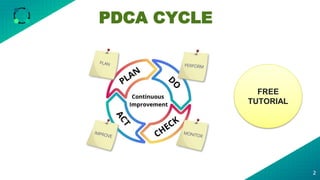
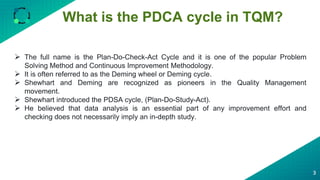
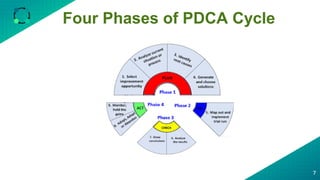
The document discusses the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle, which is a popular problem-solving and continuous improvement methodology. It describes the four steps of the cycle as Plan, Do, Check, Act. Each step is then further broken down into sub-steps or phases. For example, the Plan step involves selecting an improvement opportunity, analyzing the current situation, identifying root causes, and generating and choosing solutions. The document provides examples and explanations of how to implement each phase of the PDCA cycle for process improvement. It also lists some useful tools that can be used with the PDCA cycle and highlights benefits such as encouraging problem-solving, testing solutions before implementation, and bringing organizations closer to their goals through




![[1] Select Improvement Opportunity:
9
Generate a list and select
Redefine team
Write problem / opportunity / aim statement
Describe the problem
Management review
The team selects the problem to be solved (to be improved)
The problem and objectives are clearly identified
The current situation is analyzed.
Solution alternatives are identified, selected and scheduled](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdca-221222095442-4dfef341/85/PDCA-pdf-9-320.jpg)
![[2] Analyze Current Situation:
10
Define the process/problem to be solved
Identify the customer(s).
Prepare Baseline data
Check any Performance gaps are available?
Look at benchmarks, standards, regulatory requirements
Validate problem and statement
Management review](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdca-221222095442-4dfef341/85/PDCA-pdf-10-320.jpg)
![[3] Identify Root Causes:
11
This is a very very important step
Utilize the Cause and Effect Diagram (Fishbone Diagram or Ishikawa Diagram, or Why-
Why analysis to identify the most likely cause(s).
Use Genchi Gembutsu Method
Select root cause
Management review](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdca-221222095442-4dfef341/85/PDCA-pdf-11-320.jpg)
![[4] Generate and Choose Solutions:
12
Generate a list and select solutions
Directly linked to root cause & supported by data
Team brainstorming and shared decision making
Be honest about barriers
Choose the best solution based on criteria
Define and map out a solution
Develop solution(s) to remove the root cause(s)
Select the best solution(s) to remove the root cause(s)
Verify that effectiveness of the selected solutions
Verify that selected solutions do not cause any undesirable effects
Set a Target that you want to achieve](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdca-221222095442-4dfef341/85/PDCA-pdf-12-320.jpg)
![Implementation of Do Phase:
[5] Map Out and Implement a Trial Run:
13
Map out a trial run
Communication and education/training are key factors
Be specific
Implement a trial run
Ensure all the countermeasures are completed
It involves collecting data for later analysis
It ensures the solution is appropriately tested
Implementation of Check Phase:
The check phase has two sub-phases which are mentioned below.
6. Analyze the Results
7. Draw Conclusions](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdca-221222095442-4dfef341/85/PDCA-pdf-13-320.jpg)
![[6] Analyze the Results:
14
Evaluate results based on collected data
Team-based analysis
Objective and subjective data
Revisit the process as it was mapped out
Be honest!
Evaluate both Results and Process
Involves analyzing the collected data and comparing the actual results against the
planned objectives.
Allows discussing whether further improvements are possible
You may have to repeat the Do and Check a number of times until you get the optimum
results](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdca-221222095442-4dfef341/85/PDCA-pdf-14-320.jpg)
![[7] Draw Conclusions:
15
Team-based discussion
Was the root cause eliminated?
What worked?
Did the desired change occur?
What didn’t work?
What could be improved/changed?
Implement the best solution(s) to remove the root cause(s)
What did we learn?
Implement the best solution(s) to address the escape point(s)
Validate the effectiveness of the implemented solutions by Customer's perspective
Monitor the effectiveness of the implemented solutions and assure that they do not
cause any undesirable effects
Remove Interim Containment Actions
Implementation of Act Phase:
The last phase is the act phase and it has two sub-phases as mentioned below.
8. Adopt, Adapt, or Abandon the Intervention
9. Monitor; Hold the gains](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdca-221222095442-4dfef341/85/PDCA-pdf-15-320.jpg)
![[8] Adopt, Adapt, or Abandon the
Intervention:
16
Team-based discussion and beyond
Test again on a larger scale?
Communication, education, and training
Revise plan and repeat trial
Communication, education, and training
Revisit root cause analysis and/or list of solutions
Need additional/new members on the team?
Involves acting on the feedback and lessons learned and implementing the solution
It is also concerned with: Standardizing, Documenting, Sustaining the improved
process
Integrating it into the organization’s system.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdca-221222095442-4dfef341/85/PDCA-pdf-16-320.jpg)
![[9] Monitor; Hold the gains:
17
Standardize the change
Change to department policy?
Continue to monitor improvement
Same data collection tools and process
Continue reporting to staff and management
Move to new improvement opportunity
Standardize Success and Learn from Failures](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/pdca-221222095442-4dfef341/85/PDCA-pdf-17-320.jpg)


