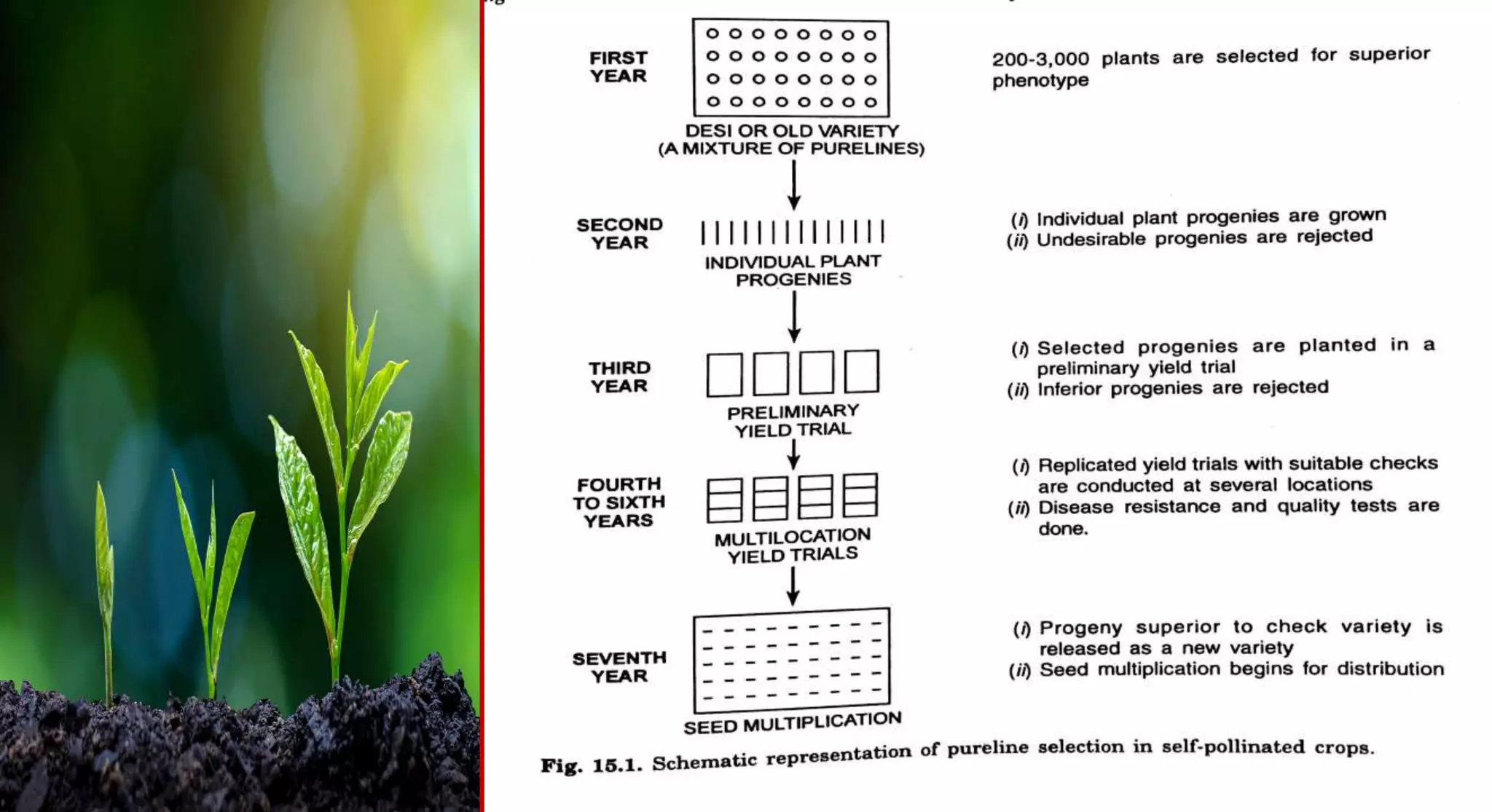
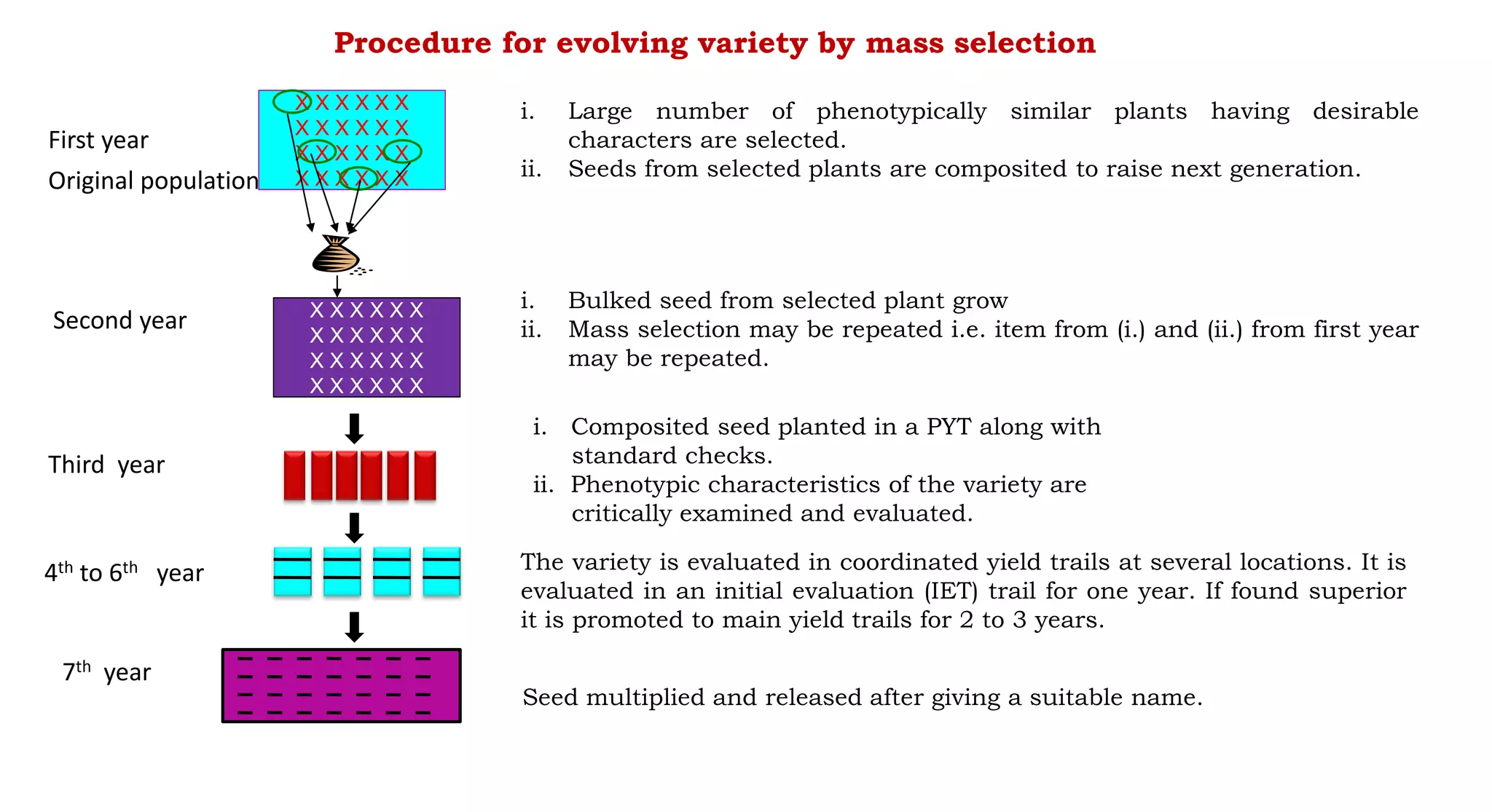
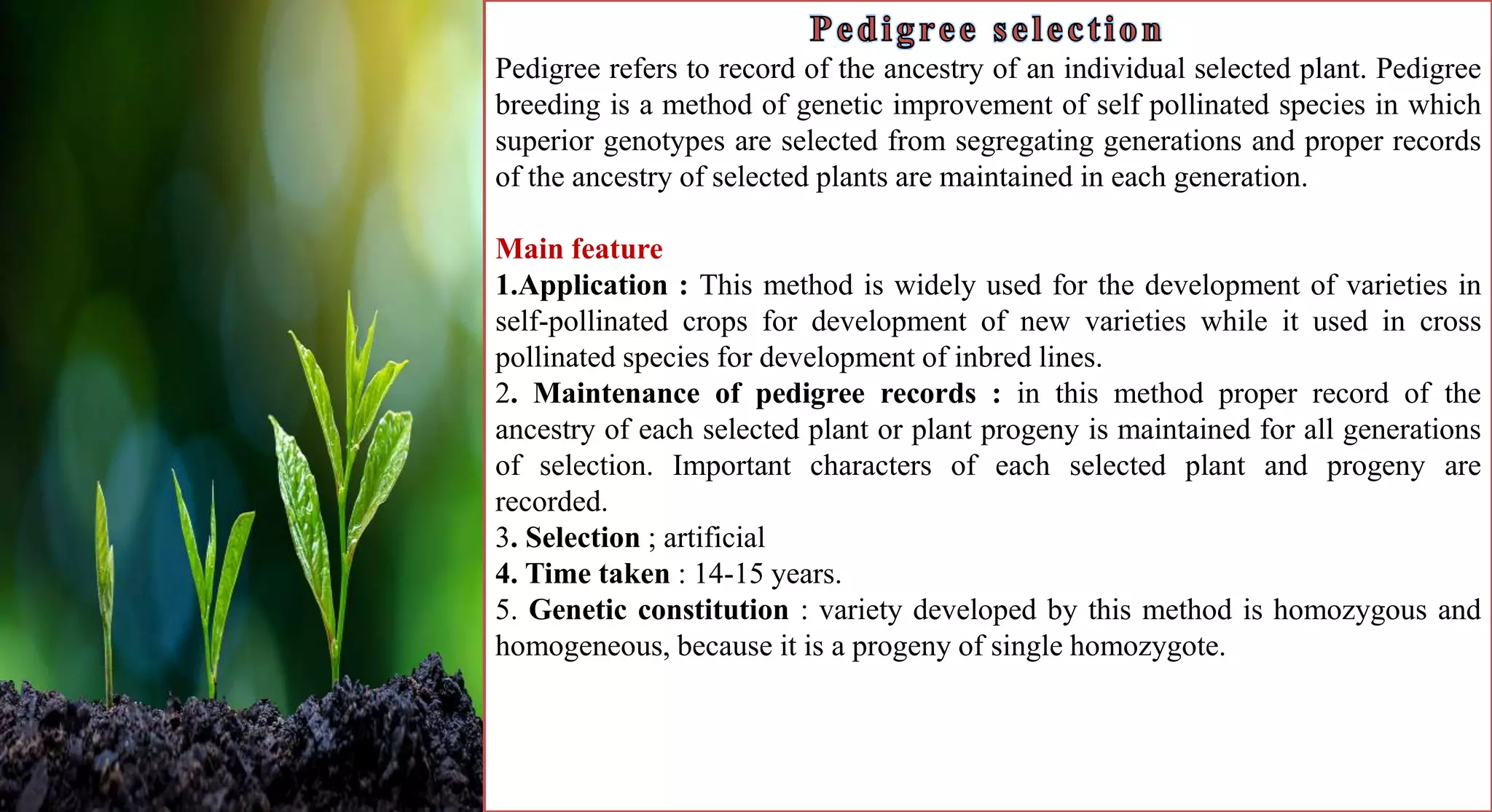
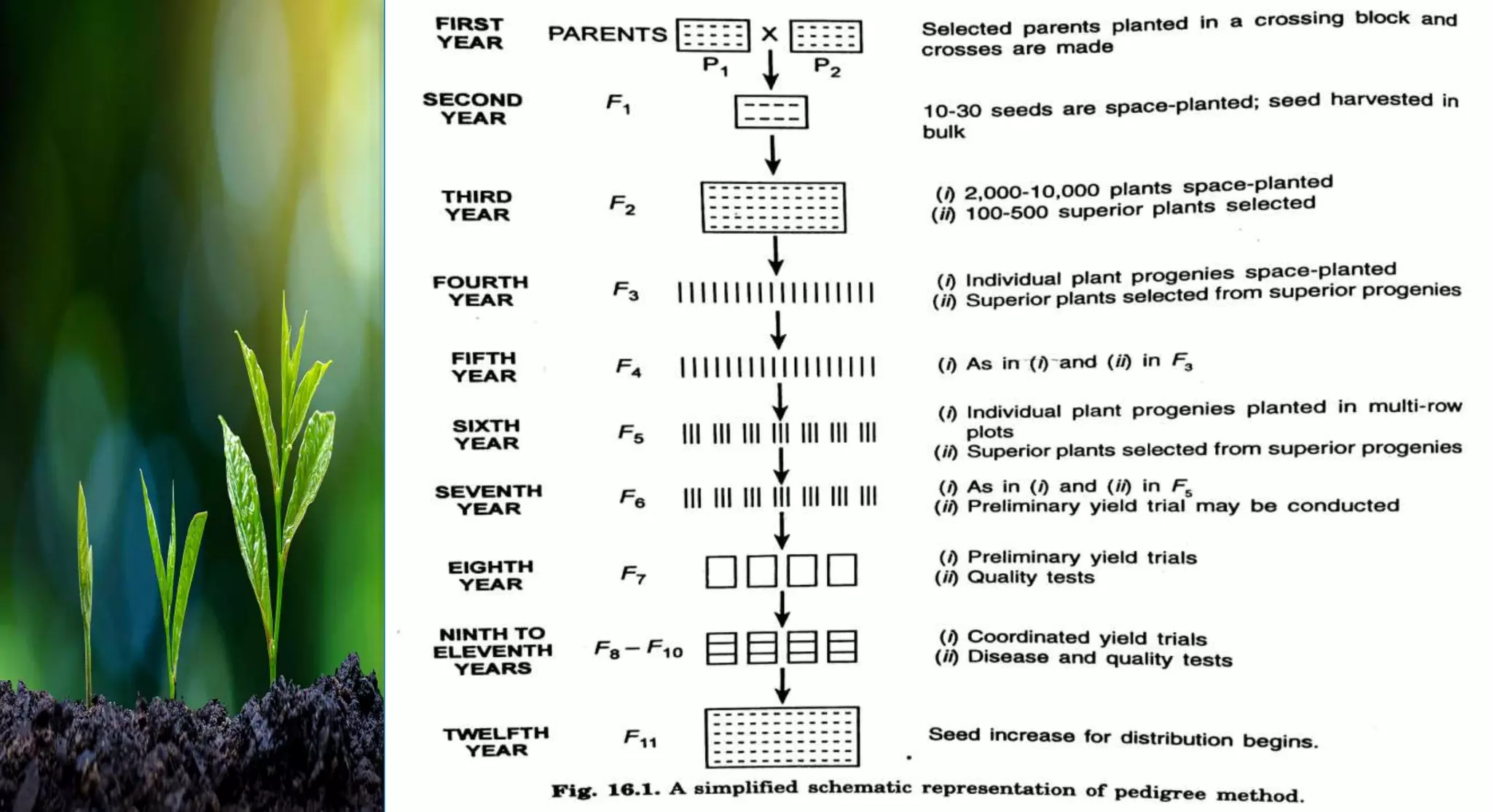
