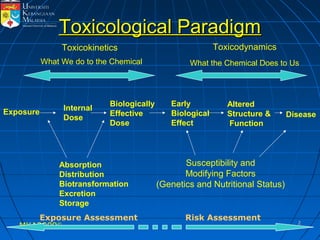
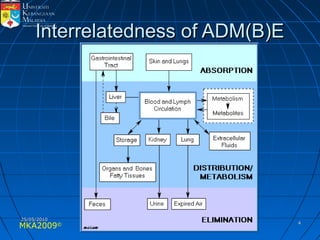
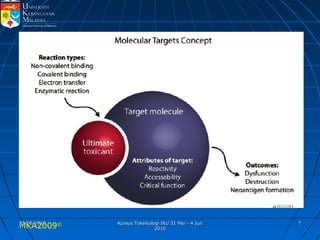
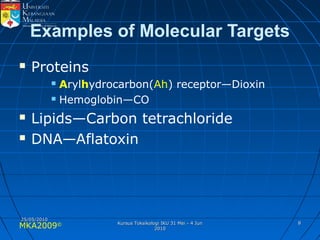
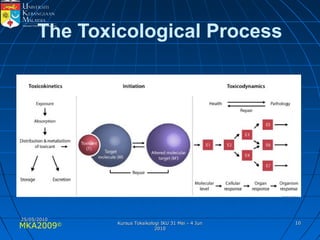
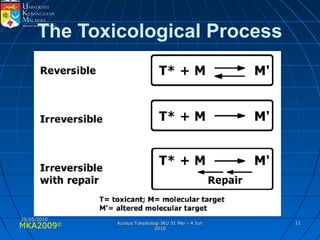
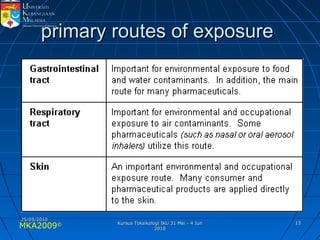
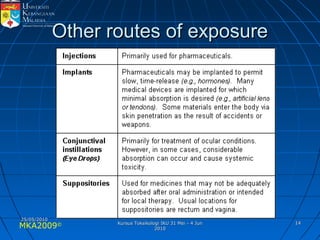
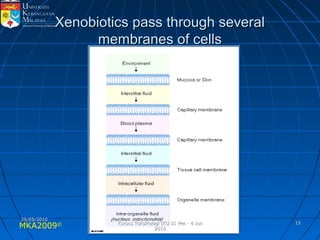
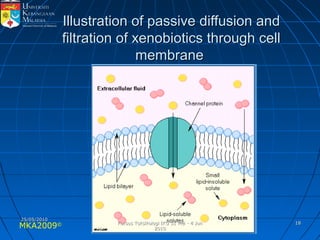
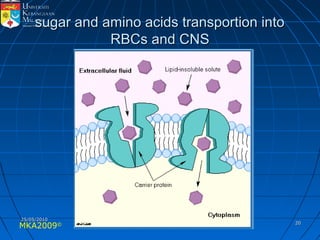
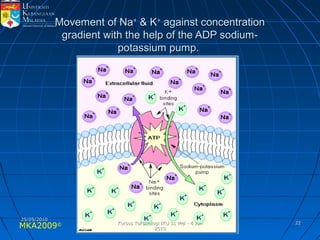
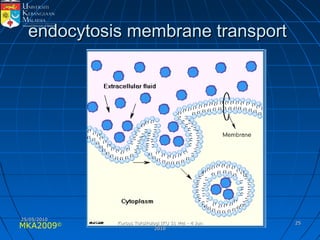
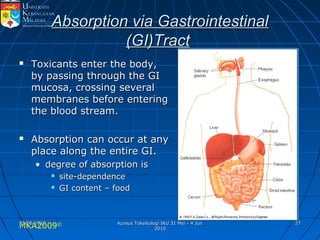
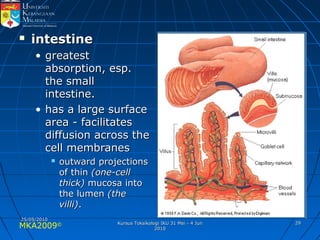
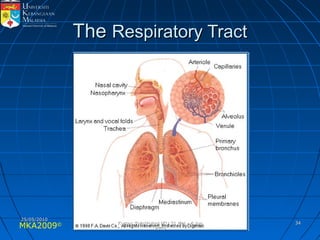
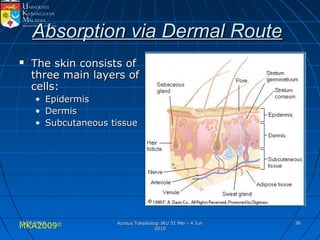
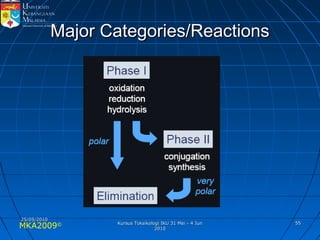
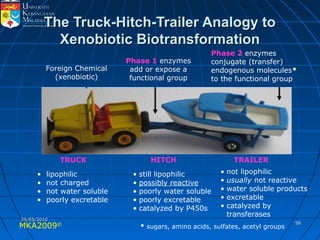
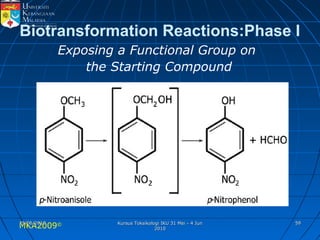
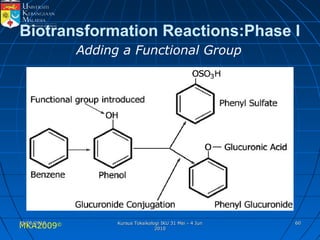
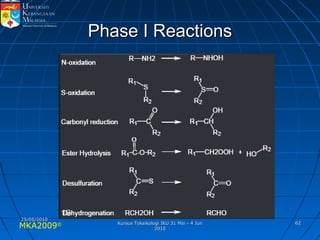
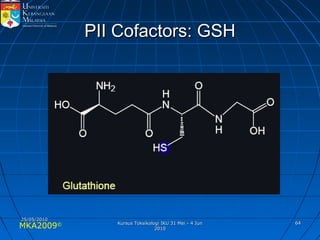
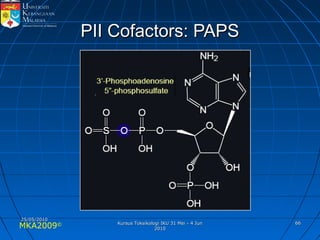
