1) The document provides guidance on performing thermal analysis in Ecotect by properly modeling geometry, assigning materials and properties, calculating inter-zonal adjacencies, and analyzing hourly temperature profiles, heat gains/losses, and more.
2) Key recommendations include modeling geometry in Ecotect rather than importing, ensuring all zones are fully enclosed, checking and correcting surface normals, and assigning primary and alternate materials to surfaces.
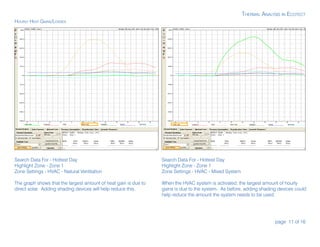
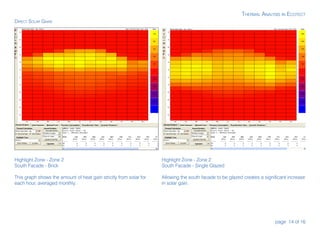
3) The analysis section describes how to view temperature distribution, direct solar gains, monthly loads, and a passive gains breakdown to evaluate performance under different conditions and identify areas for improvement.