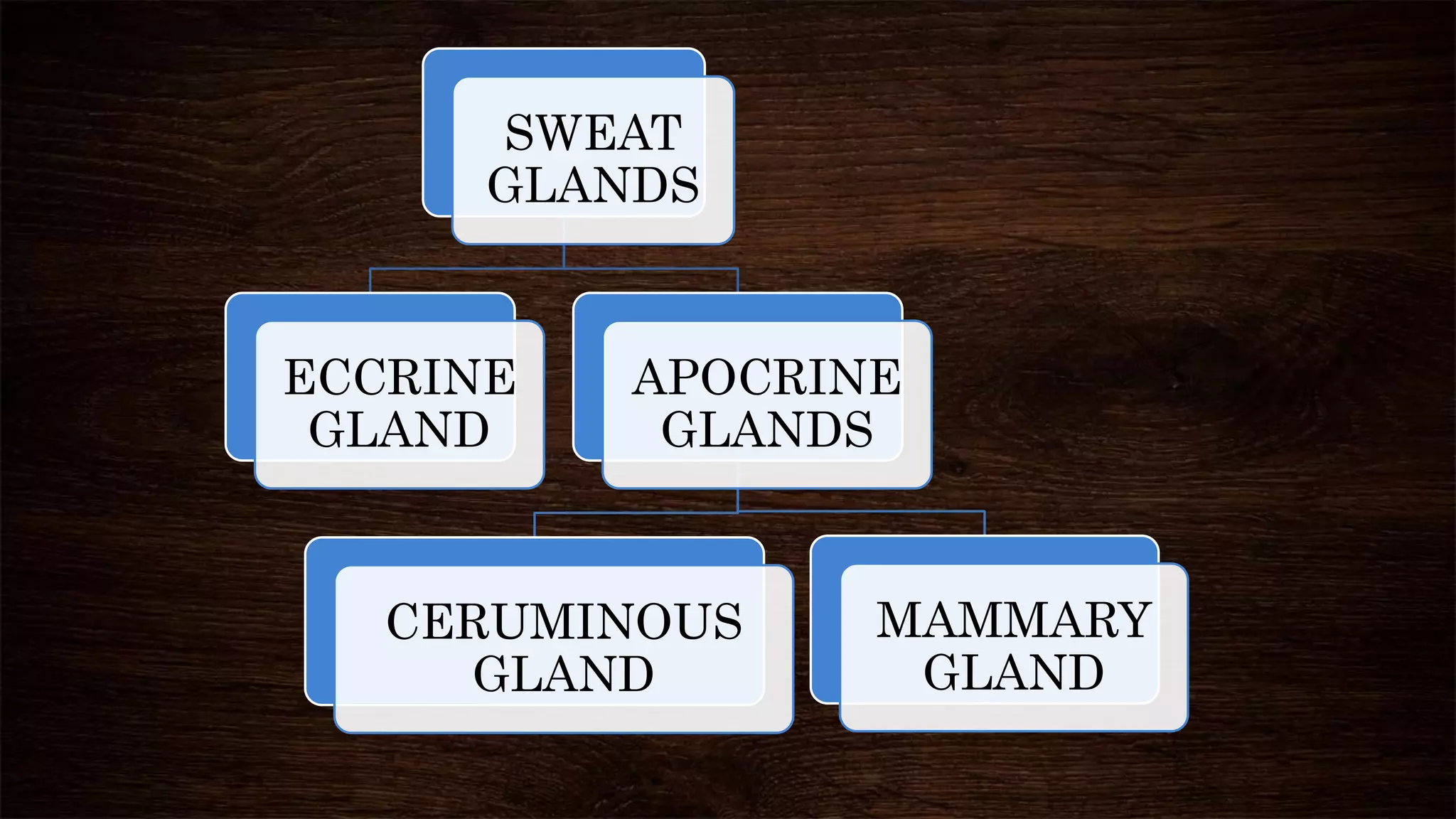
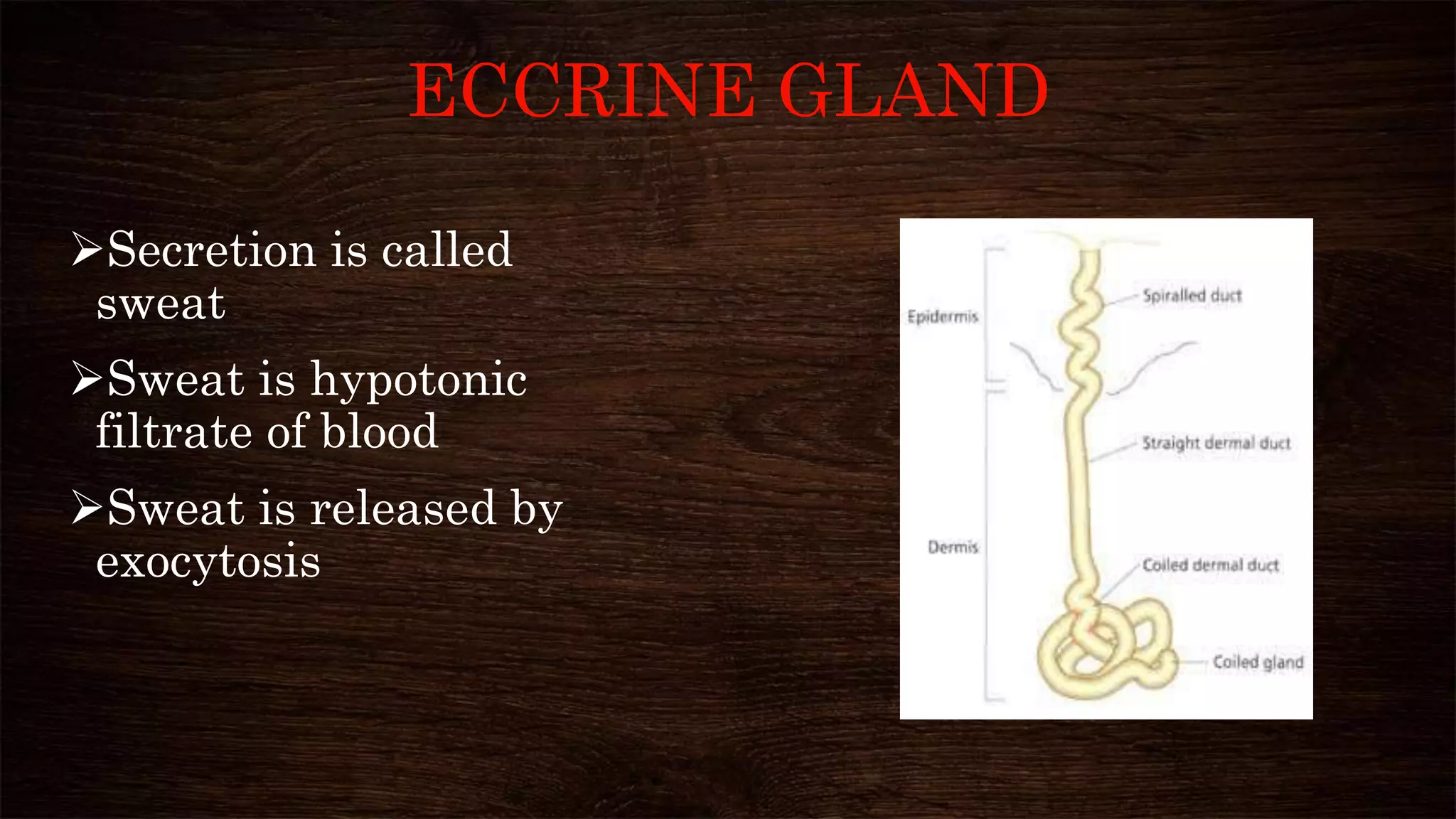
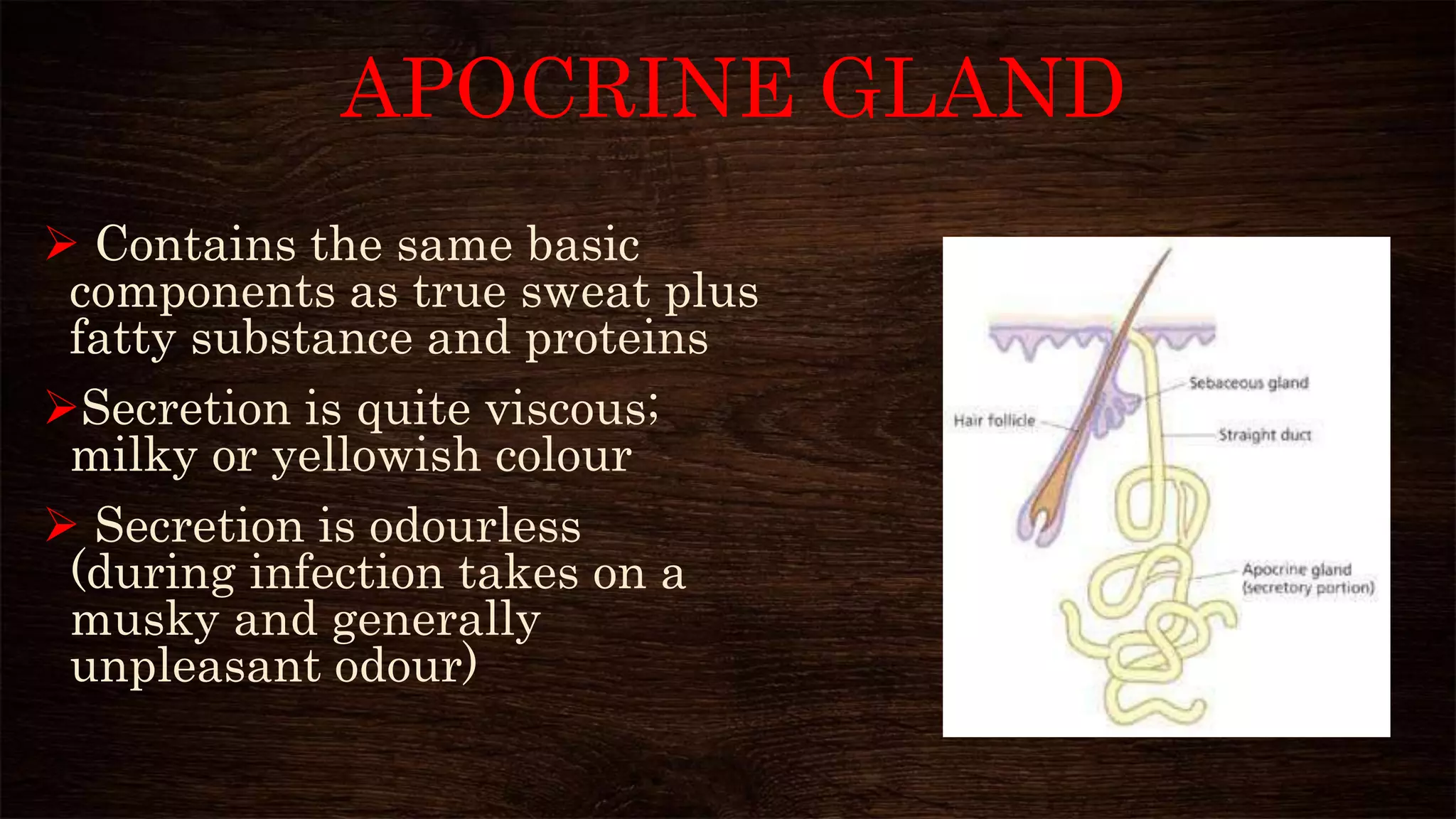
