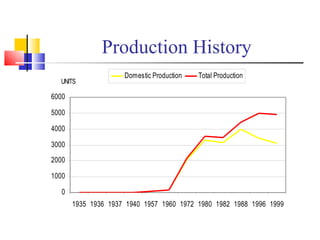
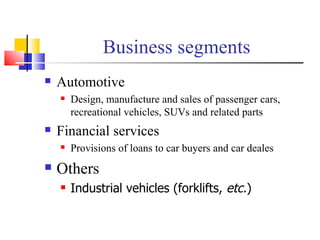
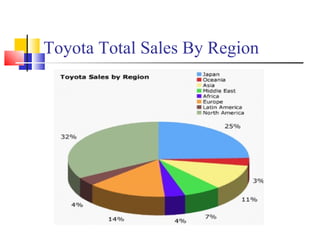
Toyota Motors is the third largest automotive manufacturer in the world based on annual vehicle sales. Some key details:
- Toyota produces over 5.5 million vehicles annually across 56 manufacturing plants on 6 continents.
- It employs around 200,000 people worldwide and is headquartered in Toyota City, Japan.
- The Toyota Production System focuses on eliminating waste and improving efficiency through practices like just-in-time manufacturing and single-minute exchange of dies.
- This lean manufacturing approach helped Toyota become one of the most profitable automakers and the world's largest by 2007.