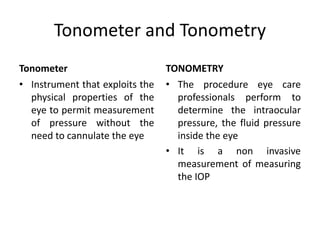
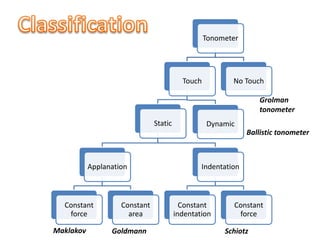
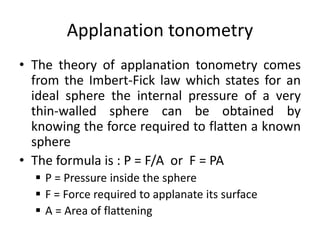
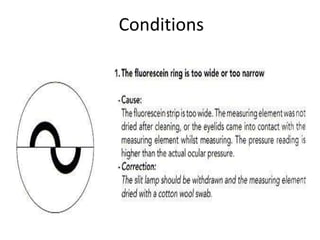
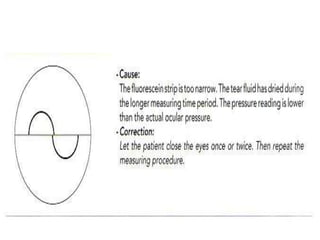
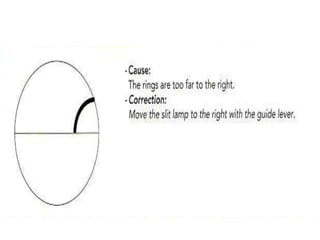
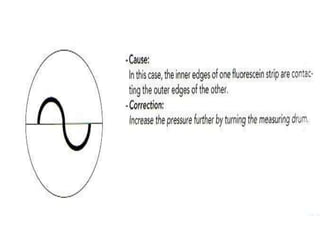
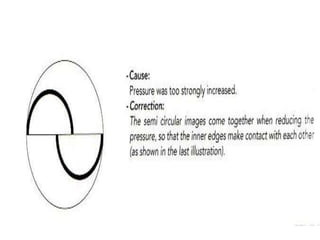
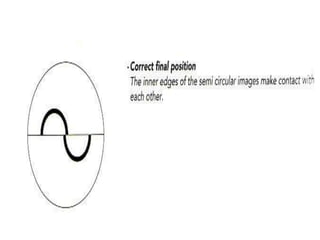
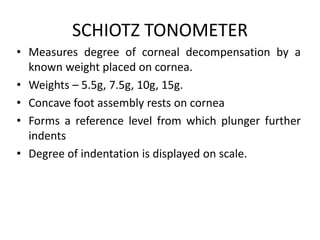
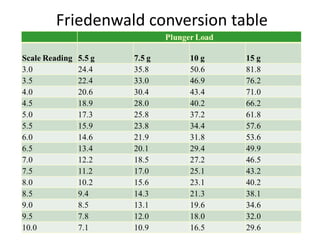
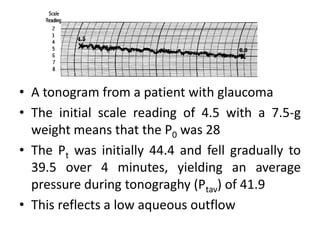
Tonometry is the measurement of intraocular pressure (IOP) inside the eye. There are several types of tonometers that use different principles like indentation, applanation, and contour matching. The Goldmann applanation tonometer is considered the gold standard. It works by applanating the cornea with a known force and area to indirectly measure IOP. Tonography provides additional information about aqueous humor dynamics by recording IOP changes over time using an electronic Schiotz tonometer. Newer dynamic contour tonometry matches the probe contour to the cornea to reduce deformation compared to applanation tonometry.