This presentation provides an overview of Toyota, the global auto industry, and Toyota's production system. Some key points:
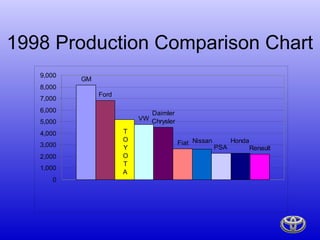
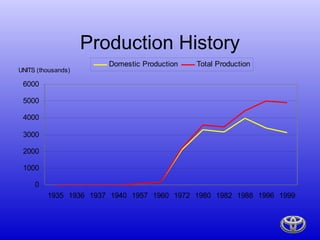
- Toyota is the 3rd largest automaker by sales, producing over 5.5 million vehicles per year across 56 plants on 6 continents.
- Toyota pioneered the Toyota Production System, which revolutionized manufacturing through lean principles like just-in-time production and eliminating waste.
- Toyota's strategy focuses on advancing environmental and fuel cell technologies, cost reduction, and expanding financial services to strengthen competitiveness against global competition.