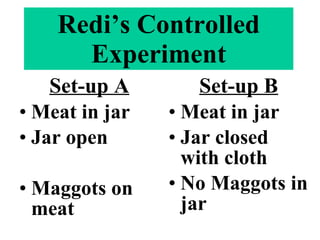
All living things share several key characteristics: they are made of cells, use energy, respond to their environments, grow and develop, and reproduce. Francesco Redi conducted controlled experiments in the 1600s which disproved the idea of spontaneous generation and showed that living things only come from other living things, not non-living sources. All living things need certain basic requirements to survive including energy, water, living space, and stable internal conditions.