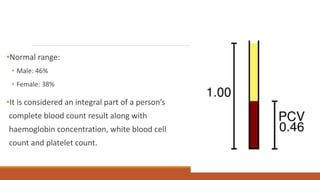
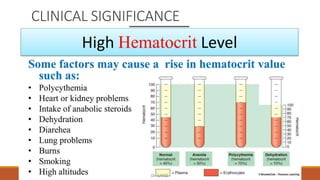
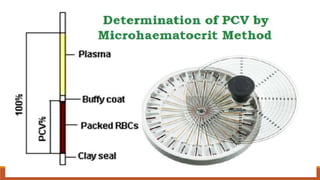
Hematocrit, also known as packed cell volume, is the percentage of red blood cells in blood. It is an important indicator in a complete blood count. The normal ranges are 46% for males and 38% for females. Hematocrit can be measured through microhematocrit and macrohematocrit methods. Microhematocrit involves centrifuging a blood sample in a capillary tube and reading the percentage of red blood cells. Macrohematocrit uses a Wintrobe tube and centrifugation to separate plasma from red blood cells to determine the hematocrit percentage. Precise measurement requires avoiding errors like not including the buffy coat layer or improper sealing of tubes.