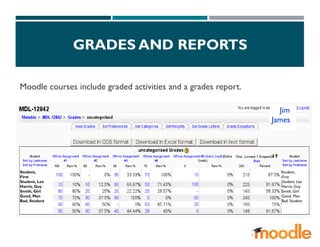
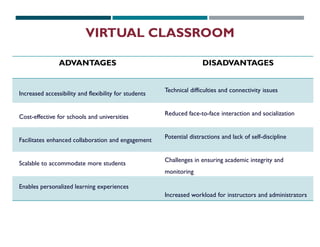
The document discusses the concept and features of virtual classrooms, highlighting their advantages such as flexibility, accessibility, and cost-effectiveness while also noting disadvantages like technical issues and the lack of personal interaction. It outlines two types of virtual classrooms: asynchronous, allowing students to learn at their convenience, and synchronous, facilitating real-time communication and interaction. The conclusion emphasizes the need for robust infrastructure and continuous evaluation to overcome challenges and maximize the benefits of virtual classrooms.