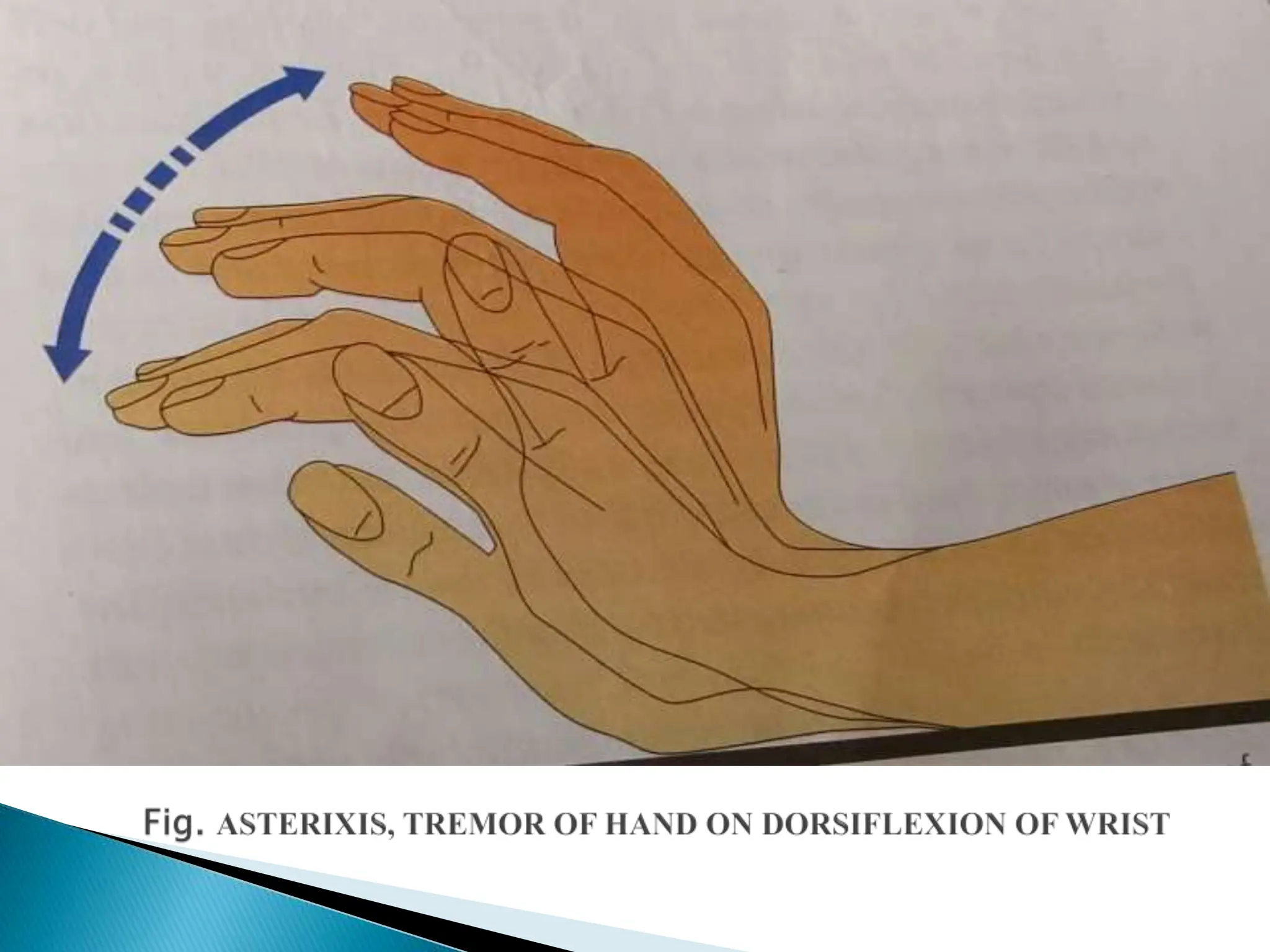
Hepatic encephalopathy is a brain disorder caused by liver dysfunction. There are three types: type A from acute liver failure, type B from portosystemic shunting without liver damage, and type C from chronic liver disease. Symptoms range from insomnia to coma and are graded on a scale of 0 to 4 based on consciousness, intellectual function, and neurological signs. Treatment includes lactulose to reduce ammonia absorption, antibiotics like neomycin, and liver transplantation for severe cases.