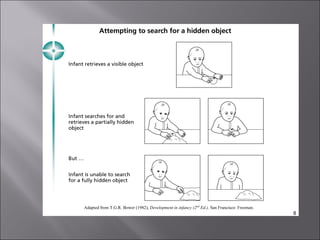
The document discusses the concepts of growth and development, highlighting key theories from Piaget and Erikson, as well as addressing criticisms of Piaget's methodology and cultural biases. It explores moral reasoning through an example involving a husband, Heinz, contemplating theft to save his dying wife, illustrating the conflict between legal adherence and ethical decision-making. The theories presented emphasize the influence of social interaction and continuous learning in the development process.