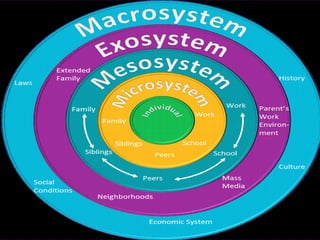
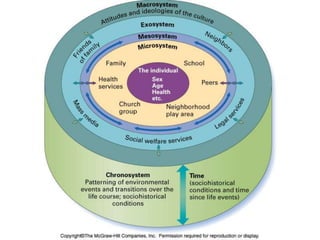
The document discusses various theories of development, including social cognitive theory, ecological contextual theory, and ethological theory. It outlines the principles of each theory, emphasizing the role of social interactions, environmental factors, and biology in shaping human behavior and development. Key figures like Albert Bandura and Urie Bronfenbrenner contributed significantly to these theories, providing frameworks relevant in fields such as education and psychology.