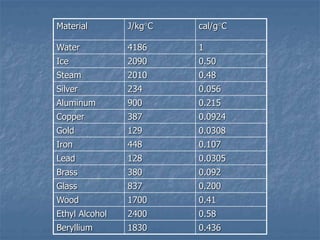
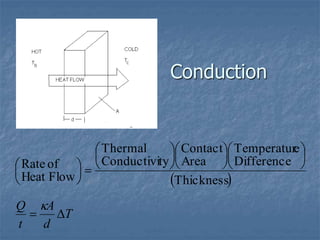
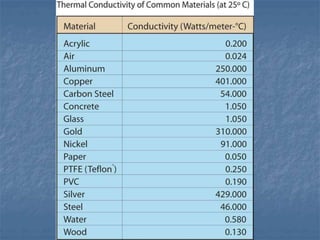
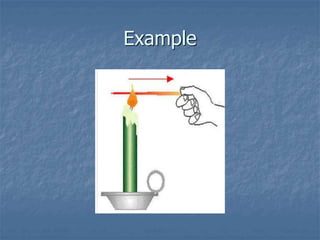
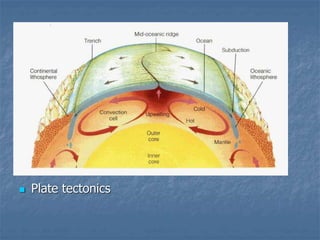
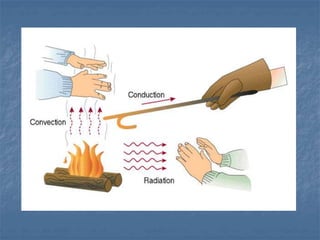
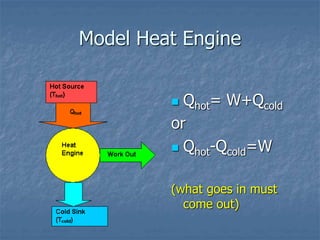
Thermodynamics deals with quantities like temperature, heat, work, pressure, and volume. Heat is the random motion of particles, and temperature is a measure of how fast particles are moving on average. Heat transfer occurs through conduction, convection, and radiation. The first law of thermodynamics states that energy is conserved, so heat added equals work done plus change in internal energy. Heat engines operate in cycles to convert heat into work. Engine efficiency is defined as the ratio of work output to heat input. The second law states no engine can reach 100% efficiency. The Carnot engine is theoretically the most efficient type.