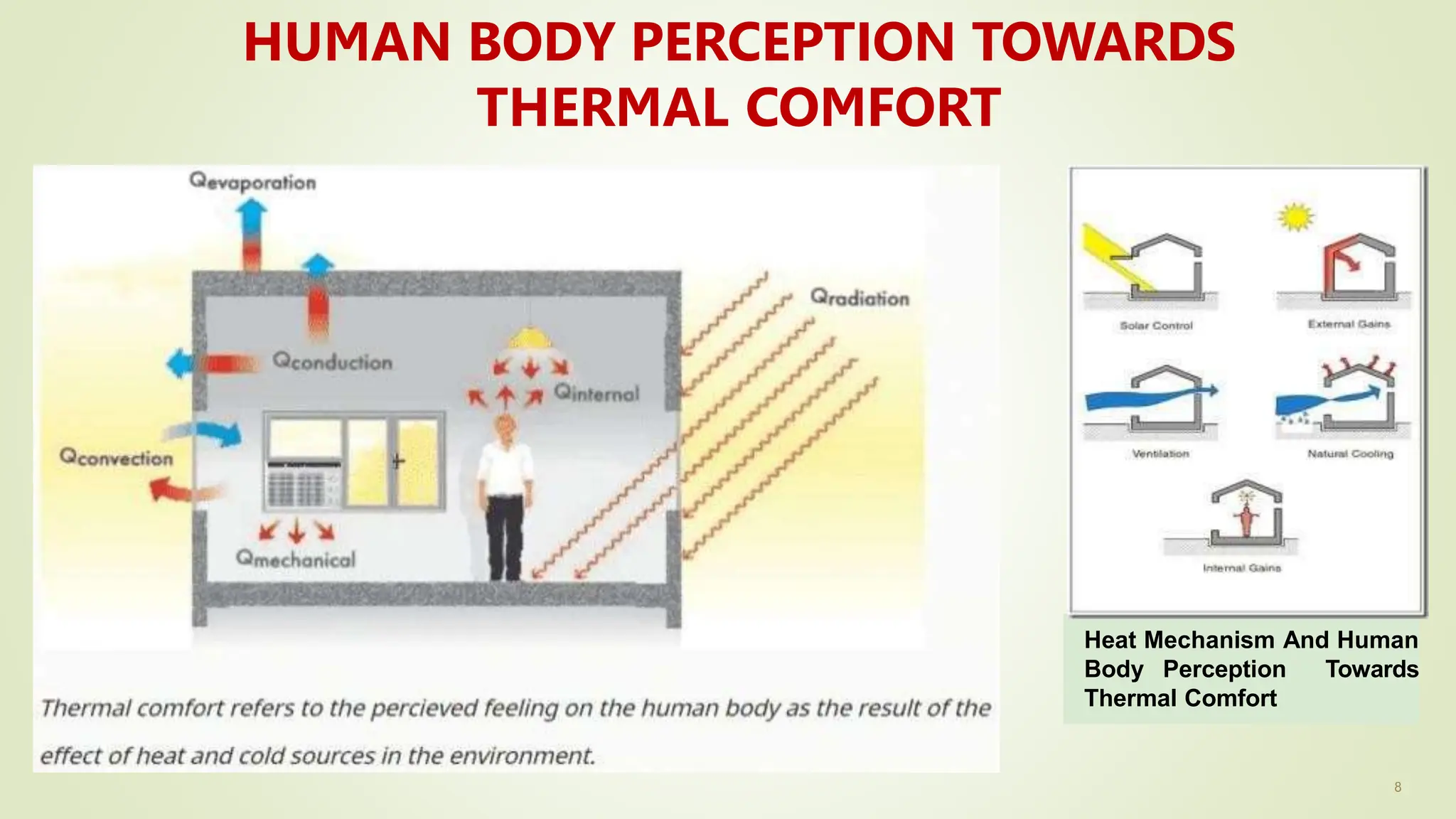
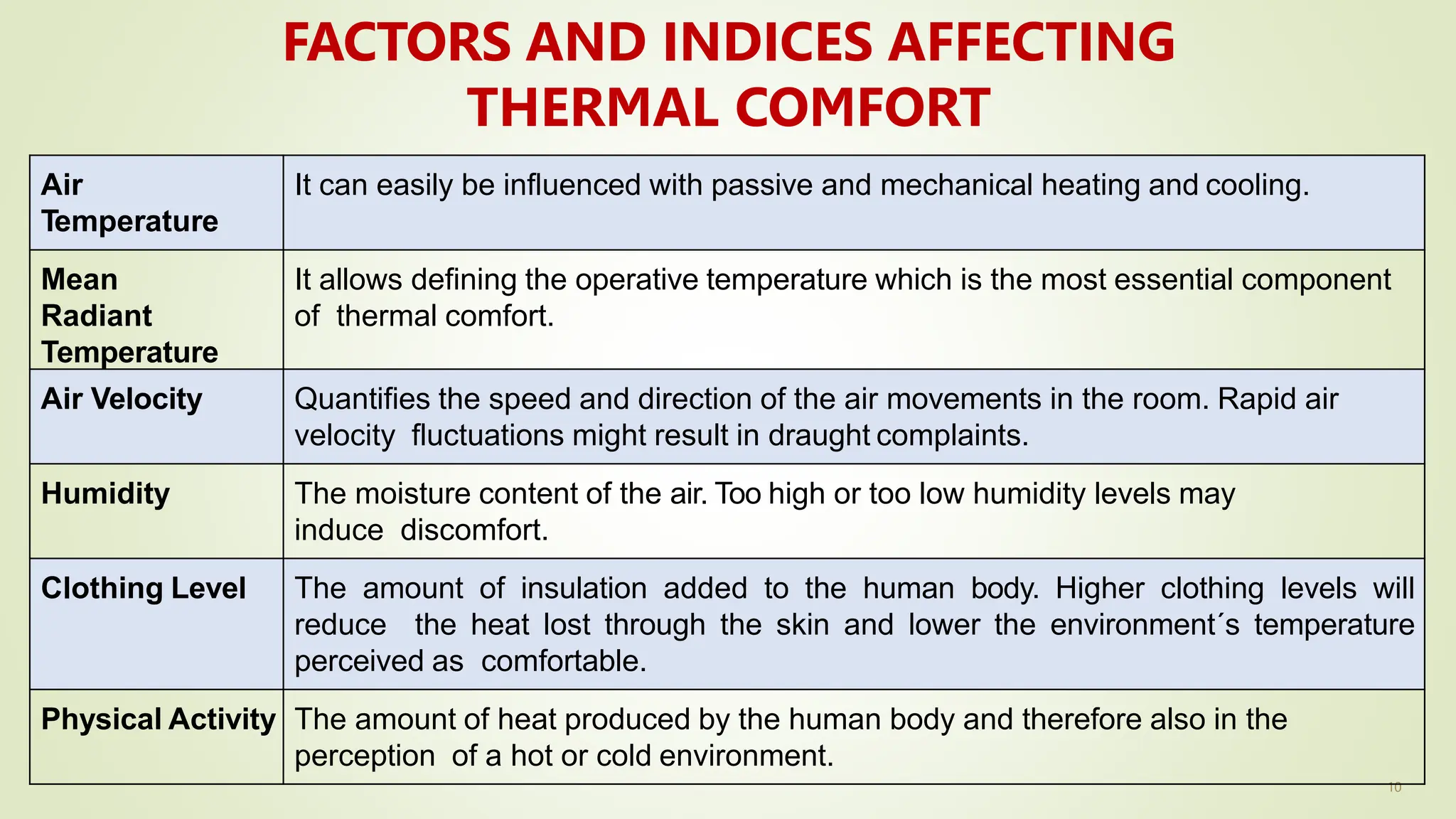
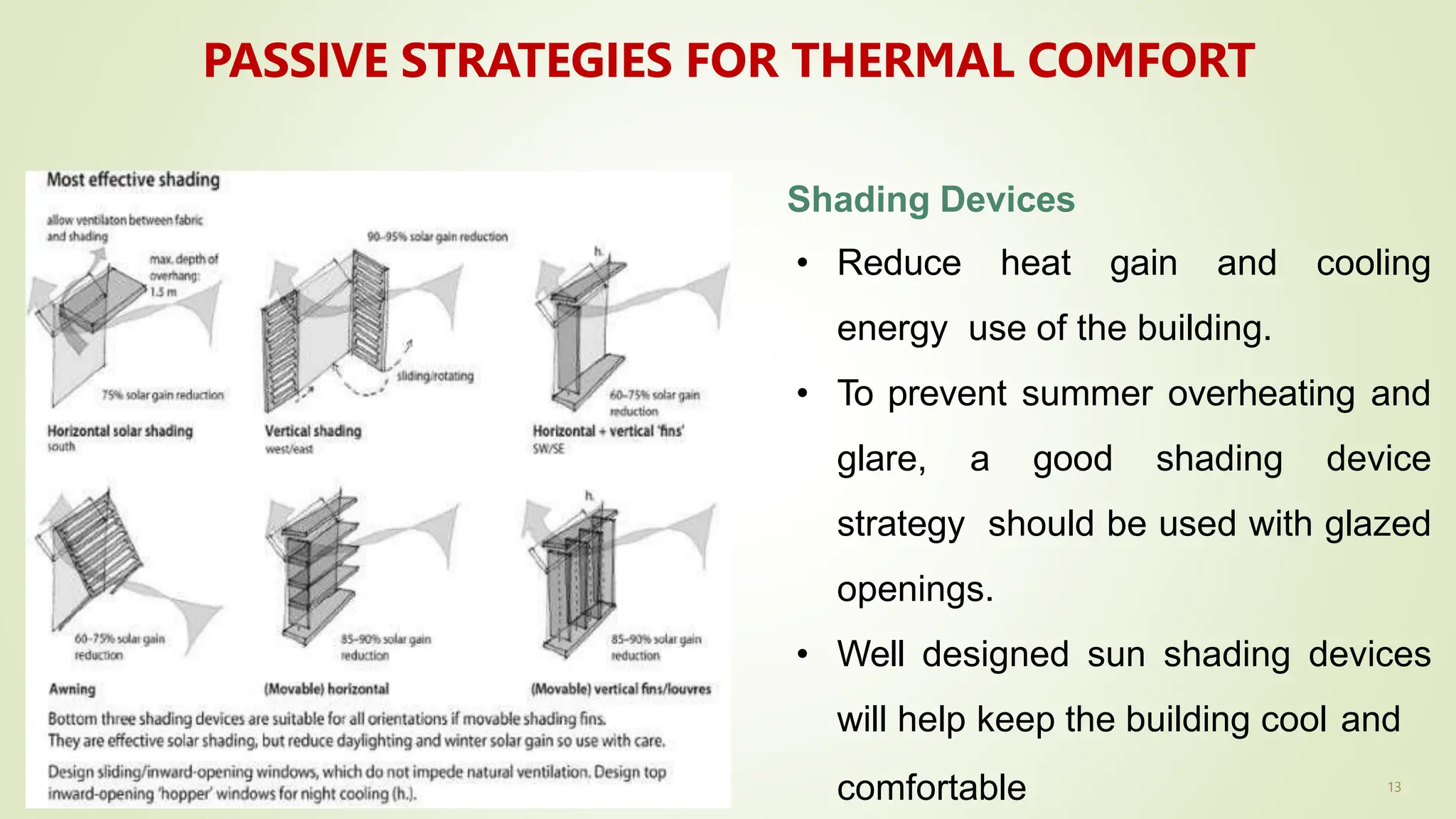
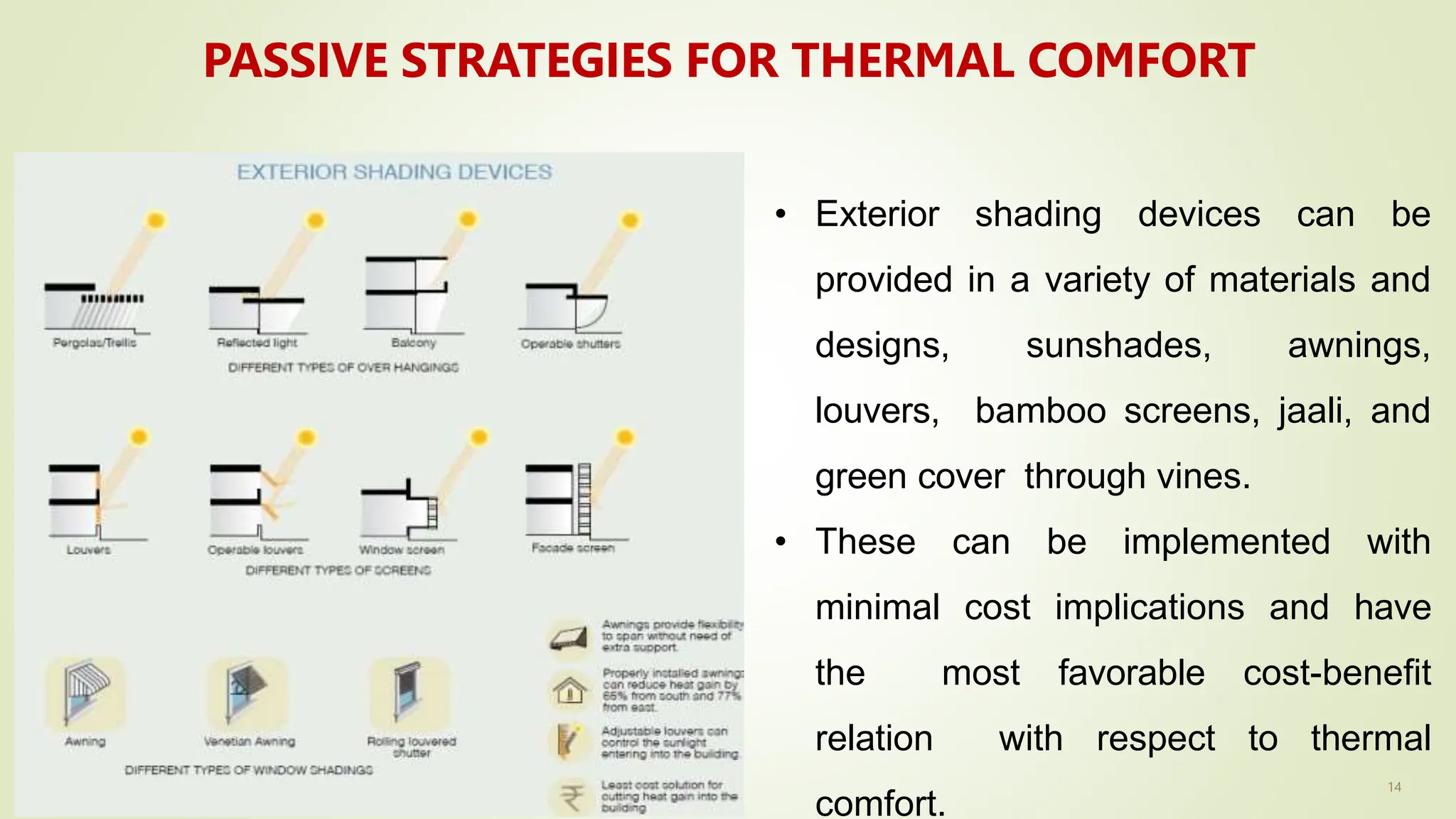
