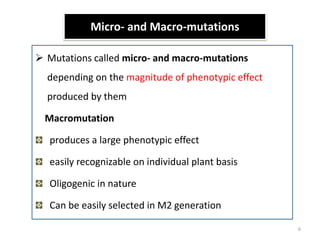
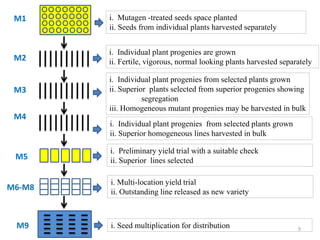
Mutation breeding involves deliberately inducing mutations in plant varieties to generate genetic diversity for crop improvement. The document discusses the history, techniques, and achievements of mutation breeding. It describes how mutations can be induced using physical or chemical mutagens and the procedures for handling segregating populations. Mutation breeding has been used to develop improved varieties with traits like increased yield, abiotic/biotic stress resistance, and quality. India has released many successful mutant crop varieties, especially in rice and chickpeas, through research centers like IARI. While mutation breeding can lead to quick gains, it also has limitations like unpredictability and costs of screening large populations.

























![Number of mutant varieties released in the
world
https://mvd.iaea.org/#!Search?page=1&size=15&sortby=Name&sort=ASC&Criteria[0][f
ield]=Country&Criteria[0][val]=136 28](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mutationbreedingppt-161203184149/85/Mutation-breeding-ppt-28-320.jpg)












