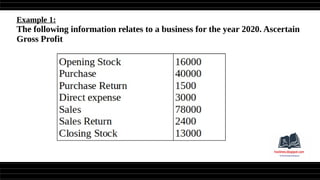
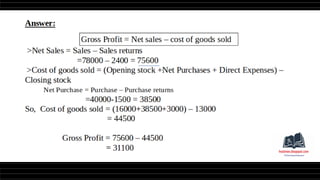
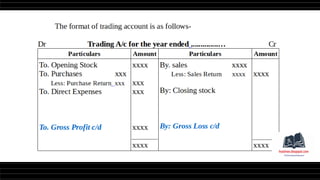
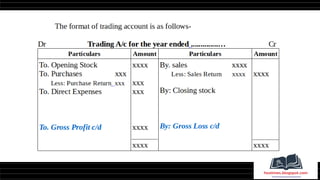
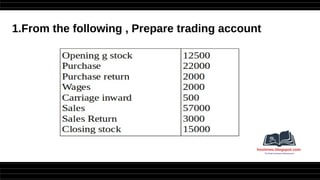
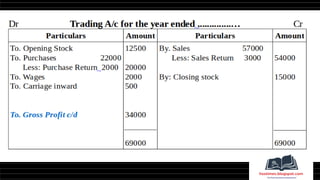
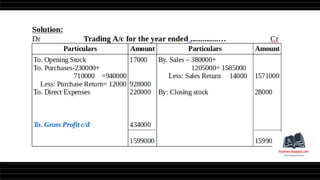
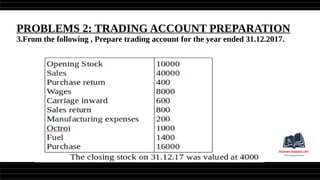
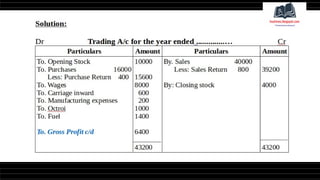
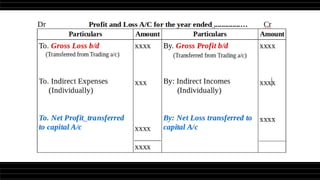
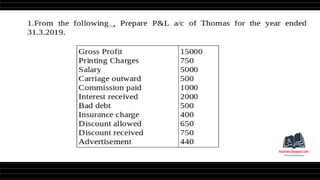
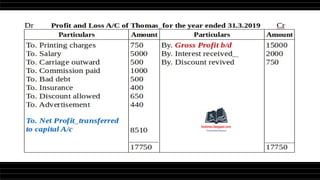
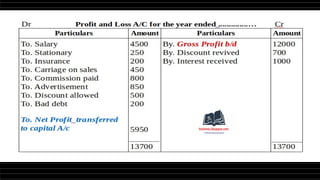
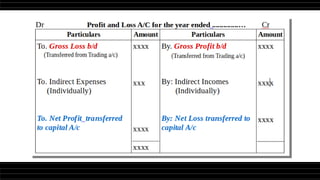
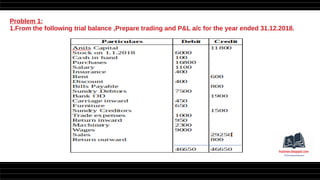
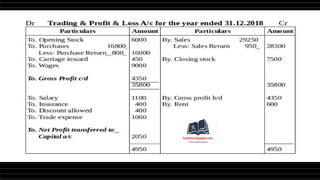
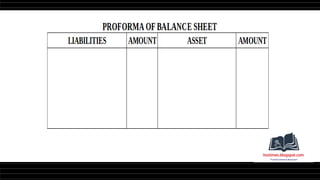
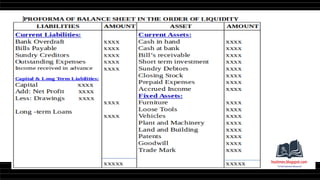
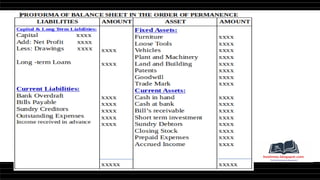
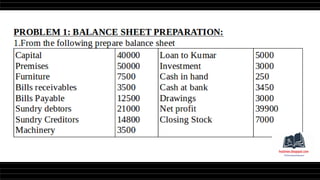
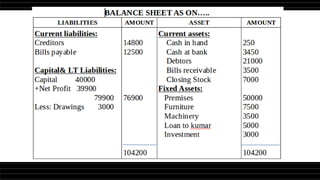
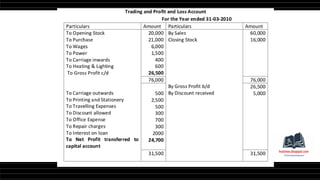
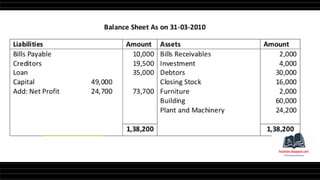
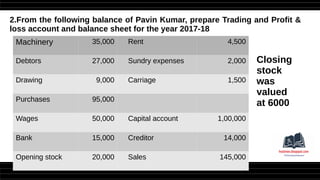
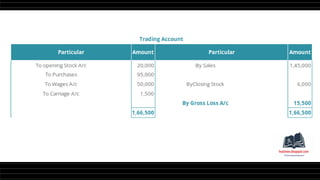
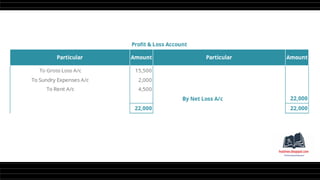
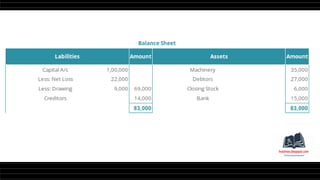
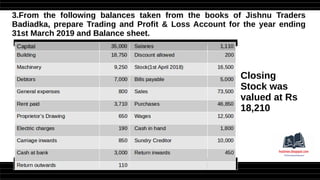
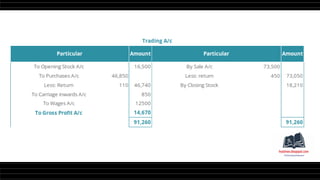
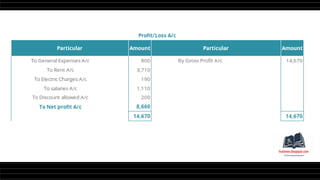
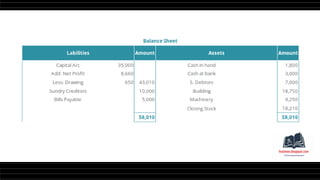
This document provides a comprehensive overview of financial statements, focusing on the trading account, profit and loss account, and balance sheet. It emphasizes their objectives, key components, and the processes for preparing and closing entries related to each account type. The text also includes examples and problems for practical application of the concepts discussed.