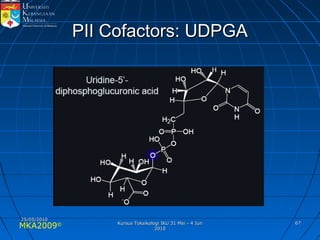
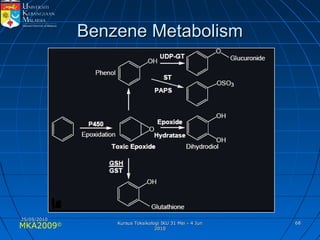
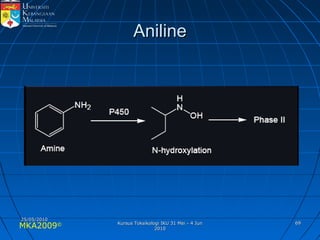
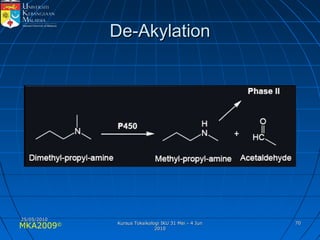
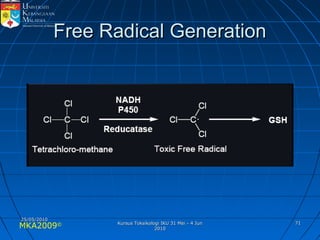
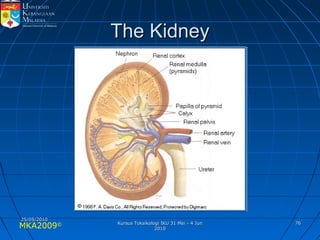
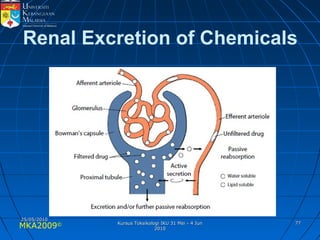
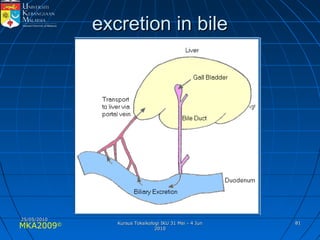
Absorption, distribution, biotransformation and excretion (ADME) are the four main processes involved in toxicokinetics, which is the study of how substances move through the body. Absorption involves substances gaining entrance into the body through various routes of exposure like ingestion, inhalation or dermal contact. Absorption can occur through passive diffusion, facilitated transport or active transport across cell membranes. The small intestine is usually the main site of absorption due to its large surface area. Distribution, biotransformation and excretion determine what happens to substances in the body after absorption.