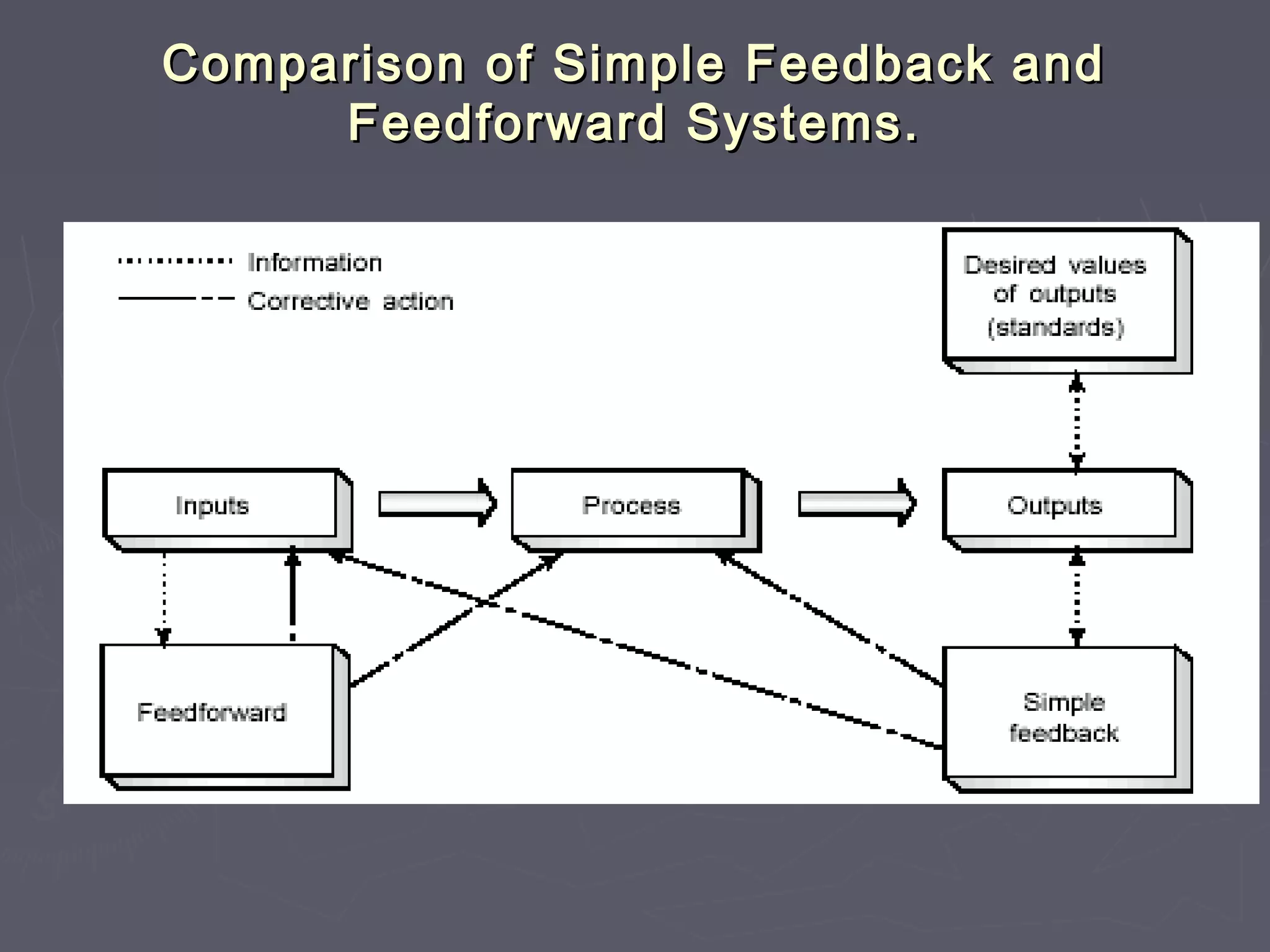
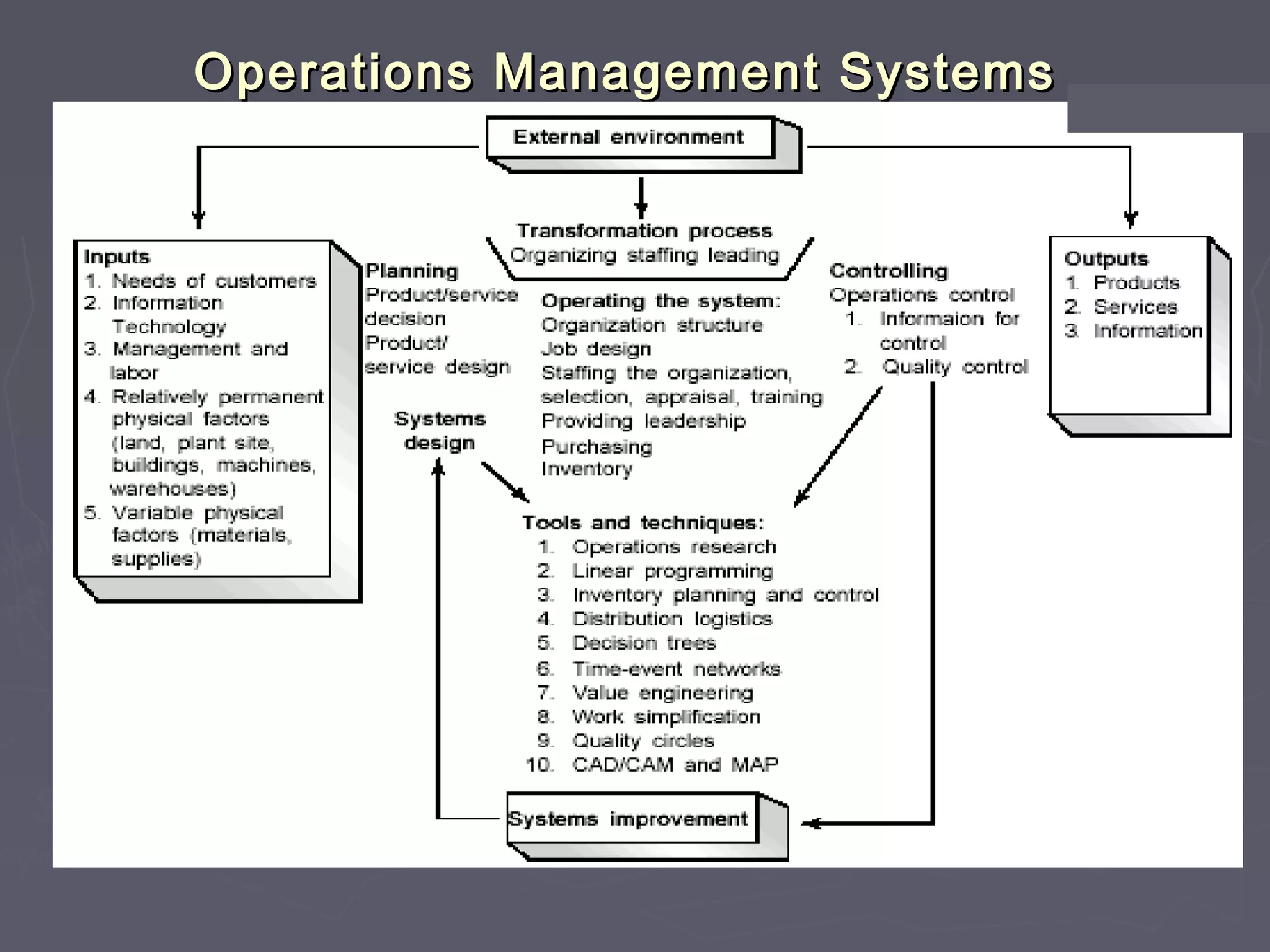
The document outlines the various aspects of controlling within organizations, detailing methods such as bureaucratic, market, and clan control. It emphasizes the significance of establishing standards, measuring performance, and making necessary corrections, while also discussing challenges and limitations in the controlling process. Additionally, it touches on budgeting, productivity, operations management, and the importance of continuous improvement in achieving organizational objectives.