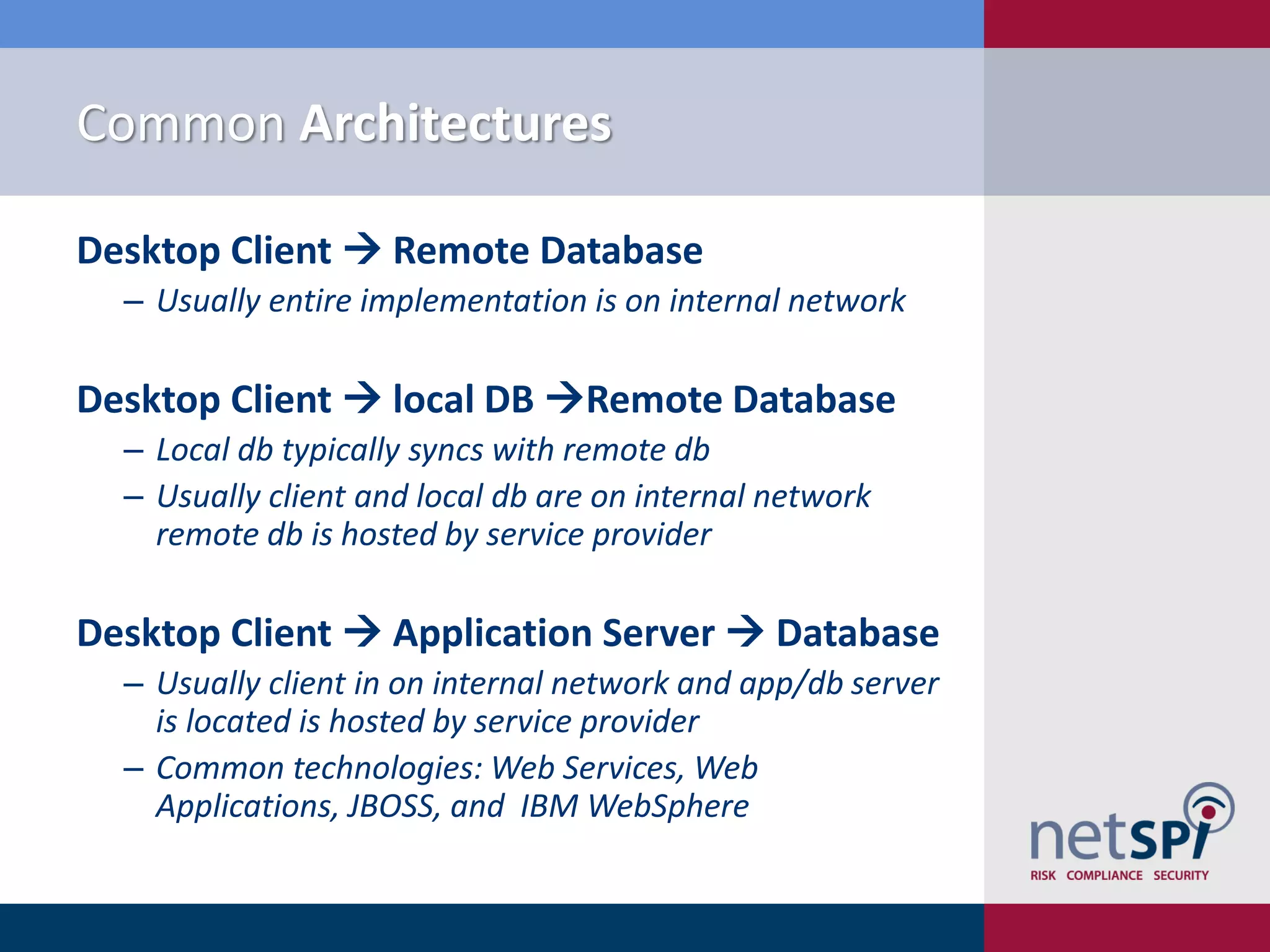
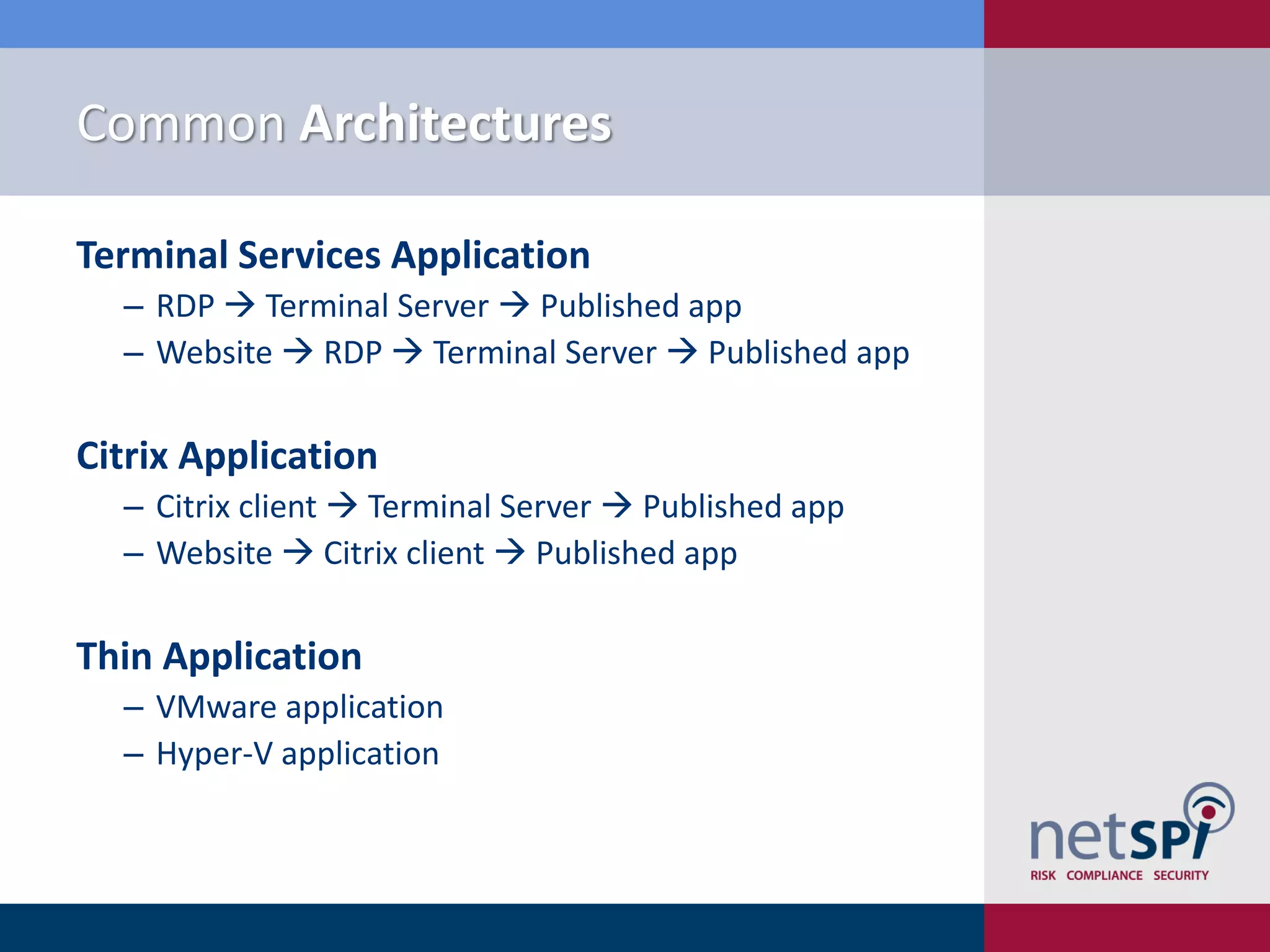
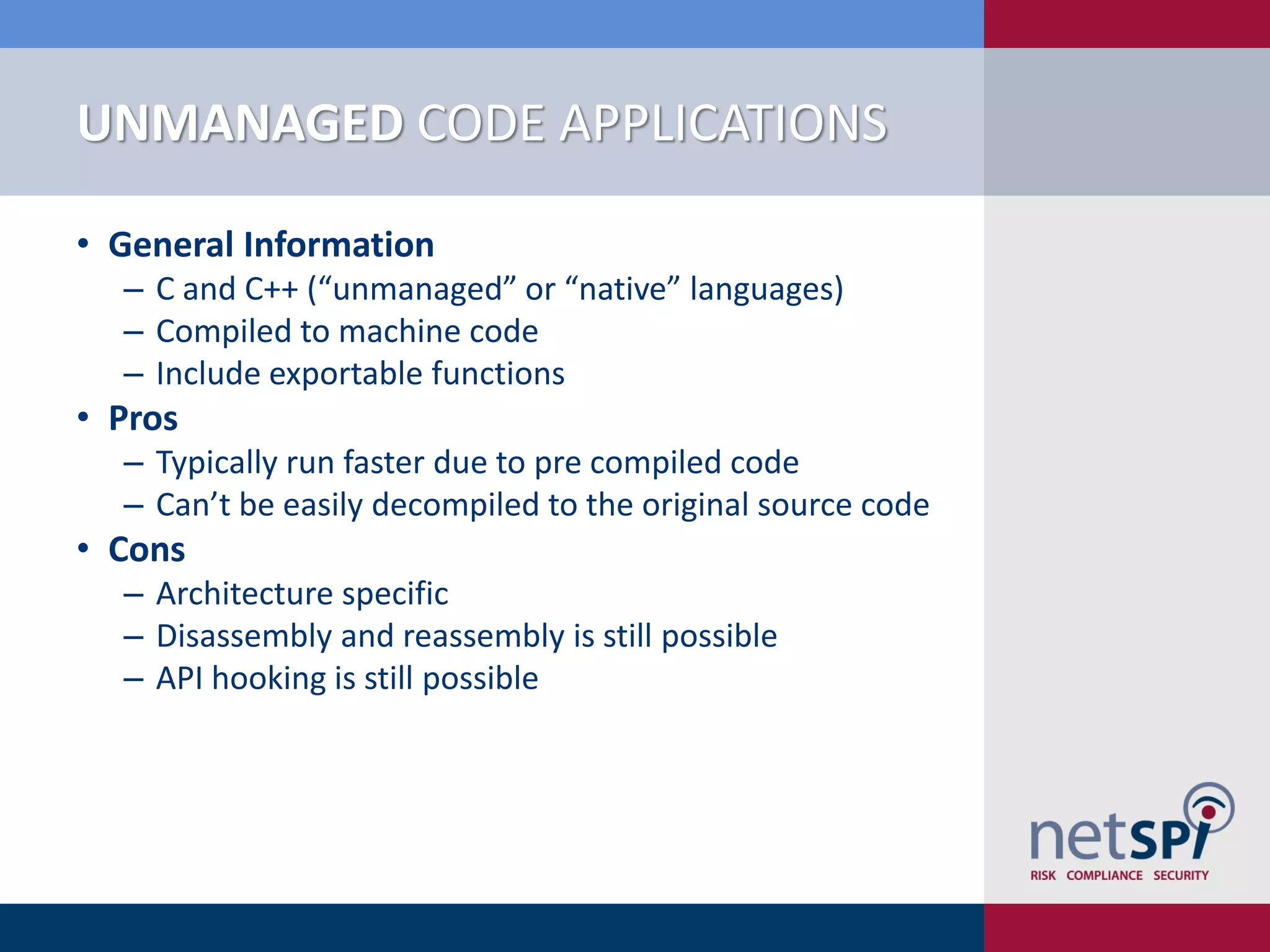
