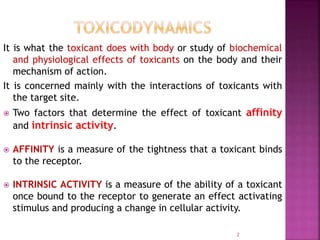
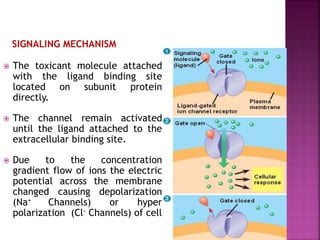
1. Toxicology is the study of the biochemical and physiological effects of toxicants on the body and their mechanisms of action, focusing on interactions with target sites. Two factors that determine effect are affinity, how tightly a toxicant binds to a receptor, and intrinsic activity, its ability to activate the receptor and produce a cellular response.
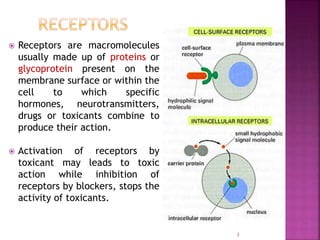
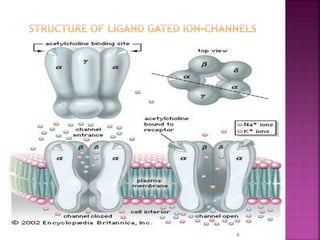
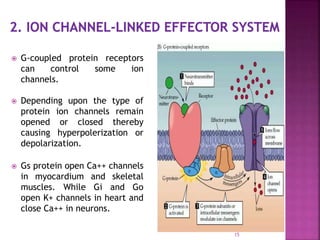
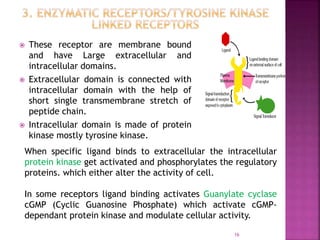
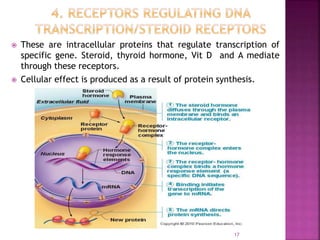
2. Receptors are membrane proteins that toxicants bind to in order to produce effects. There are four main classes of receptors: ligand-gated ion channels, G-protein coupled receptors, enzymatic receptors, and receptors that regulate DNA transcription.
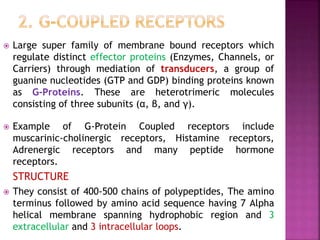
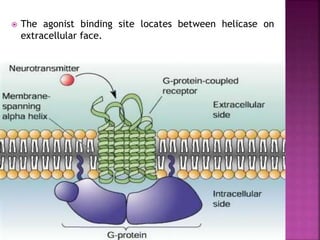
3. G-protein coupled receptors are the largest family and activate distinct effector proteins through G-proteins. Their activation