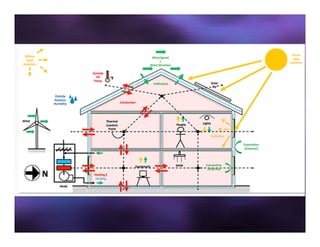
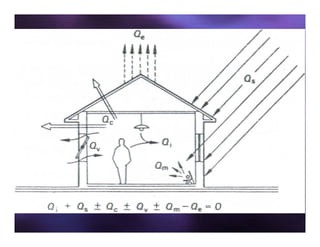
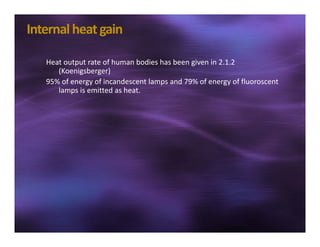
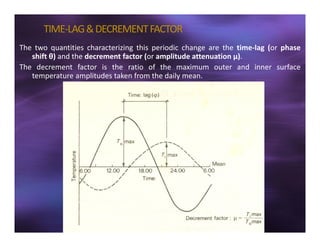
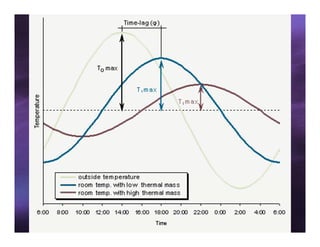
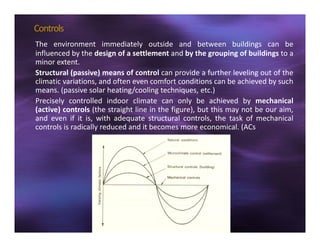
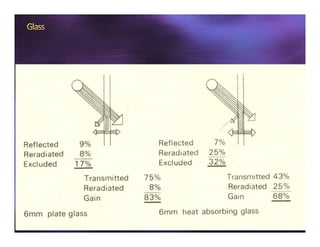
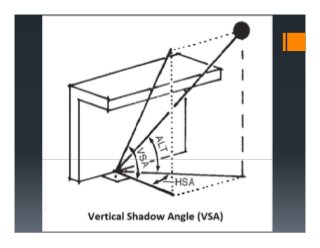
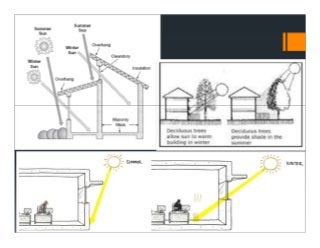
This document discusses sun shading devices used to control solar radiation entering buildings. It describes different types of internal and external shading devices, including curtains, blinds, louvers and overhangs. It explains how shading devices improve thermal comfort and energy efficiency by reducing heat gains and cooling loads. The document also discusses how to select and design shading devices based on factors like orientation, climate and sun path. It describes how to calculate the horizontal and vertical shadow angles needed to determine a shading device's size and effectiveness.