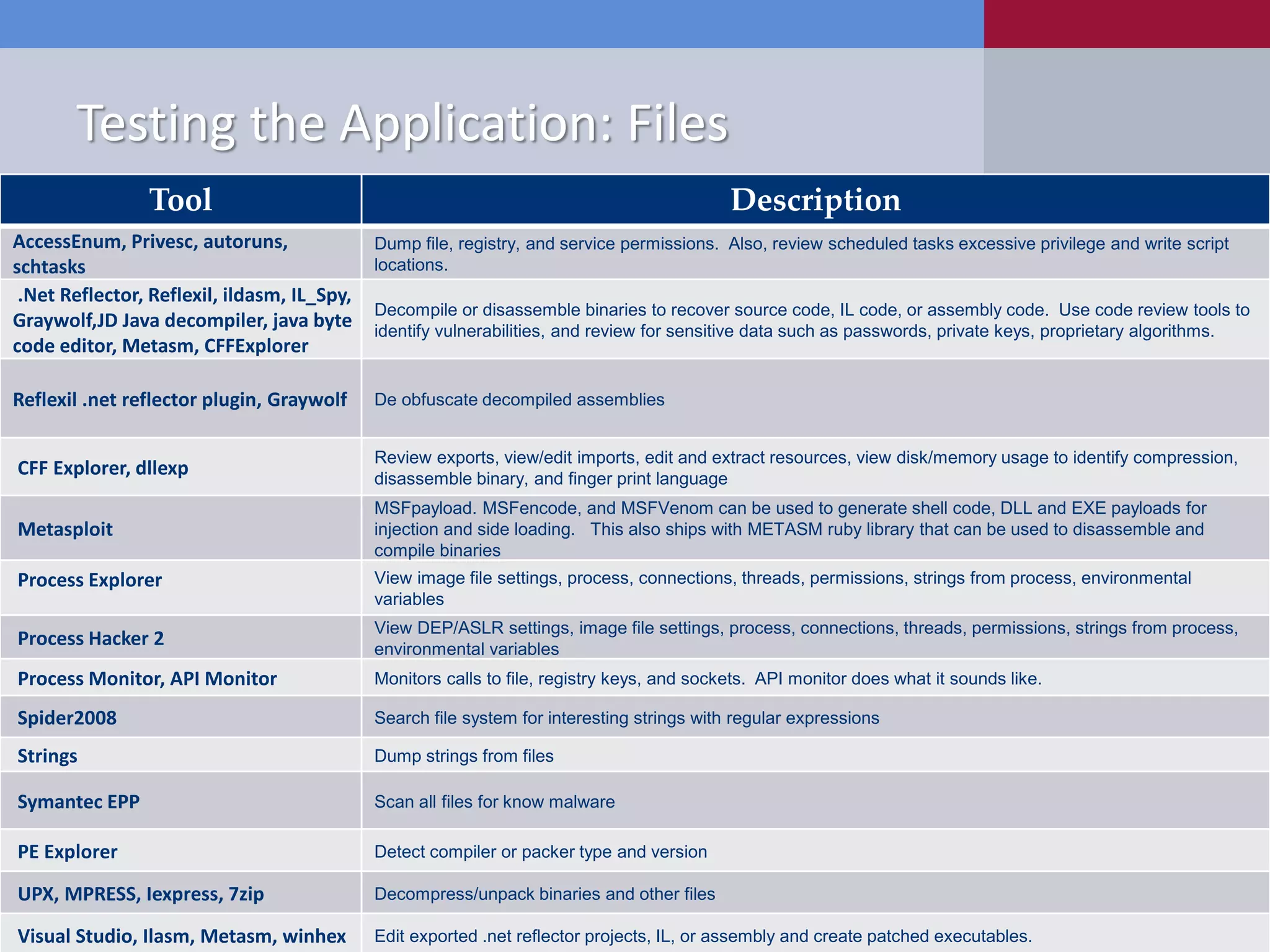
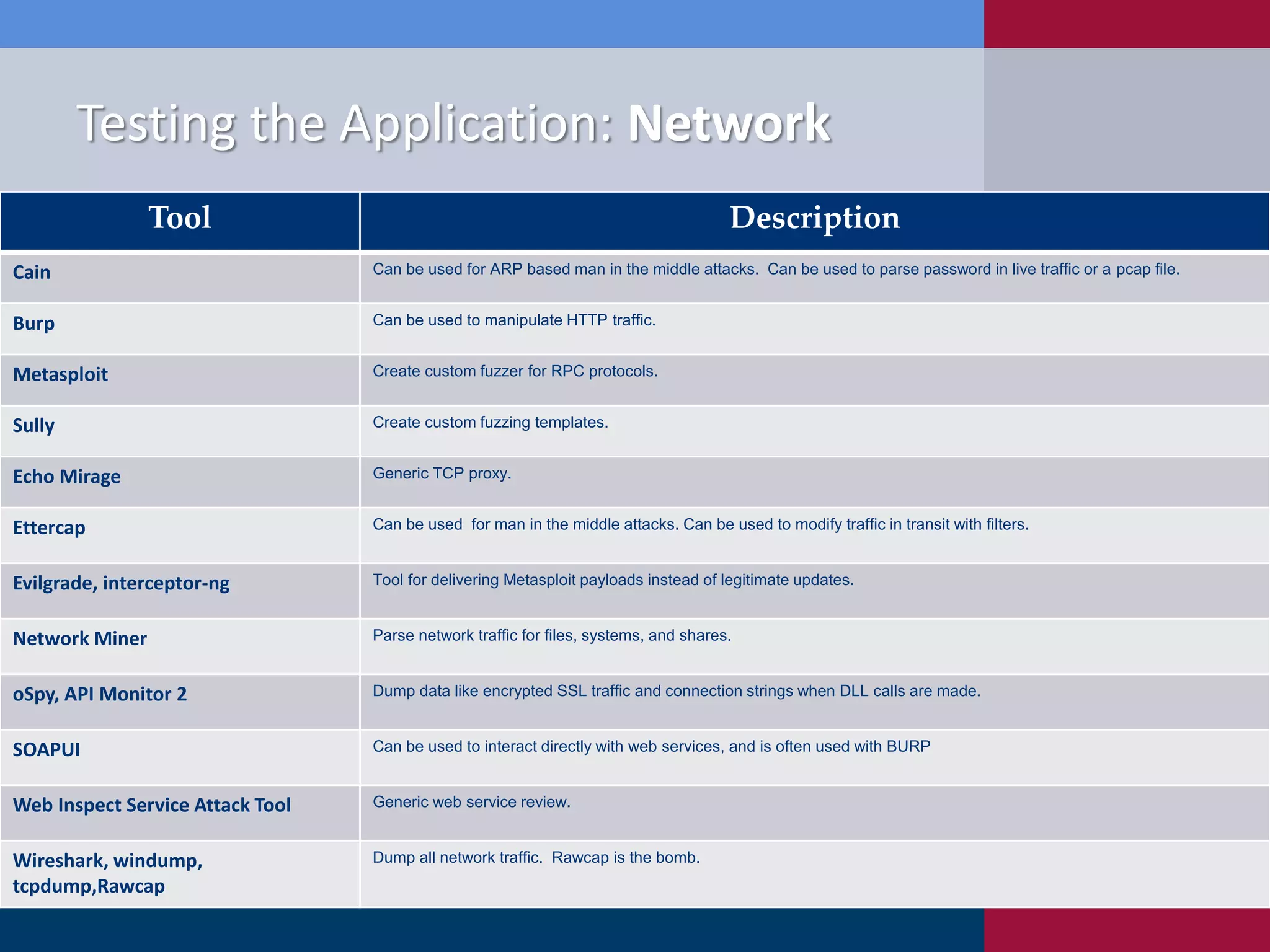
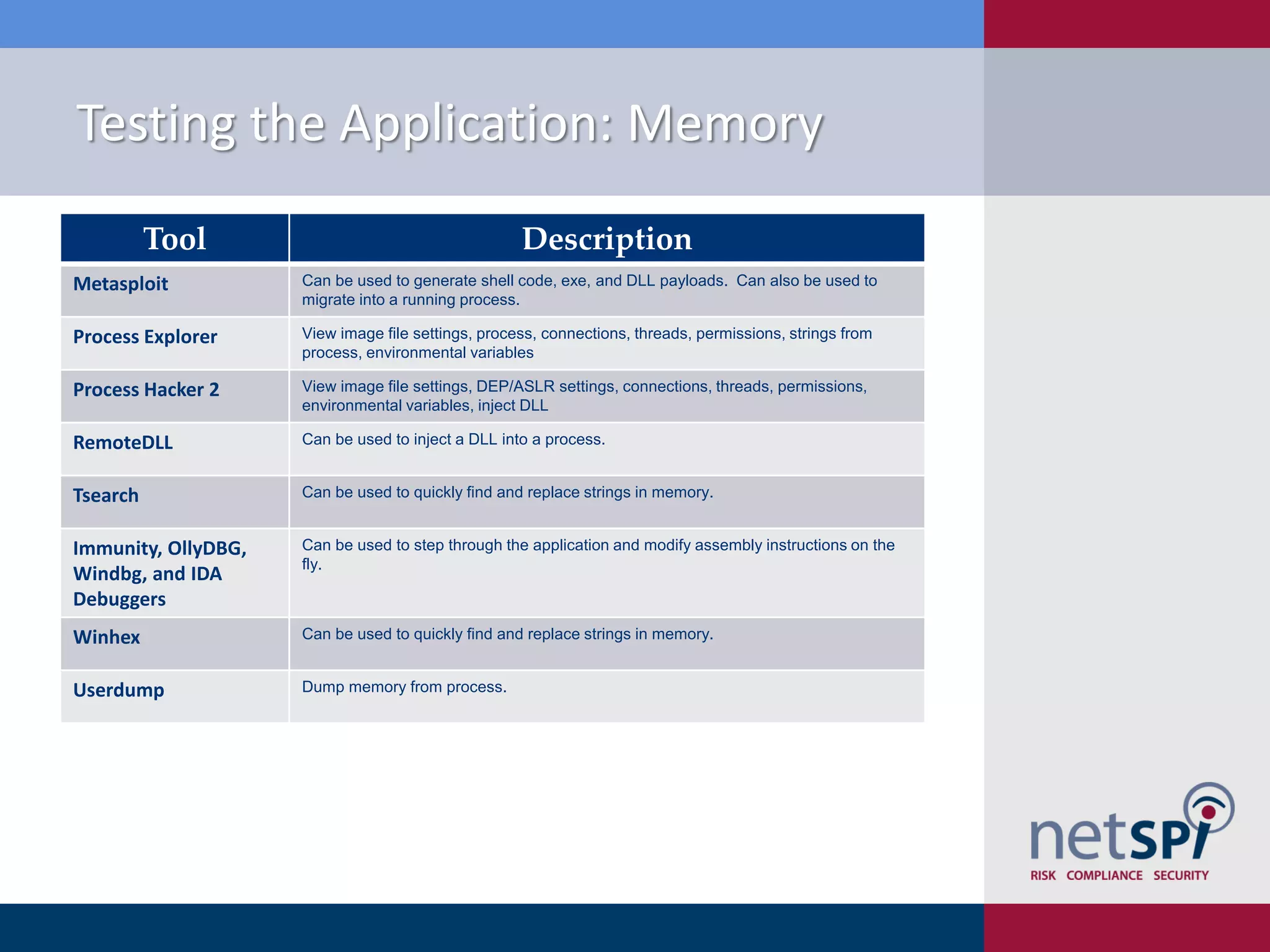
