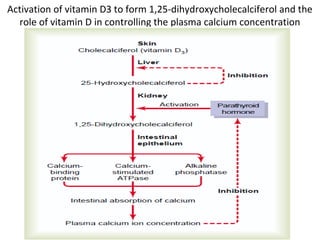
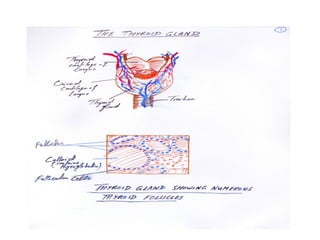
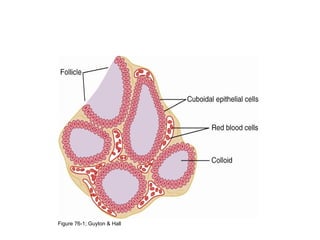
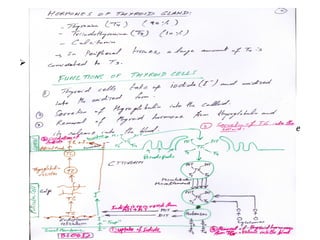
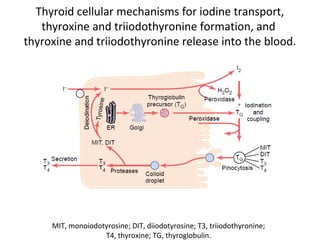
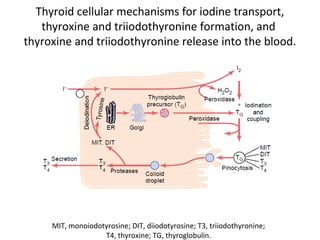
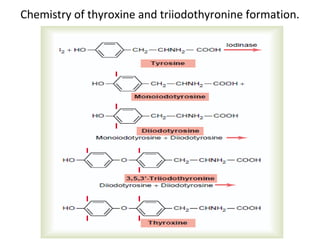
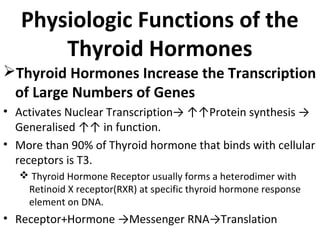
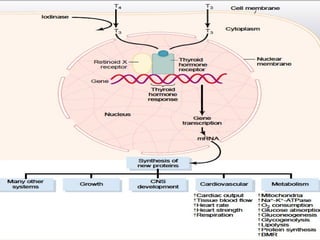
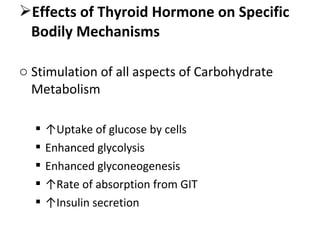
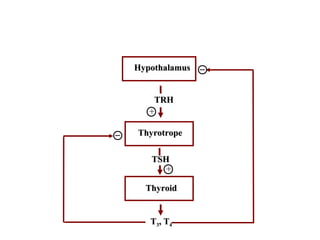
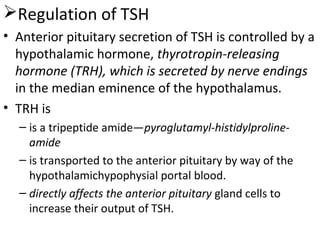
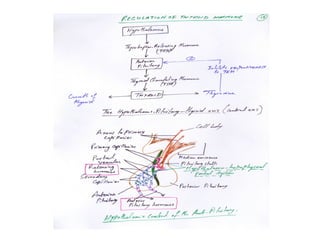
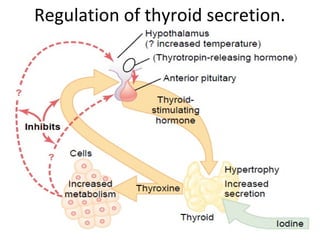
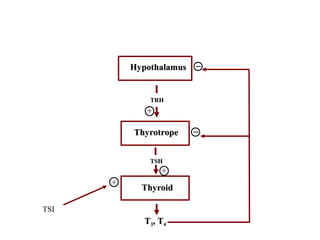
The thyroid gland, located below the larynx and anterior to the trachea, secretes key hormones including thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), and calcitonin, with T4 being the predominant hormone. Thyroid hormone production is regulated by thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) from the anterior pituitary, influencing metabolic rates, growth, and various bodily functions, with T3 being more potent than T4. Dysfunctions in thyroid hormone levels can lead to conditions such as hyperthyroidism and hypothyroidism, each presenting various physiological symptoms and requiring distinct treatment approaches.

















![Metabolic Effects of Thyroid Hormones
Parameter ↓ T3, T4 ↑ T3, T4
Basal metabolic rate ↓ ↑
Carbohydrate metabolism ↓ Gluconeogenesis ↑ Gluconeogenesis
↓ Glycogenolysis ↑ Glycogenolysis
Normal serum [glucose] Normal serum [glucose]
Protein metabolism ↓ Synthesis ↑ Synthesis
↓ Proteolysis ↑ Proteolysis
Muscle wasting
Lipid metabolism ↓ Lipogenesis ↑ Lipogenesis
↓ Lipolysis ↑ Lipolysis
↑ Serum [cholesterol] ↓ Serum [cholesterol]
Thermogenesis ↓ ↑
Table 48-1, Boron & Boulpaep](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thyroid-130916143030-phpapp01/85/Thyroid-27-320.jpg)


































![0
6 8 10 12 14
50
100
PTHsecretion
(%maximalrate)
Total plasma [Ca2+
] (mg/dL)
Plasma Calcium Concentration
& PTH Secretion](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thyroid-130916143030-phpapp01/85/Thyroid-72-320.jpg)
![Hypocalcemia
Disorder
Plasma
[PTH]
Plasma
[1,25-(OH)2-D3] UrineBone
Plasma
[Ca2+
]
Plasma
[Phosphate]
Vitamin D
deficiency
Chronic renal
failure
(2°)
*
*
Phosphate
cAMP
Phosphate
( ↓ GFR)*
Osteomalacia
Resorption
Resorption
* Primary events or disturbances
Surgical
hypoparathyroidism
(2°)
*
Osteomalacia
Resorption cAMP
Phosphate
Castanzo, Table 9-17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thyroid-130916143030-phpapp01/85/Thyroid-73-320.jpg)

![Primary Hyperparathyroidism
Plasma
[PTH]
*
Plasma
[1,25-(OH)2-D3] Urine
Phosphate
Ca2+
cAMP
Bone
Resorption
Plasma
[Ca2+
]
Plasma
[Phosphate]
* Primary disturbance
Castanzo, Table 9-17](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thyroid-130916143030-phpapp01/85/Thyroid-75-320.jpg)