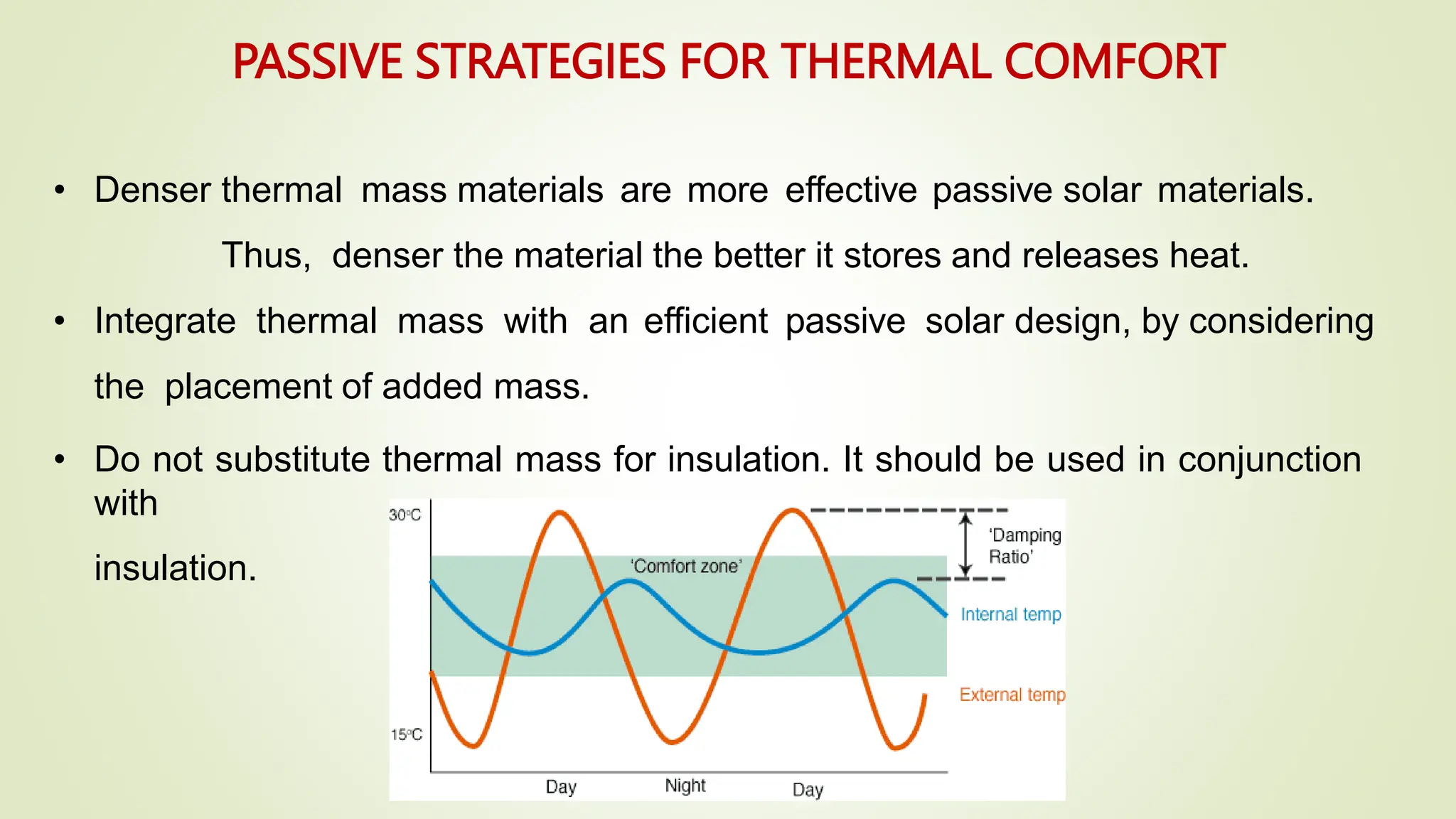
The document discusses heat transfer and thermal comfort in buildings. It defines thermal comfort and explains the factors that affect it, including air temperature, mean radiant temperature, air velocity, humidity, clothing, and activity level. It also describes the three main modes of heat transfer: conduction, convection, and radiation. Finally, it provides examples of passive strategies that can be used to improve thermal comfort, such as building orientation, shading devices, thermal mass, ventilation, insulation, and green roofs.