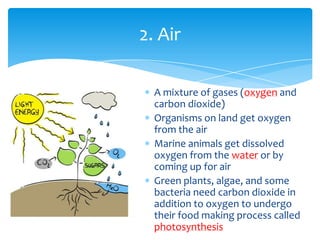
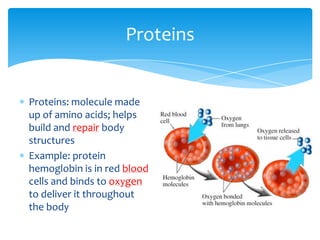
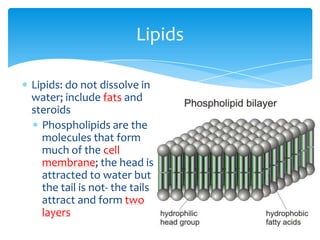
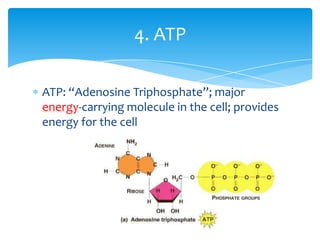
There are 6 key characteristics of living things: 1) cells, 2) response to stimuli, 3) reproduction, 4) DNA, 5) metabolism, and 6) growth and development. All living things also require 4 basic necessities to survive: water, air, food, and shelter. Within cells, there are 5 main types of molecules that serve as building blocks: proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, ATP, and nucleic acids. Each plays an important role in the structure and functions of living organisms.