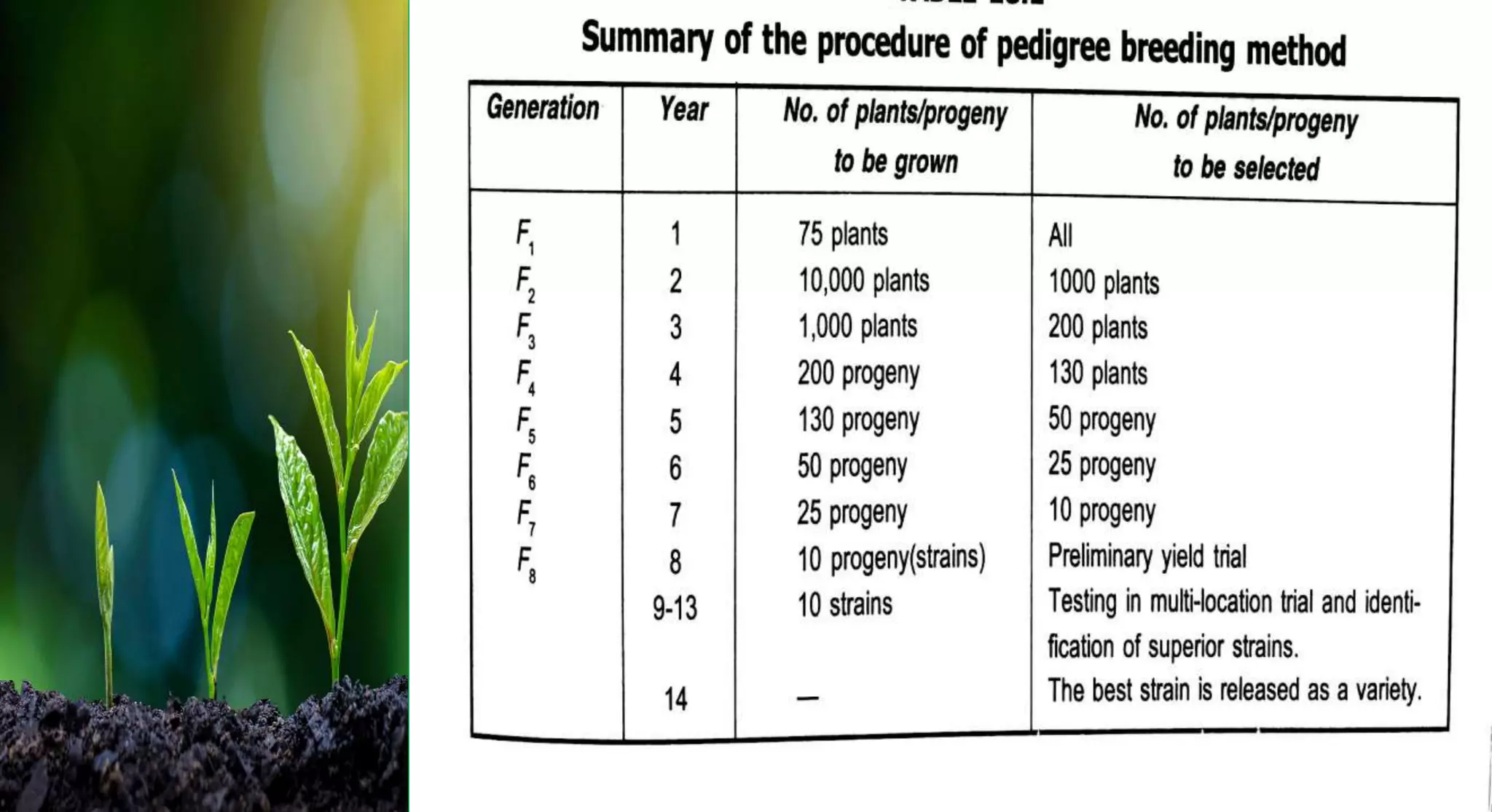
This document discusses different selection methods used in self-pollinating crops, including pure line selection, mass selection, and pedigree selection. Pure line selection involves selecting the best individual plants and propagating their progeny to create homogeneous varieties. Mass selection selects many plants with desirable traits and mixes their seeds to create heterogeneous varieties with wider adaptation. Pedigree selection maintains records of each selected plant's ancestry over multiple generations to develop homogeneous, homozygous varieties taking 14-15 years.