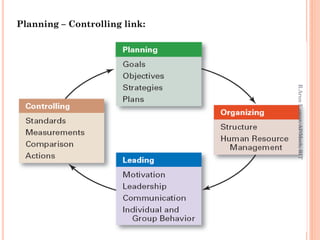
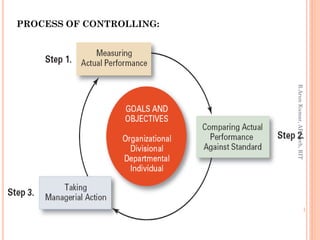
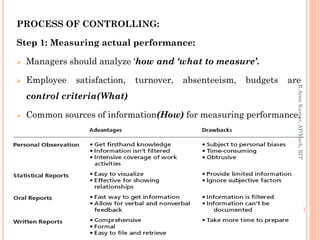
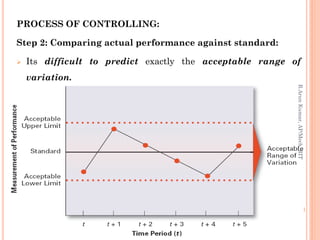
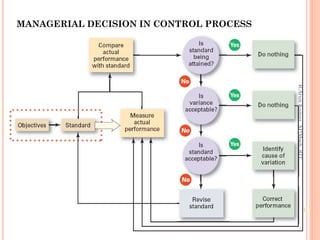
This document discusses controlling as a management function. It defines controlling as measuring performance against standards and correcting deviations. The document outlines the nature, importance and types of controlling. It describes the process of controlling as measuring actual performance, comparing it to standards, and taking managerial action. The document also discusses different types of controls based on time, including feedback, concurrent, feed forward, strategic, tactical and operational controls.