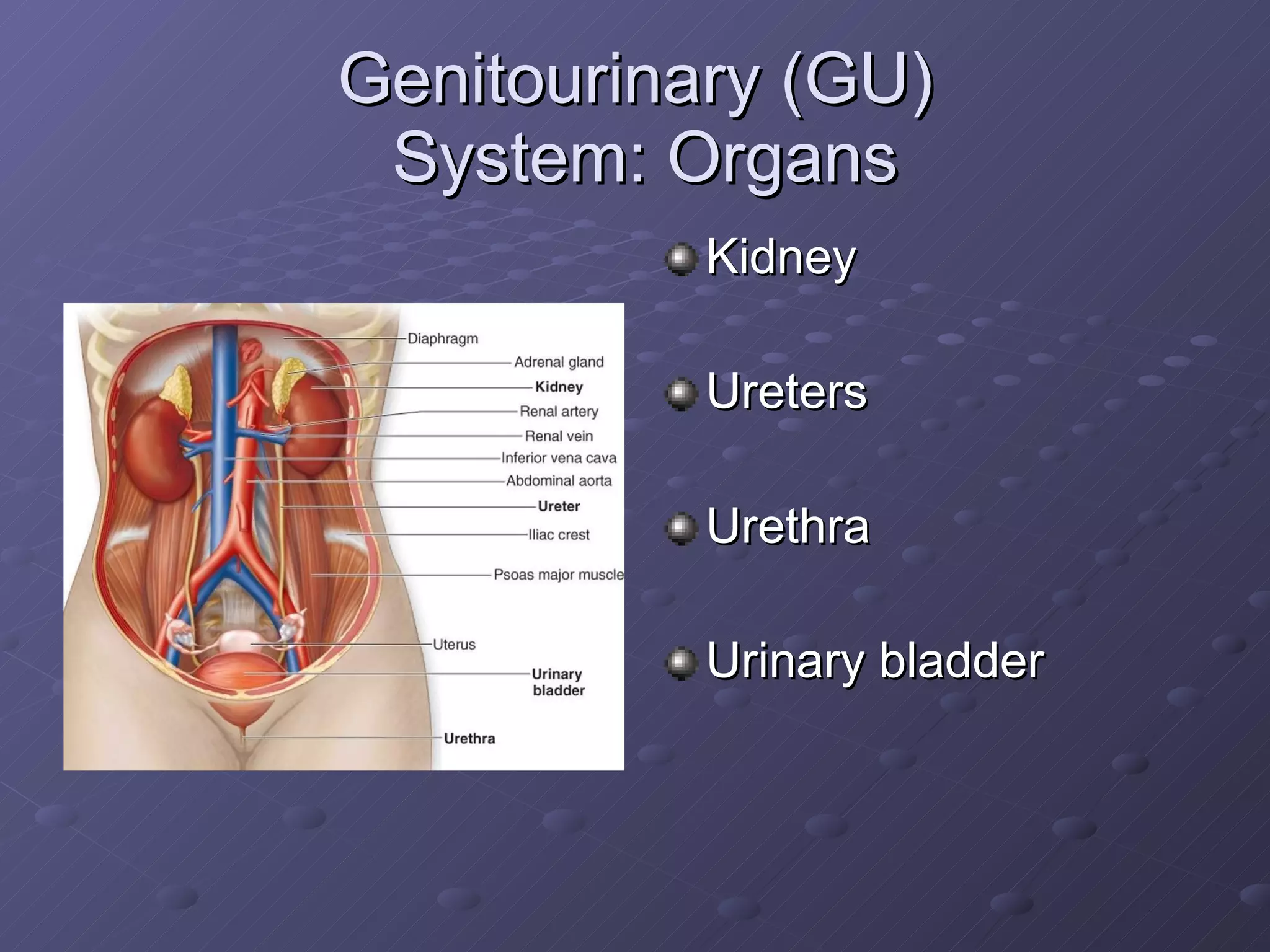
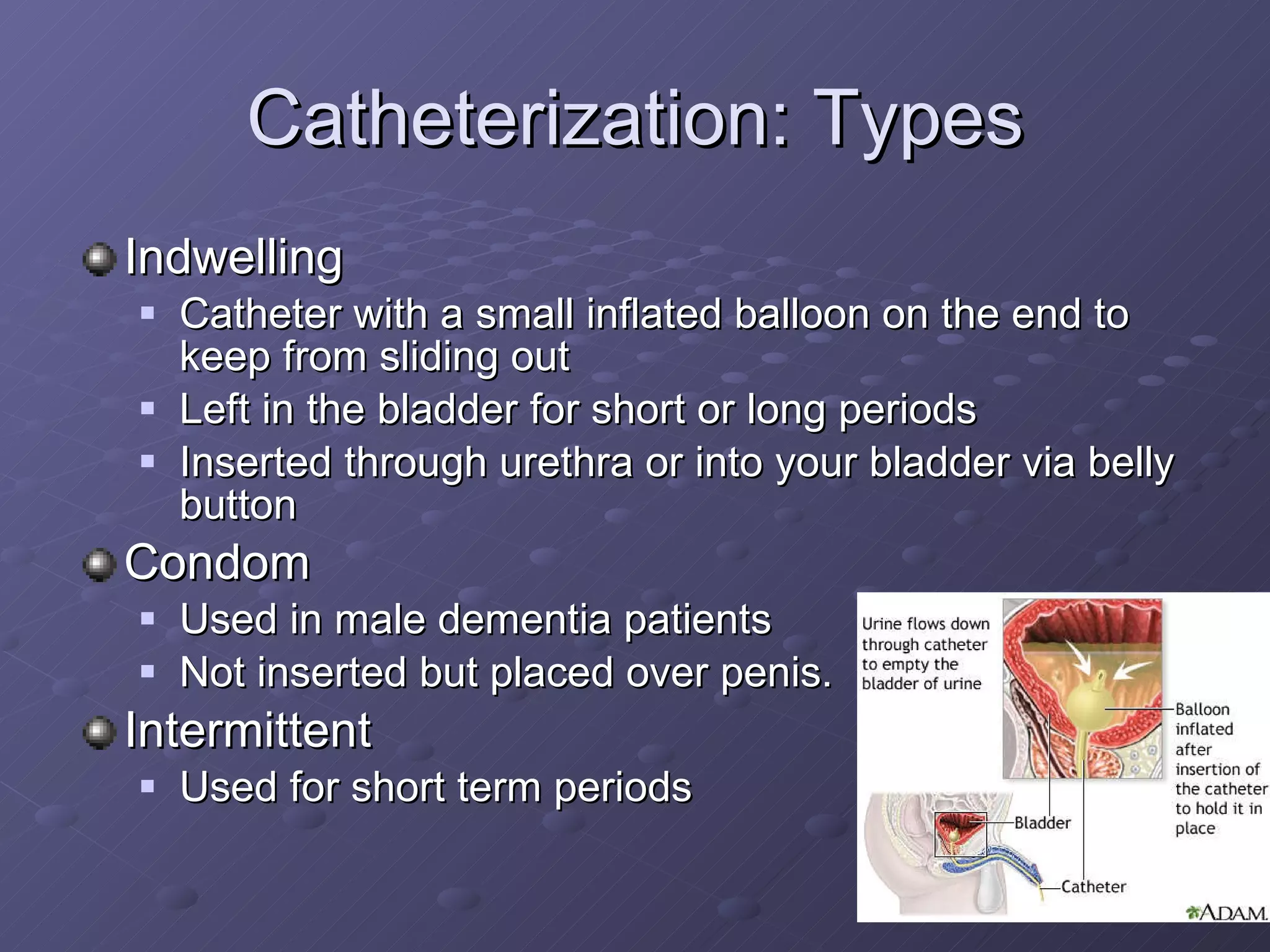
The document discusses the urinary system and various procedures related to it. The urinary system includes the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra and works to remove waste from the body and regulate water and electrolyte levels. Catheterization involves inserting a catheter into the bladder through the urethra to drain urine for various medical reasons. Cystoscopy uses a thin scope to examine the bladder and urethra to detect abnormalities. Extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy uses shock waves to break up kidney stones so they can pass through the urinary system.