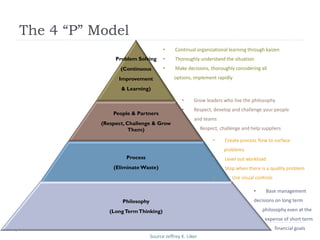
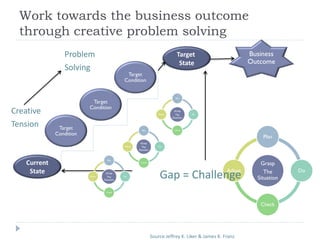
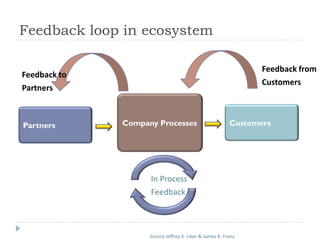
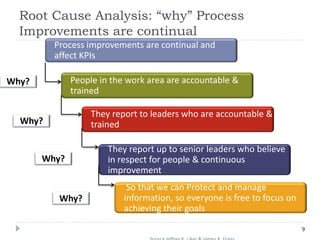
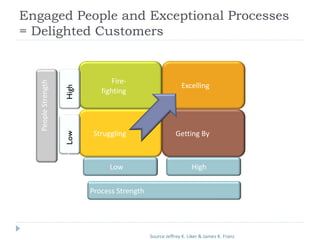
The document outlines the Toyota Way principles and methodologies for continuous improvement, emphasizing the '4P' model which includes process, people, problem-solving, and philosophy. It details the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Adjust) problem-solving framework and the importance of feedback loops in companies to enhance business outcomes and customer satisfaction. Key themes include fostering a culture of respect, continuous learning, and long-term thinking amidst process improvements.