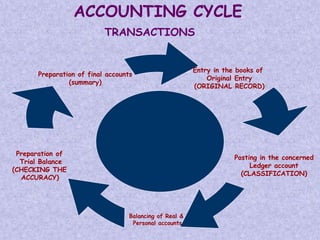
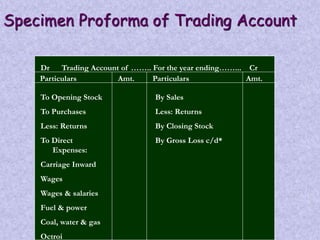
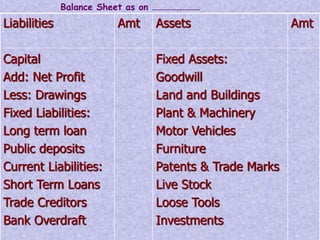
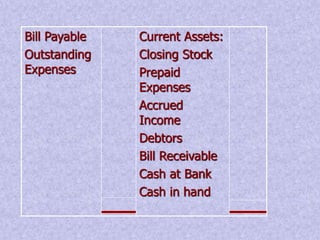
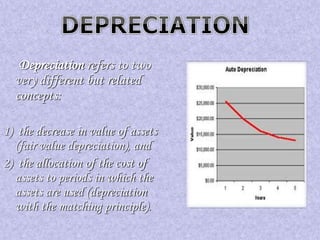
Financial statements provide important information about a business's profitability and financial position. The two key financial statements are the income statement and balance sheet. The income statement shows revenues and expenses over a period of time to determine profit or loss. The balance sheet provides a snapshot of a company's assets, liabilities, and capital as of a specific date. Financial statements are prepared periodically and used by various stakeholders to make informed decisions about a business.