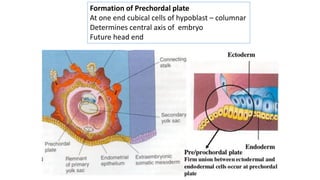
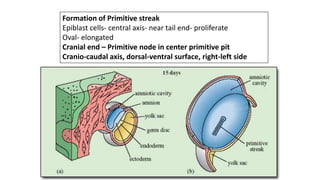
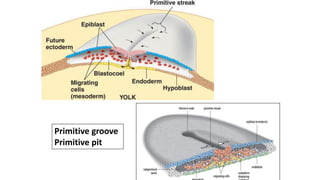
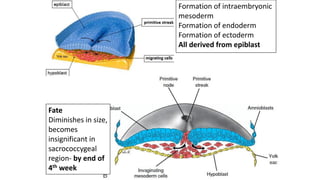
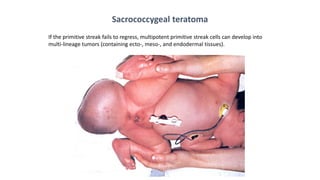
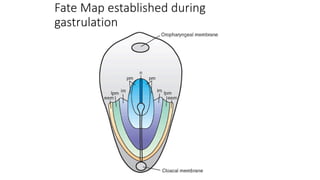
During the third week of development (days 14-21):
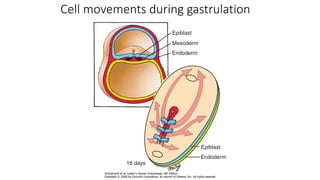
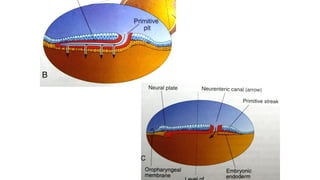
1. The primitive streak forms and gastrulation begins, establishing the three germ layers - ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
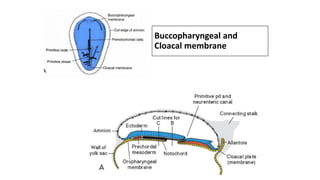
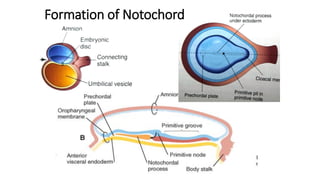
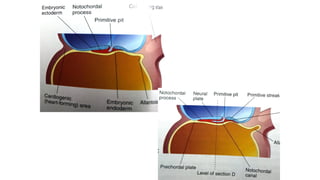
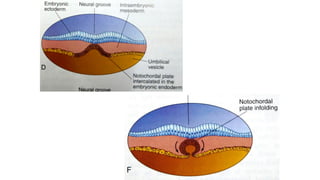
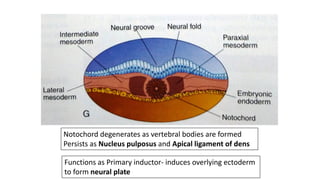
2. Neural induction occurs as the notochord induces the ectoderm to form the neural plate. Left-right asymmetry is also established.
3. Gastrulation involves cell movements that position the germ layers and establish the body plan and central axis of the embryo through structures like the primitive streak, primitive groove/pit, and notochord. The fate map of tissues is also established.