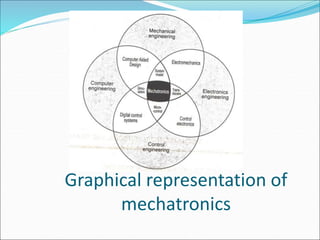
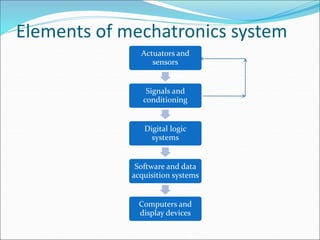
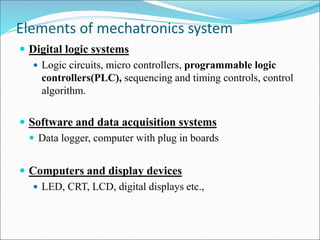
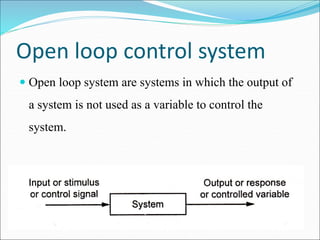
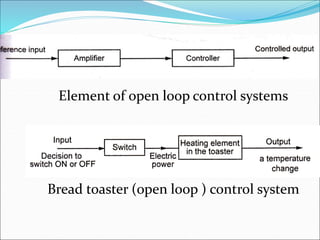
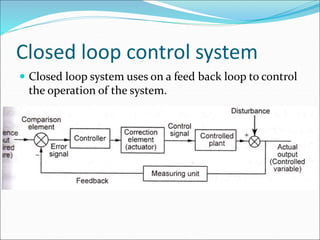
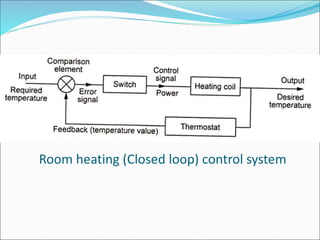
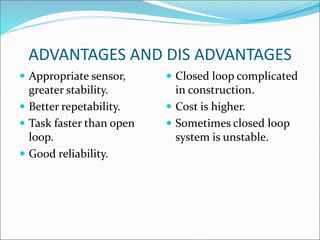
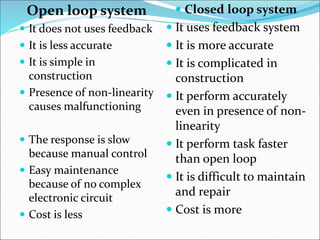
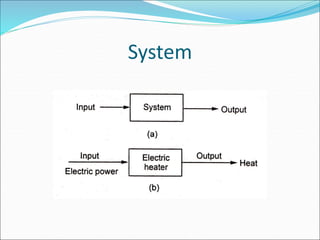
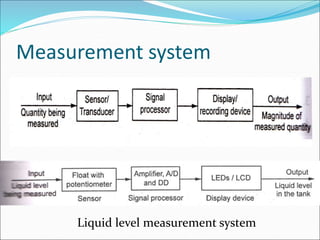
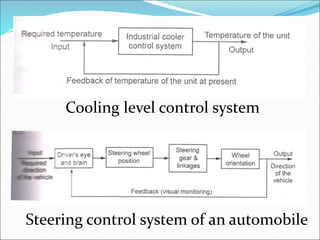
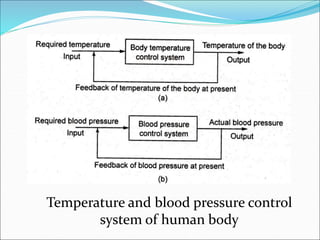
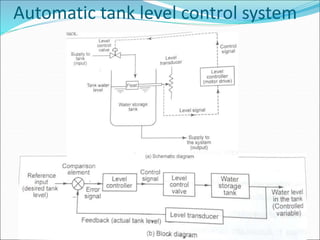
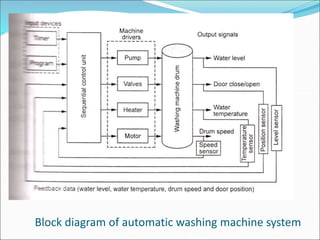
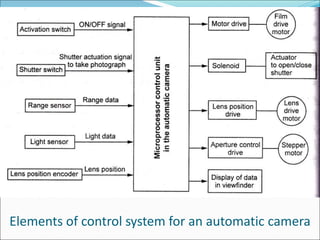
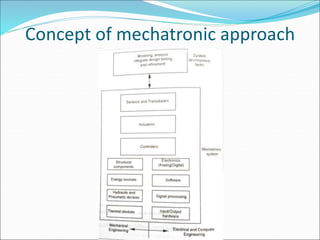
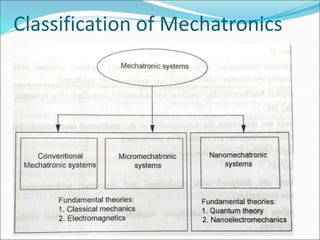
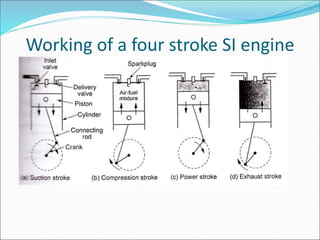
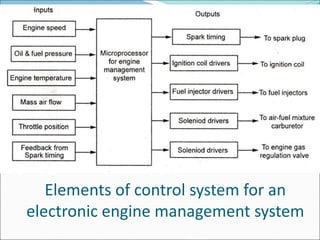
Mechatronics is the synergistic integration of mechanical engineering, electronics, control systems, and computers to design and manufacture products. It was introduced in 1969 by a Japanese engineer to describe systems incorporating digital and electronic controls into mechanical systems. Examples include automated machines, vehicles, and devices that combine sensors, actuators, and microprocessors to perform functions. Mechatronics finds applications in various fields like manufacturing, aerospace, defense, biomechanics, and more.