure displacement as a change in voltage by detecting changes in inductance caused by physical motion. They work by converting physical motion into a change in inductance based on factors like the number of turns, geometry, and permeability of magnetic materials. LVDTs have advantages like high sensitivity, ability to operate at high frequencies, lack of sliding contacts, and low power consumption, but disadvantages such as requiring large displacements, sensitivity to stray magnetic fields and vibrations, and performance changes with temperature.