This document provides an overview of Toyota, including:
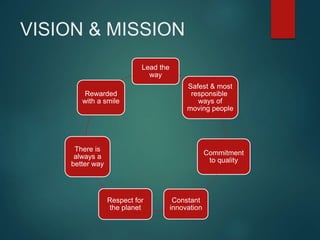
- Toyota's vision is to lead the way to the safest and most responsible ways of moving people through constant innovation and respect for the planet.
- Toyota was established in 1937 and is now the world's largest automaker, producing over 10 million vehicles in 2015.
- In addition to automotive, Toyota has diversified into financial services, housing, marine, biotechnology, and other business segments.
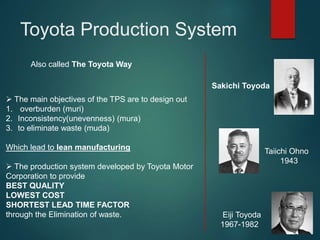
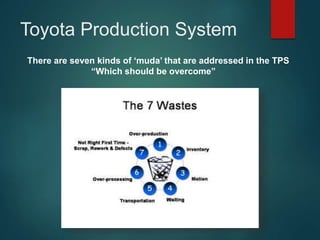
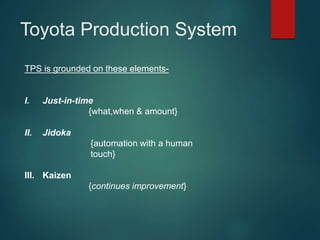
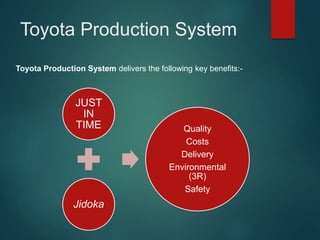
- The Toyota Production System aims to eliminate waste through just-in-time production and continuous improvement, which has delivered benefits like quality, costs, delivery, safety, and environmental protection.



![Country of Origin: Japan
FOUNDER : KIICHIRO TOYODA
[August 28, 1937; 79 years ago]
PRESIDENT & CEO : Akio Toyoda
Chairman : Takeshi Uchiyamada
Number of Employees(2016): 346,219
Unit Sales (2014): 10.2 million
Toyota's headquarters in Toyota
City, Aichi Prefecture, Japan
Organization Structure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/toyota-161004175857/85/Toyota-5-320.jpg)