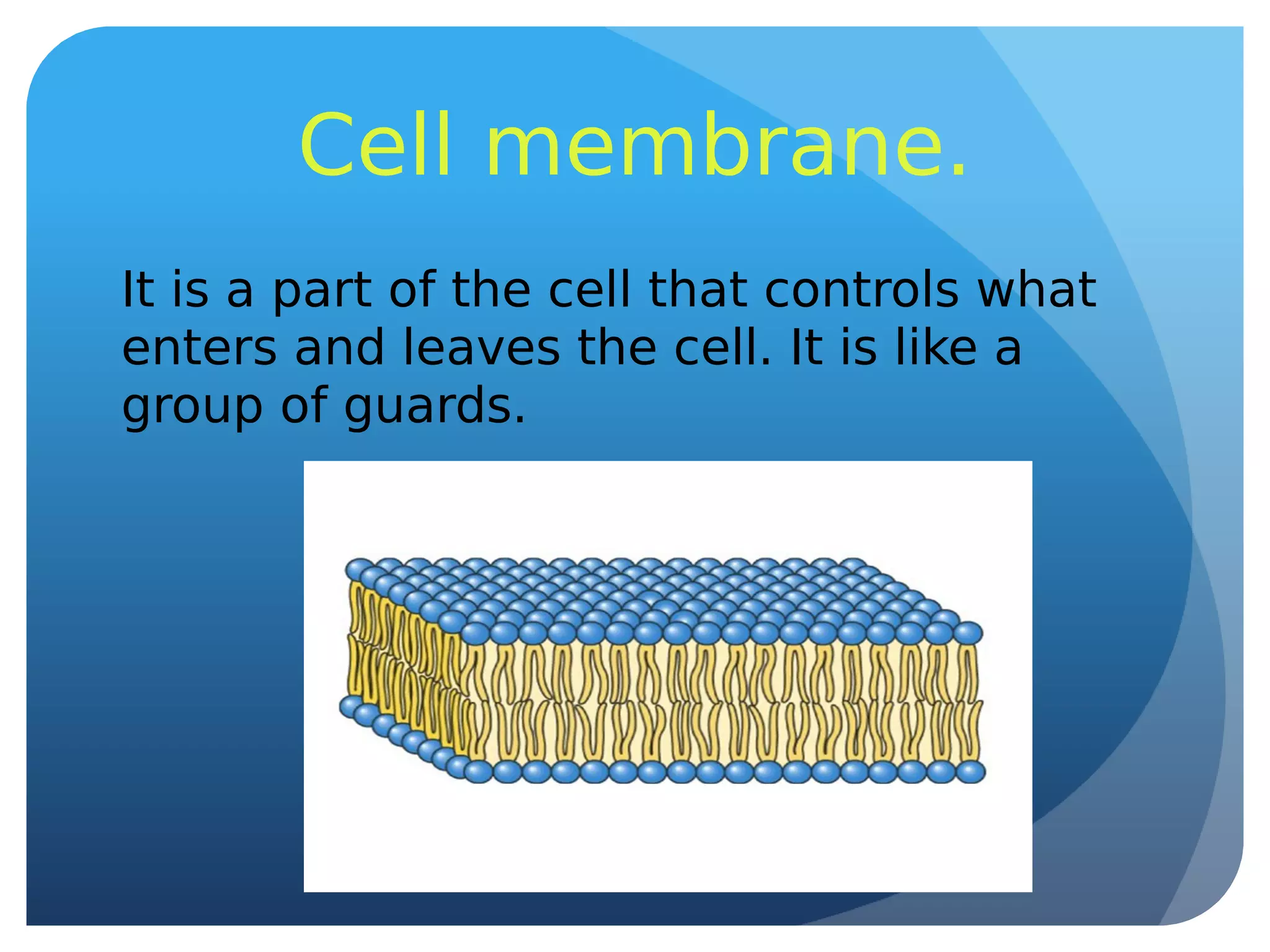
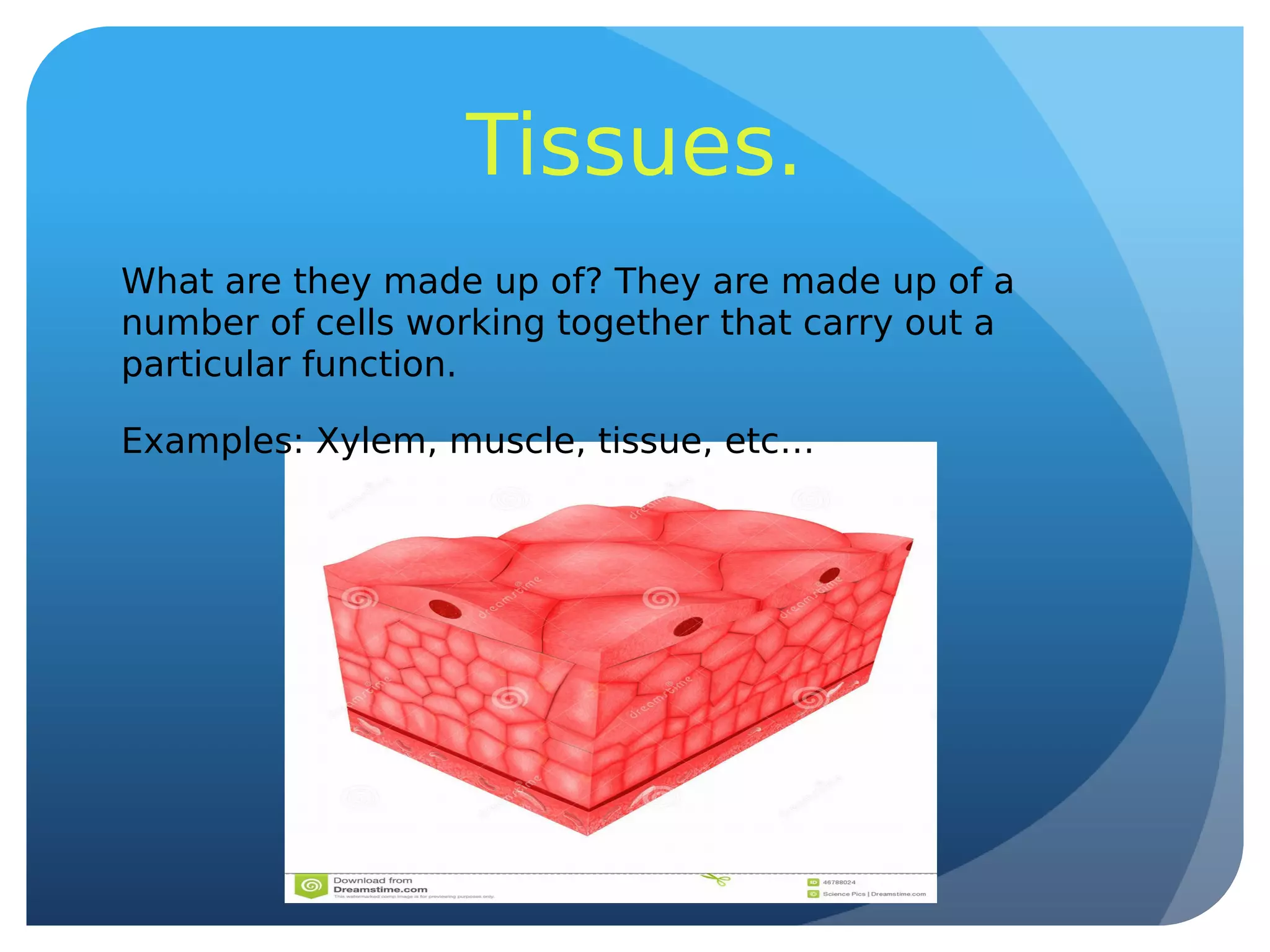
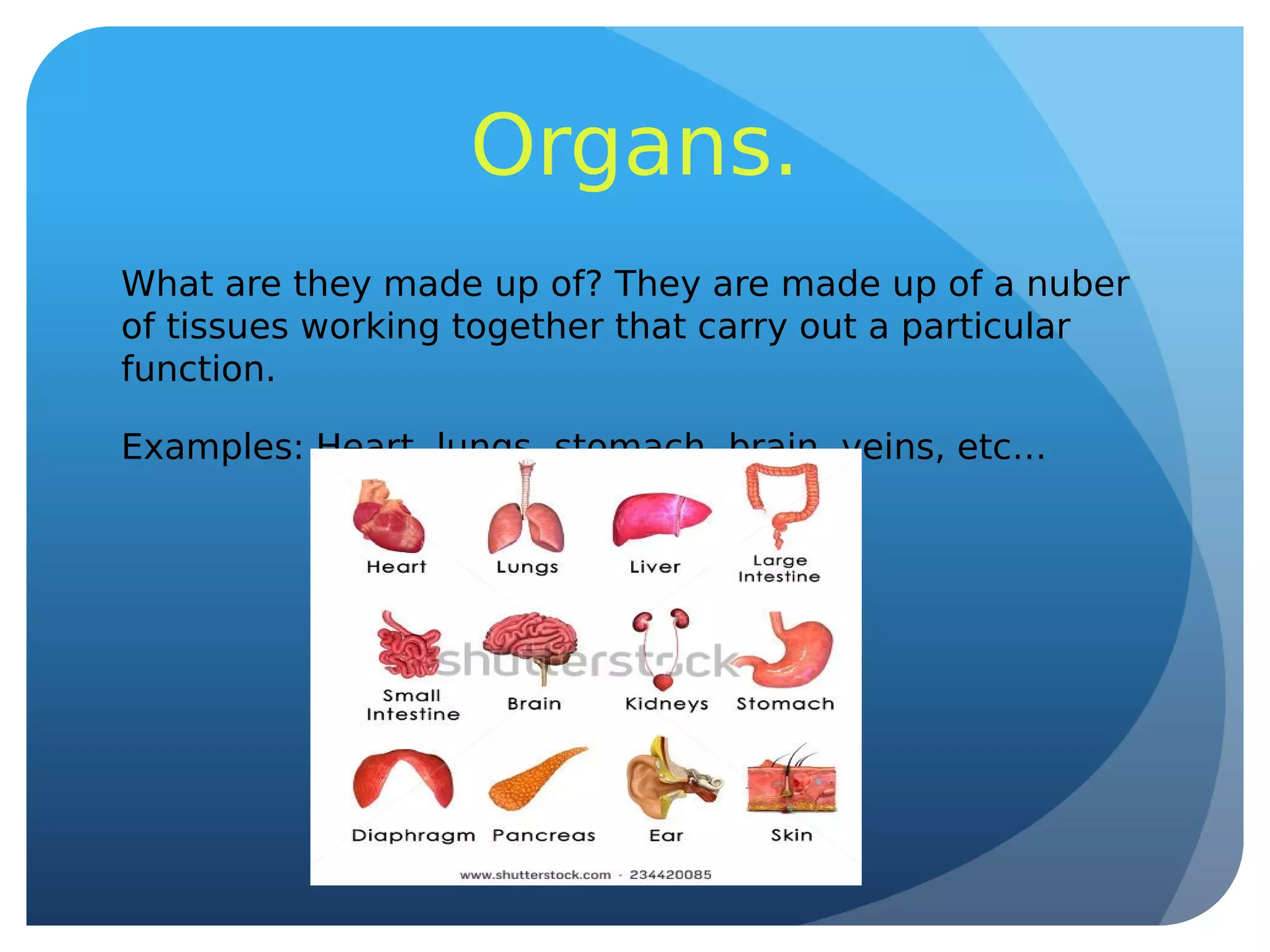
This document summarizes key aspects of living things, including their vital functions of nutrition, reproduction, and interaction with the environment. It describes the structures and functions of cells, tissues, organs, systems, and whole organisms. It also explains the processes of photosynthesis, nutrition in plants and animals, and asexual and sexual reproduction.