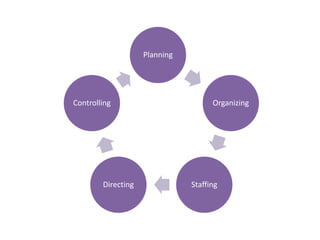
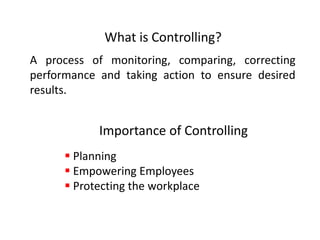
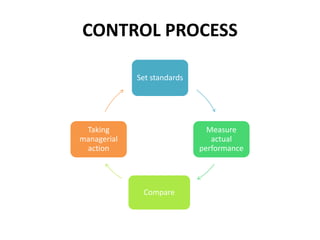
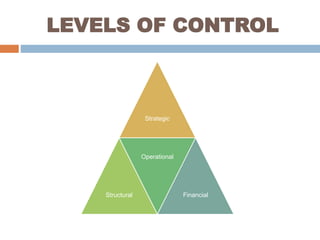
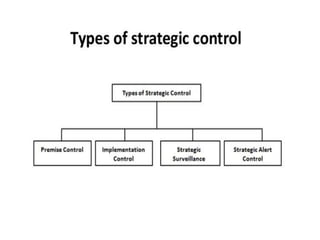
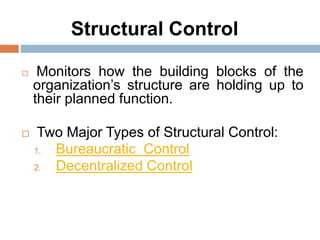
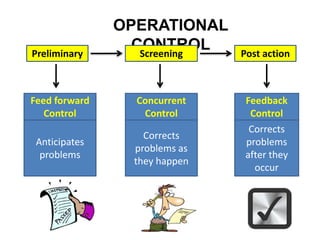
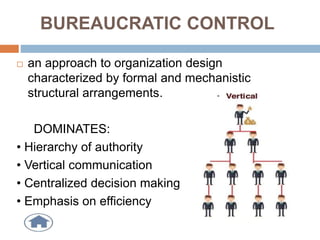
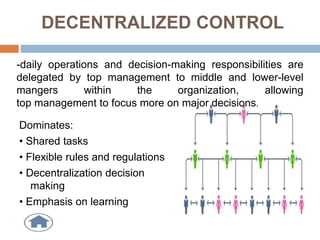
This document discusses different types of controlling in management. It defines controlling as monitoring, comparing, correcting performance and taking action to ensure desired results. It then describes five levels of control: strategic, structural, operational, financial, and bureaucratic vs decentralized structural control. Strategic control involves checking premises and strategy. Structural control monitors organizational structure. Operational control regulates daily output. Financial control involves budgets, financial statements, and audits. Bureaucratic control uses hierarchy while decentralized control shares tasks and decisions.