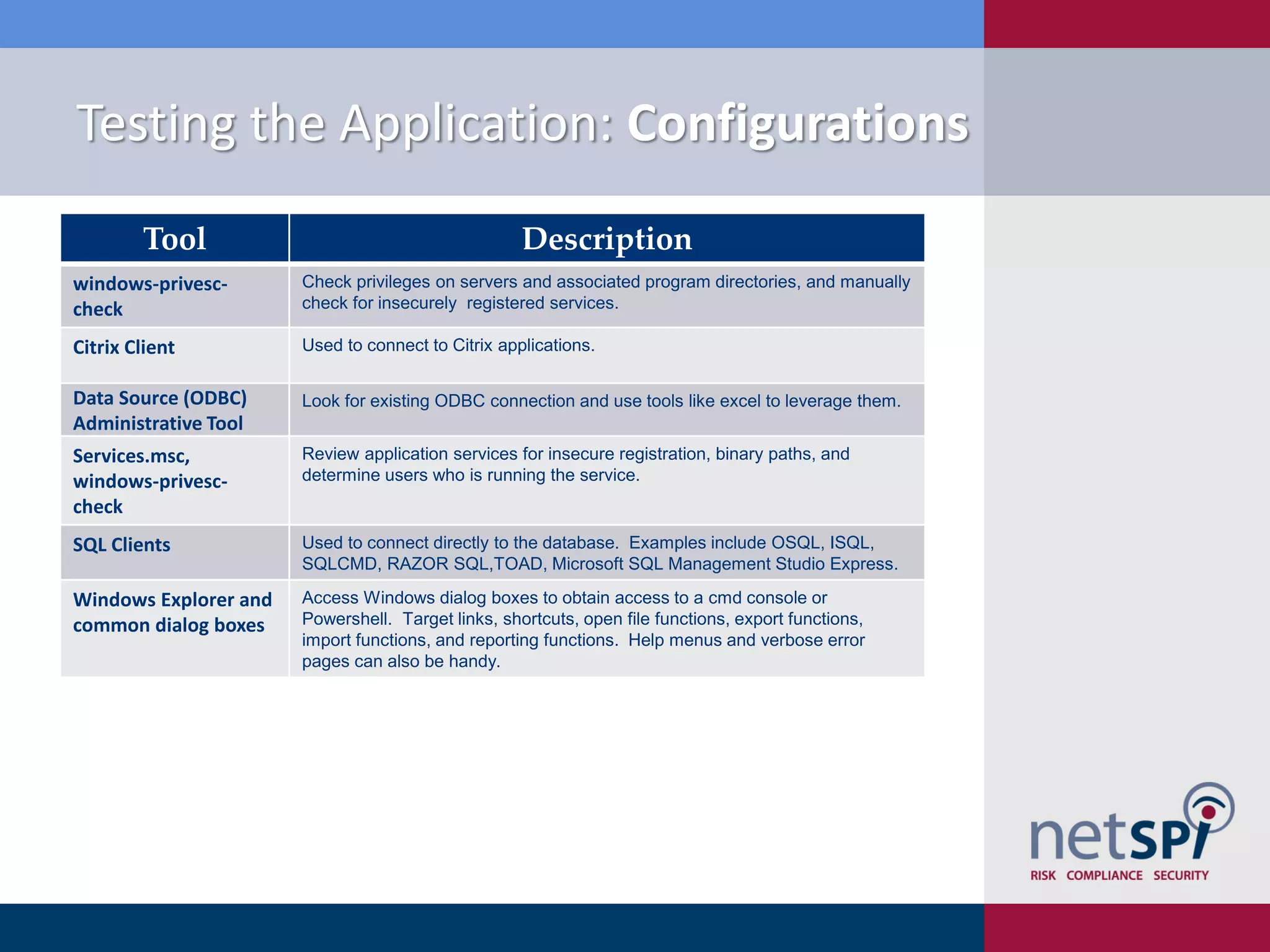
Scott Sutherland discusses penetration testing thick applications. He explains why these applications create unique risks compared to web applications due to users having full control over the application environment. This allows attacks on trusted components, exposure of data and admin functions, and privilege escalation. Sutherland outlines the goals and process for testing thick applications, including common architectures, accessing the application, and testing the application's GUI, files, registry, network traffic, memory, and configurations to identify vulnerabilities.