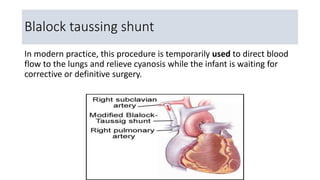
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF) is a complex congenital heart defect characterized by four defects: ventricular septal defect, overriding of the aorta, pulmonary stenosis, and right ventricular hypertrophy. It results in decreased blood flow to the lungs. Diagnosis involves cardiac examination, ECG, chest x-ray, and echocardiogram. Treatment includes medical management with prostaglandin E1 to increase lung blood flow and surgical options like the Blalock-Taussig shunt or corrective surgery to repair the defects. Complications can include conduction abnormalities, residual defects, and pulmonary valve regurgitation.