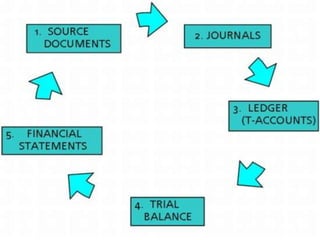
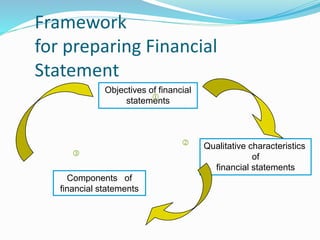
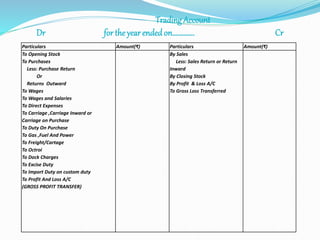
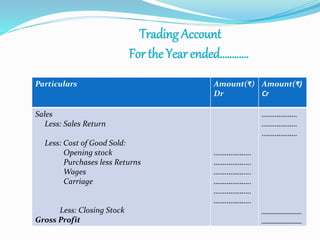
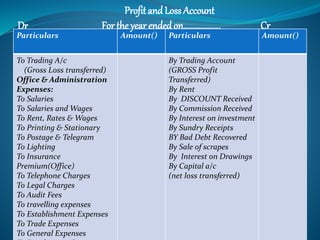
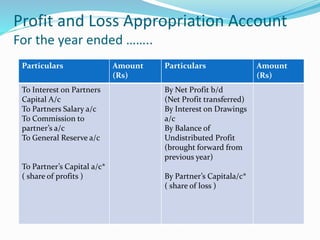
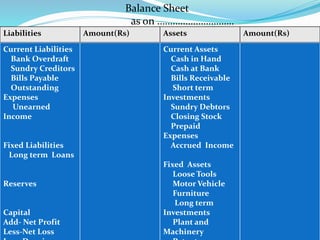
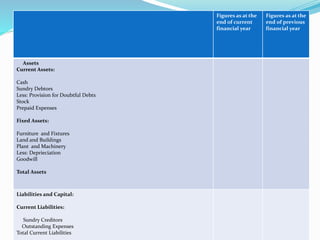
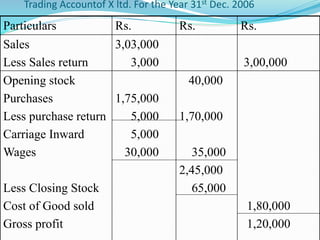
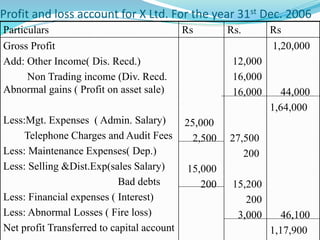
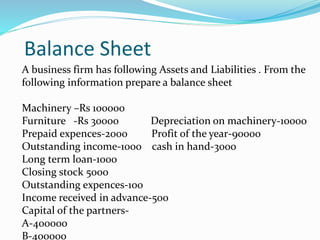
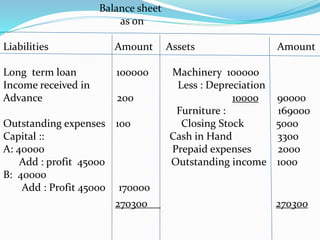
This document provides an overview of financial accounting concepts including financial statements, their objectives and components. It discusses the manufacturing account, trading account, profit and loss account and balance sheet. It describes the nature, framework and objectives of financial statements. It also covers the qualitative characteristics, importance, limitations and components of financial statements including the income statement and statement of financial position. Formats for the trading account, profit and loss account and balance sheet are also demonstrated.