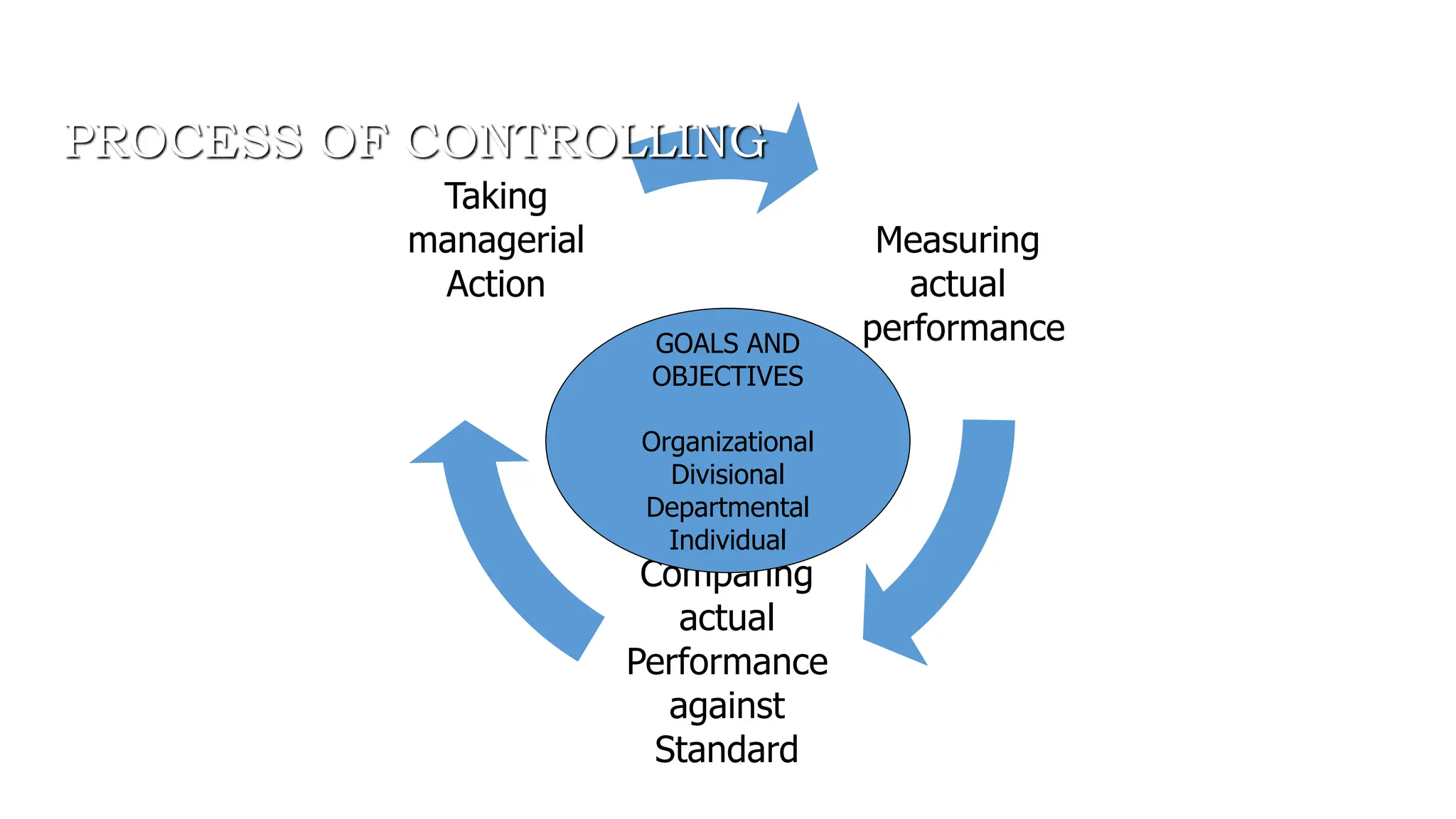
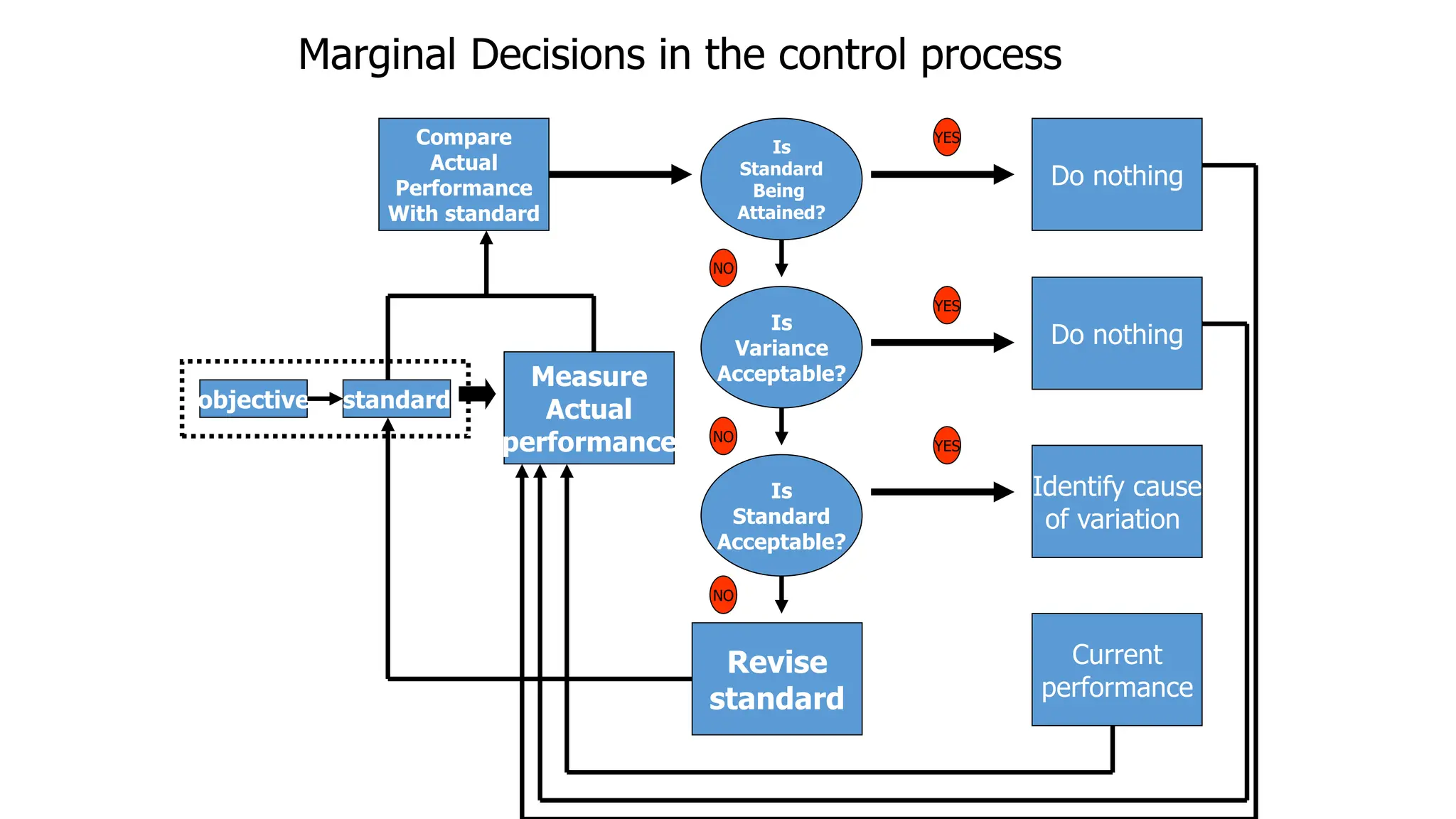
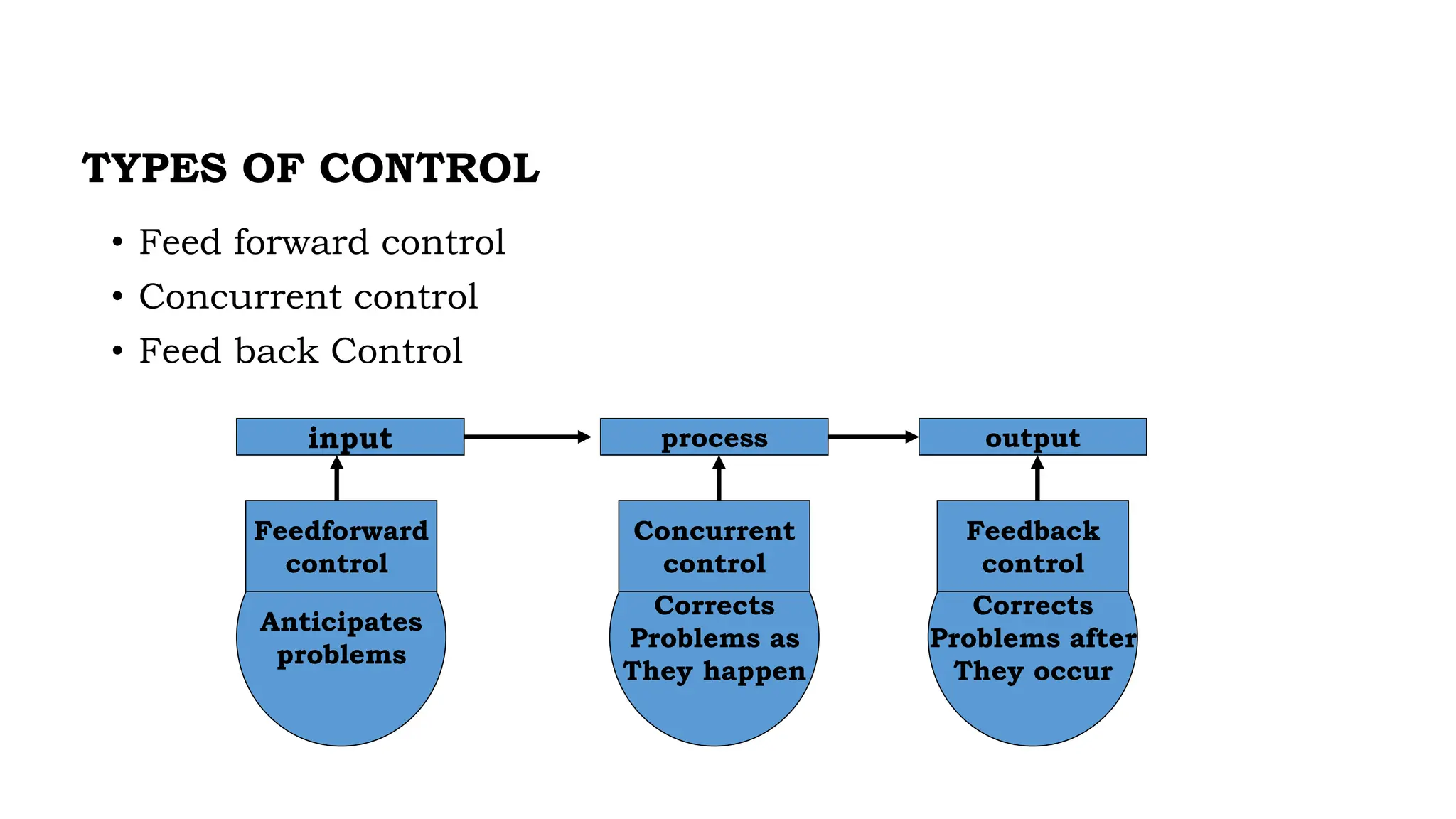
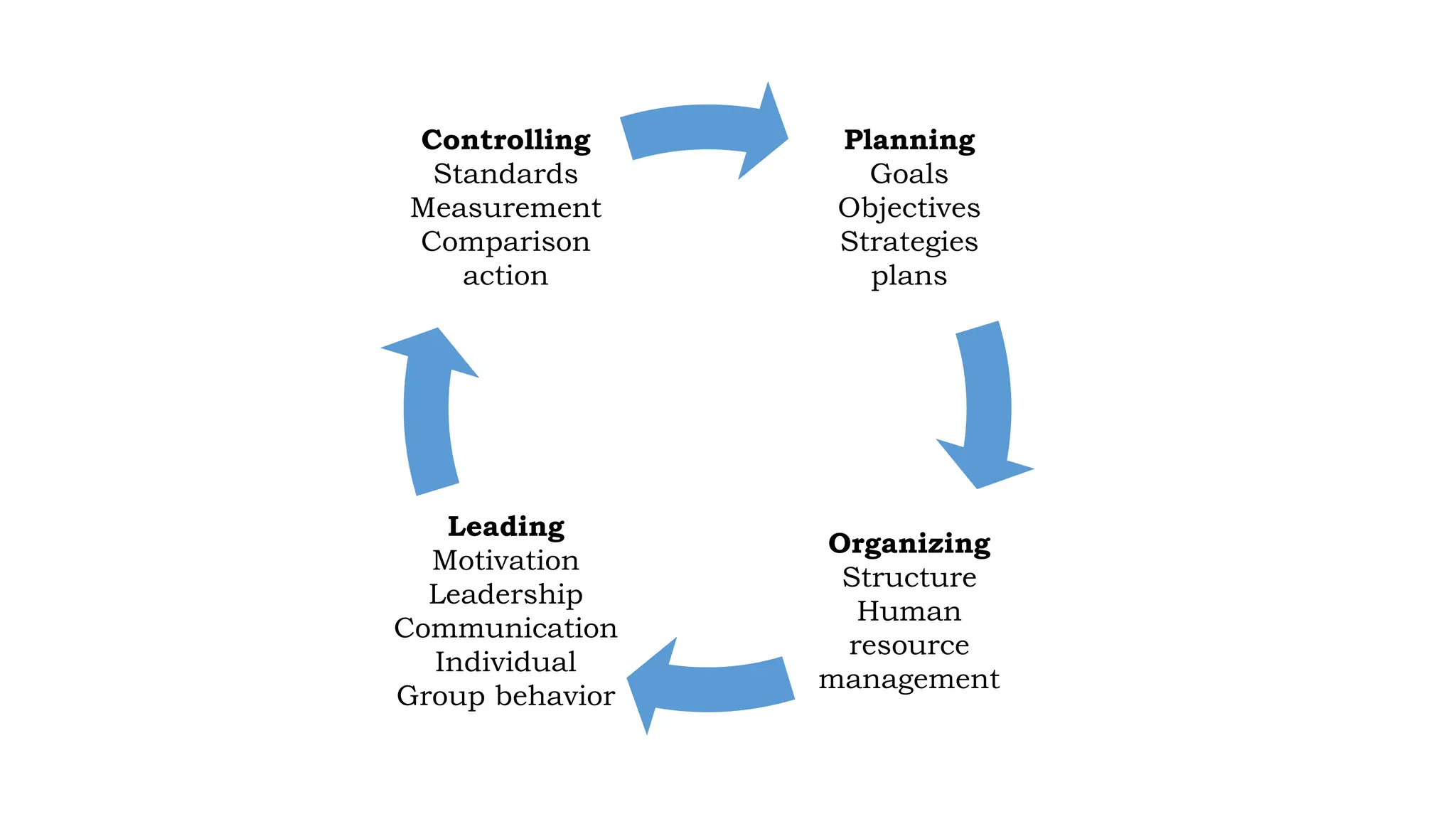
The document discusses the controlling function of management, outlining steps such as setting objectives, planning strategies, monitoring performance, and taking corrective actions to ensure alignment with standards. It emphasizes the importance of control at all levels, different types of control (feedforward, concurrent, feedback), and characteristics of an effective control system. Additionally, it details various control techniques like management audits and project evaluation methods (PERT and CPM) to enhance managerial oversight.