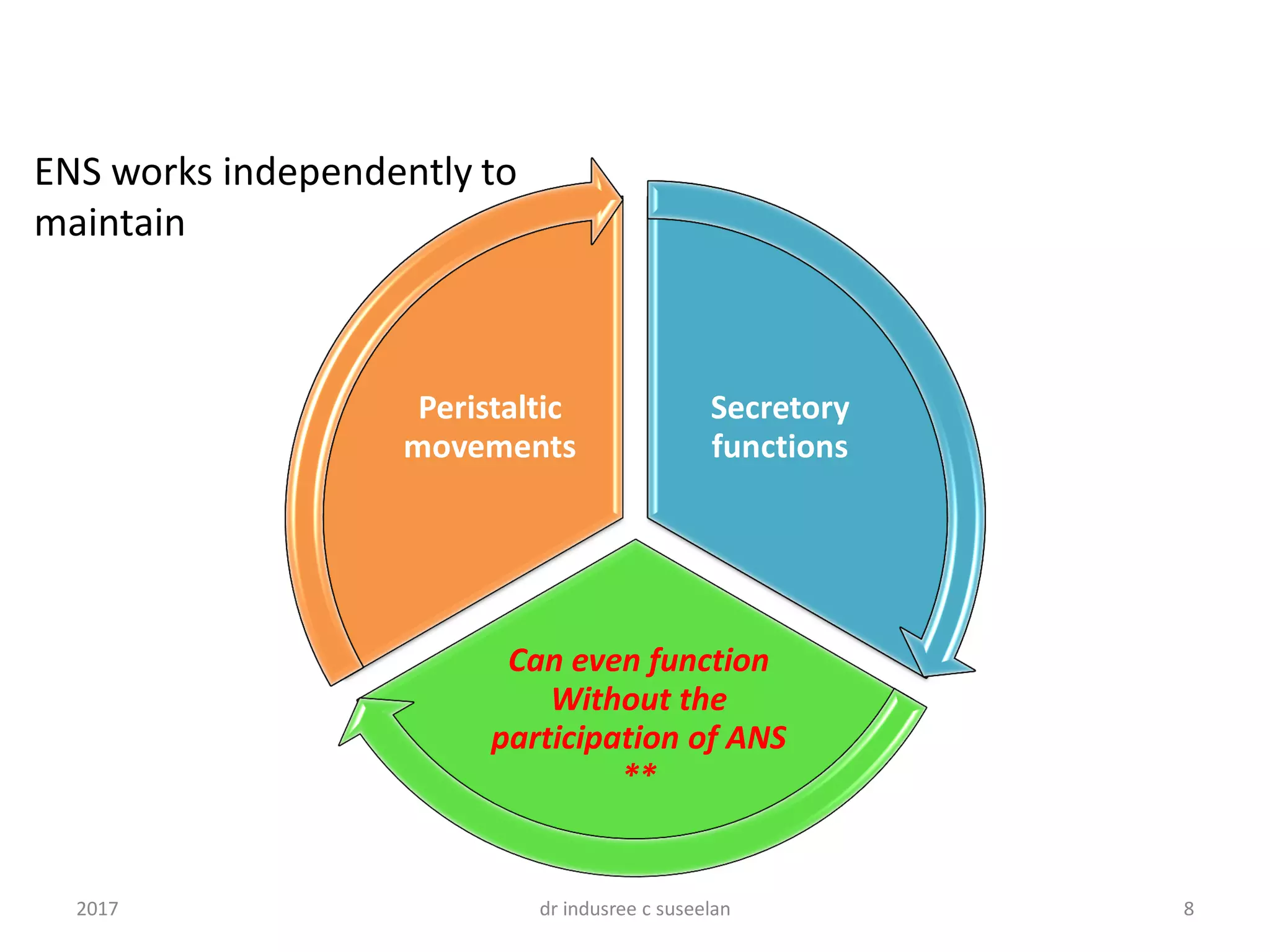
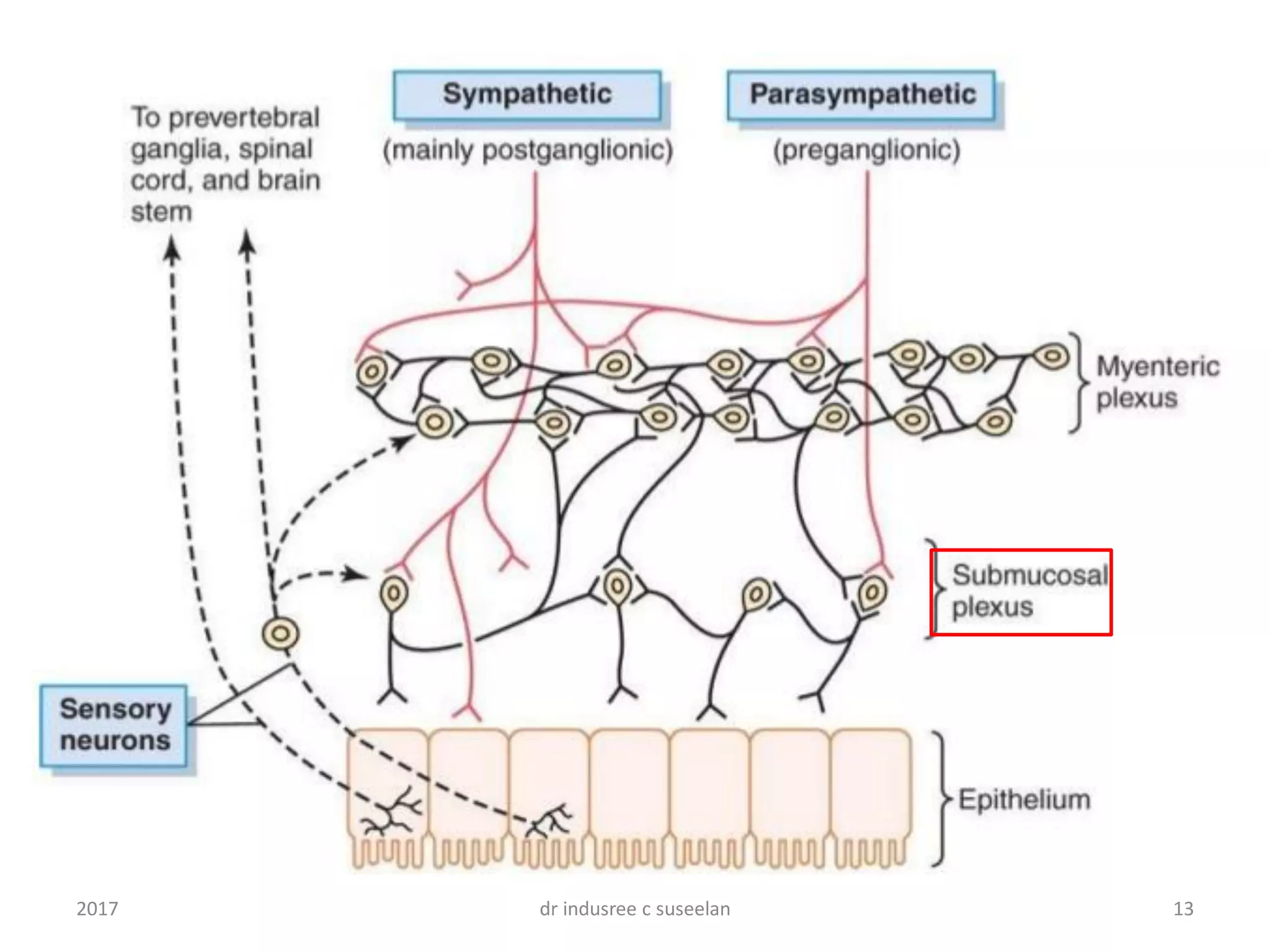
The enteric nervous system (ENS) is composed of two plexuses - the myenteric plexus and submucosal plexus. The myenteric plexus controls gastrointestinal movements through motor neurons that innervate the outer longitudinal and inner circular muscle layers. The submucosal plexus controls local intestinal secretion, absorption, and submucosal muscle contraction through mainly excitatory neurons. Together the ENS can function independently of the autonomic nervous system to regulate peristalsis and secretory functions through a network of sensory neurons, interneurons, and motor neurons.