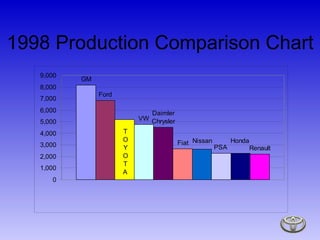
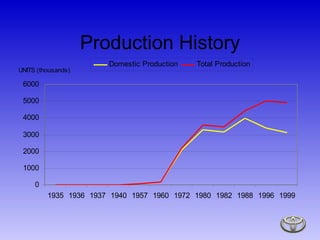
Toyota is a global automotive manufacturer that produces over 5.5 million vehicles annually. The presentation discusses Toyota's history, production systems, business segments, and strategies. Key points include how Toyota was established in 1937 and developed the Toyota Production System for efficient manufacturing. The system emphasizes just-in-time production and eliminating waste. The presentation also covers trends in the global auto industry and questions for Toyota on competition and future automotive technologies.