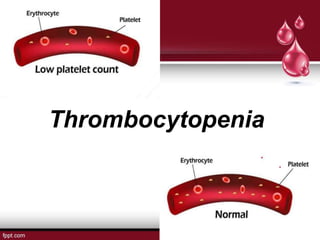
This document discusses thrombocytopenia, defined as a low platelet count. It outlines the pathophysiology as increased platelet destruction often due to antibodies against platelet proteins. Risk factors include certain cancers, toxins, infections, and medications. Signs and symptoms range from bruising to internal bleeding. Treatment involves medications to increase platelet count, transfusions, or splenectomy. Nursing care focuses on prevention of bleeding through careful monitoring and patient education.