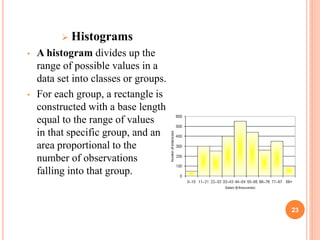
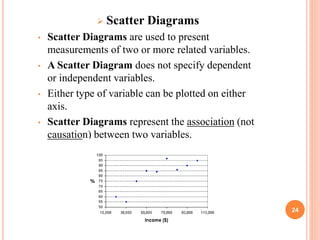
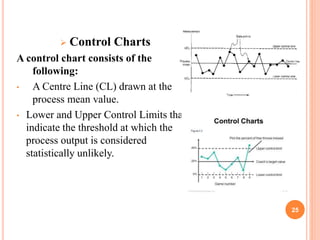
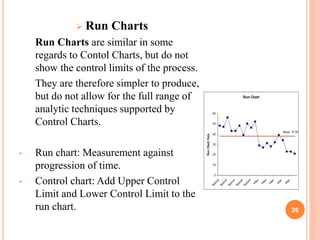
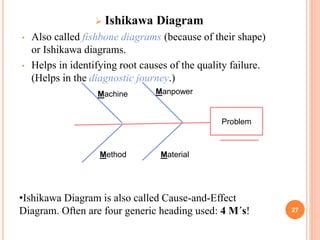
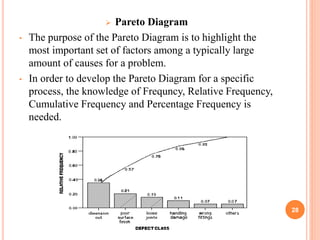
The document discusses key concepts of quality management including definitions of quality, customers, products, and total quality management. It outlines 8 principles of total quality management focusing on customer satisfaction, leadership, employee involvement, and continual improvement. The document also describes 7 common process improvement tools used in quality management including check sheets, histograms, control charts, scatter diagrams, Ishikawa diagrams, Pareto diagrams, and run charts.