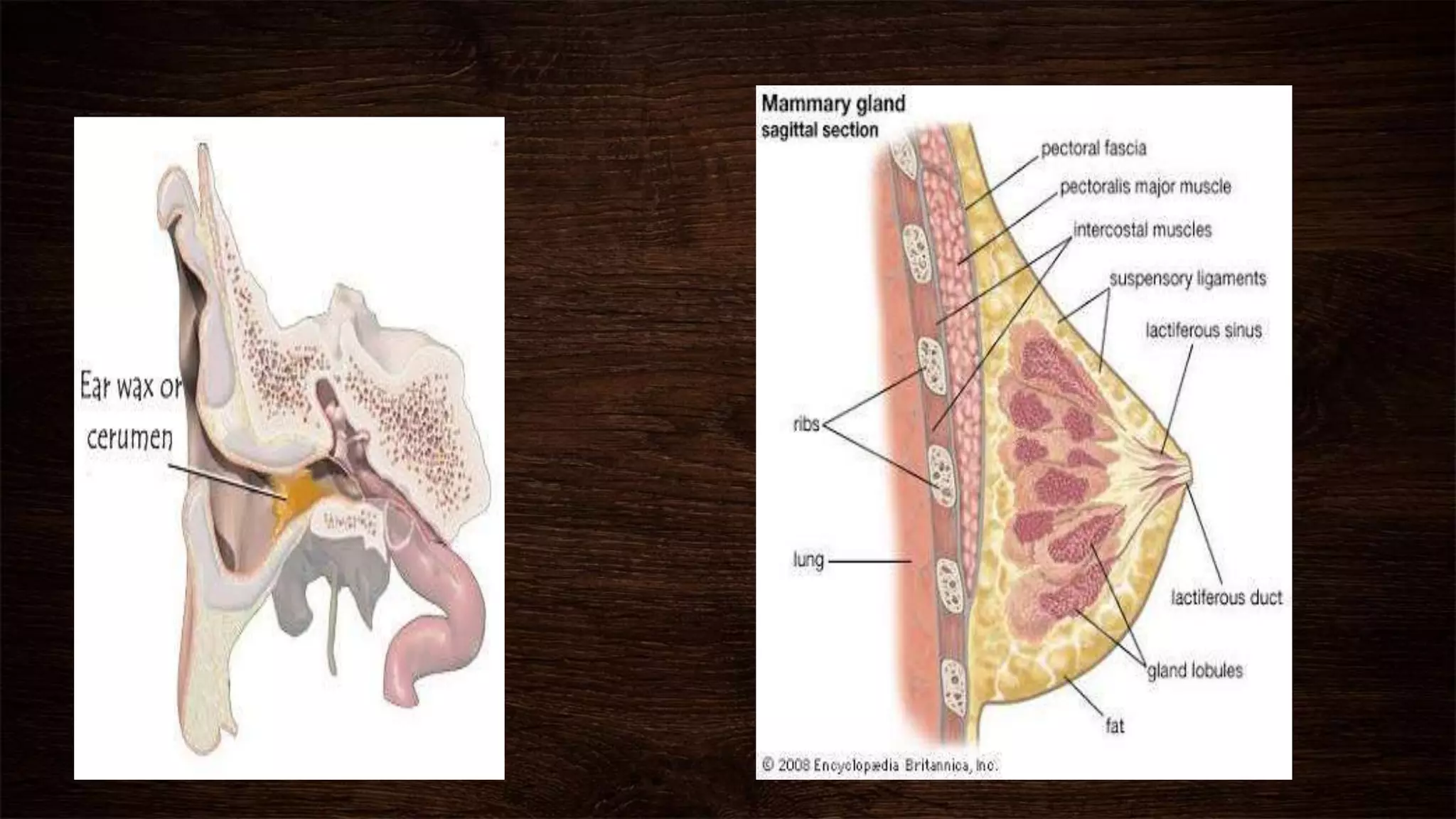
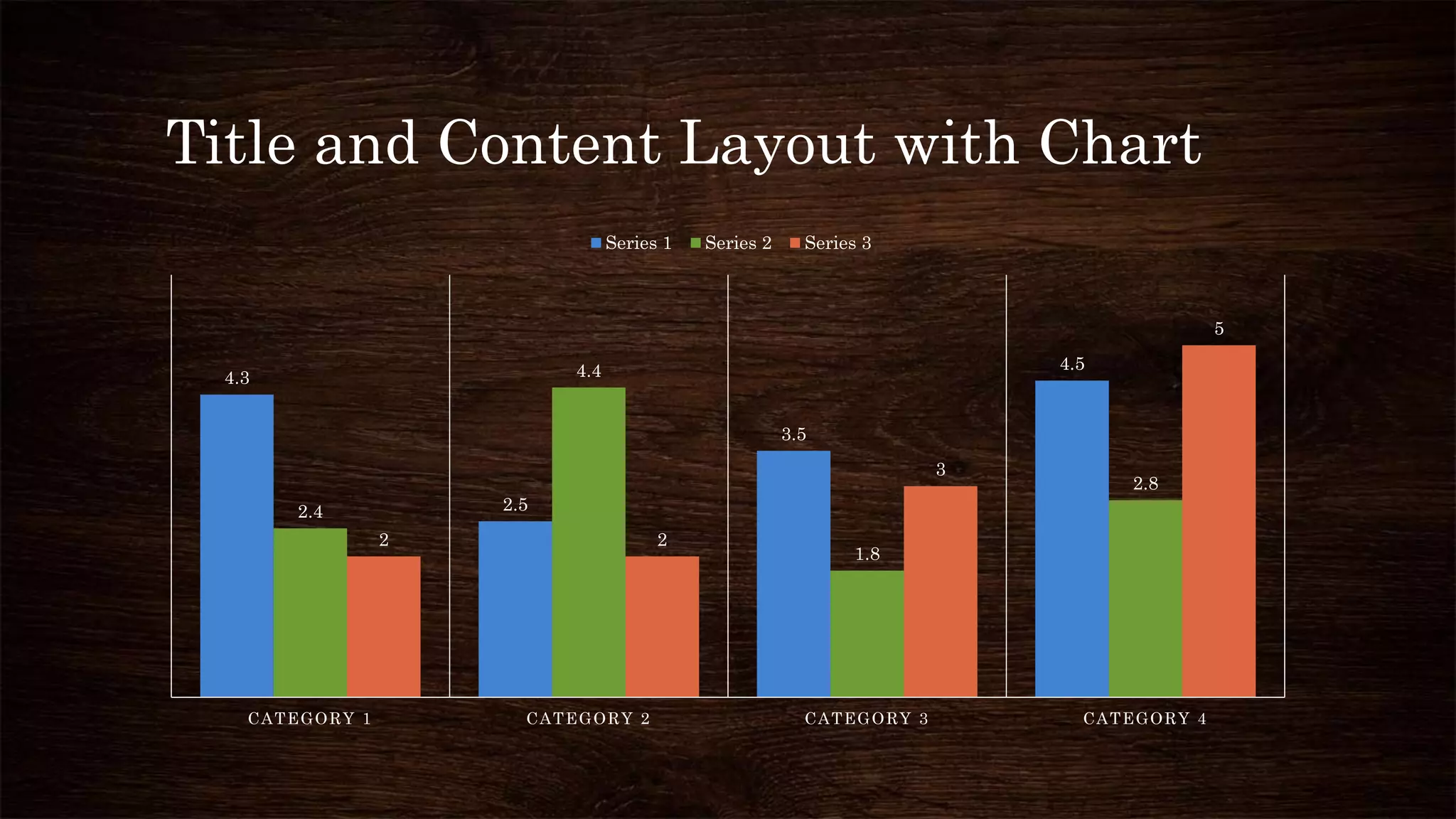
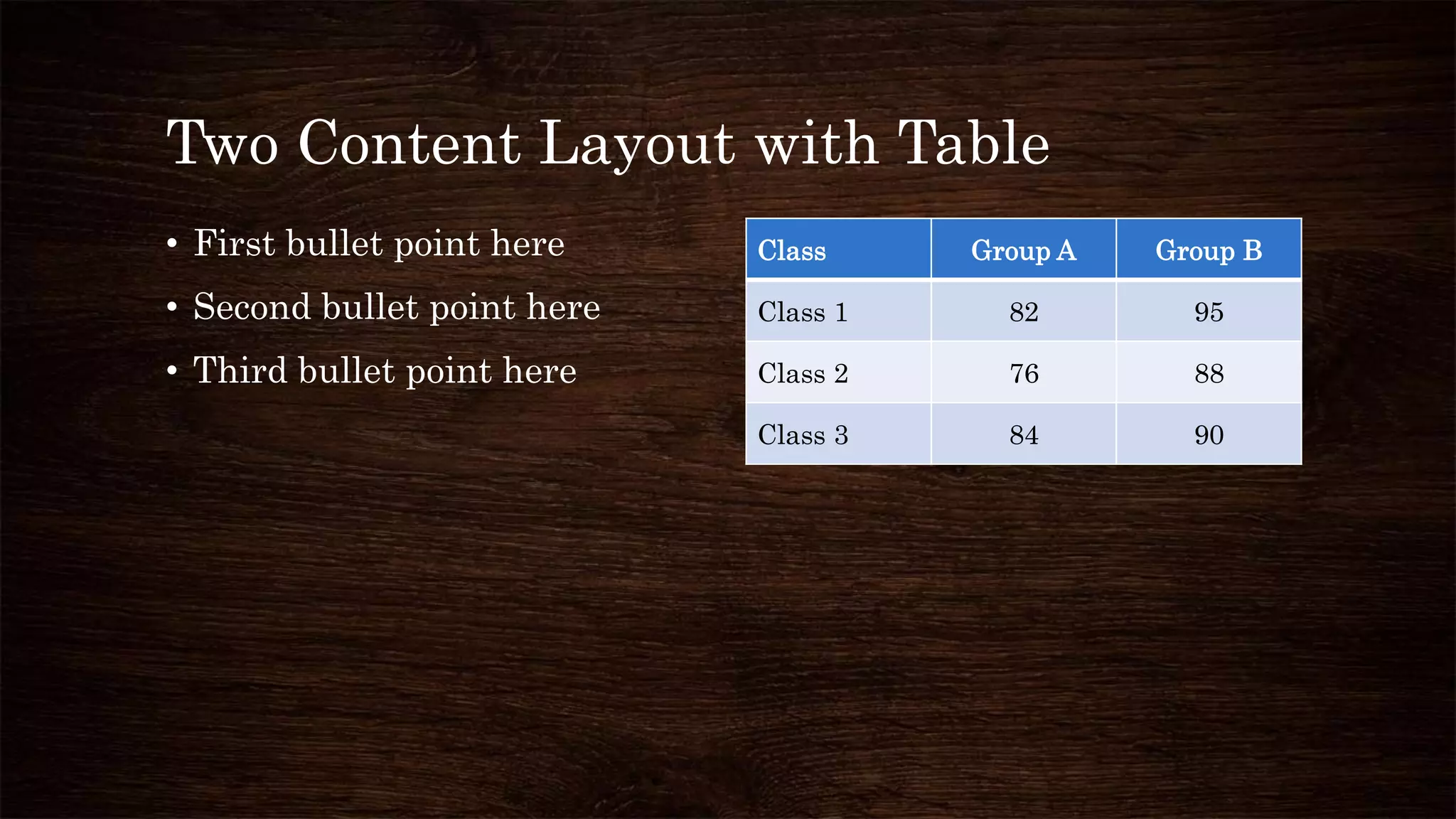
The document provides an overview of sweat glands, including their types (eccrine and apocrine), secretion mechanisms, composition of sweat, and regulation of sweating. Eccrine glands secrete a hypotonic fluid primarily composed of water and salts, while apocrine glands produce a thicker, odorous fluid. Sweat regulation is mainly controlled by the brain's thermoregulatory center and involves both thermal and emotional factors to prevent overheating.