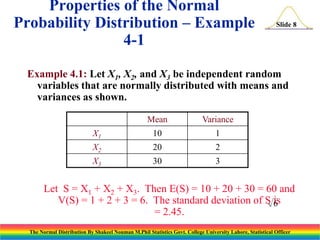
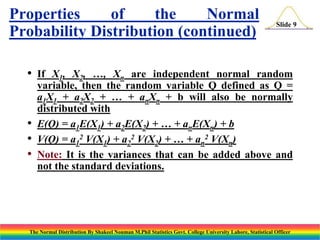
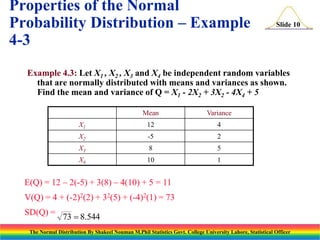
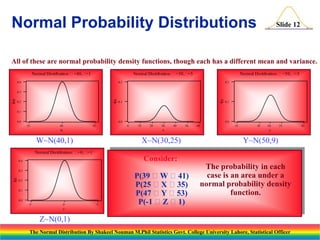
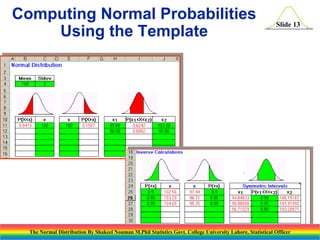
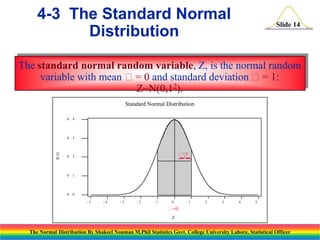
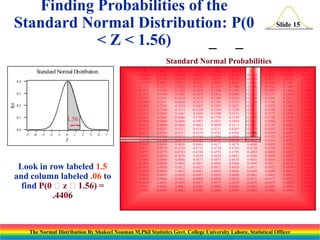
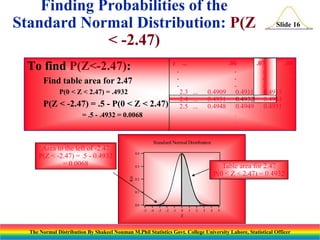
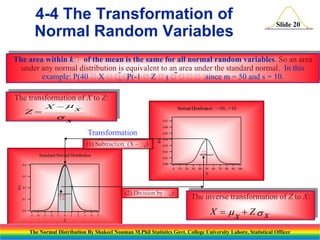
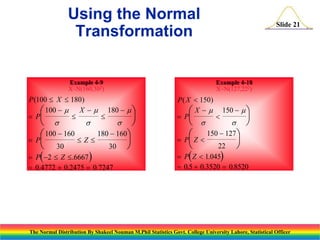
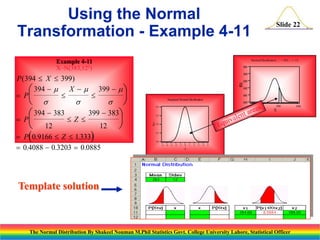
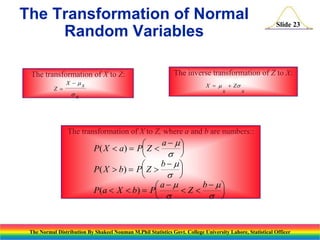
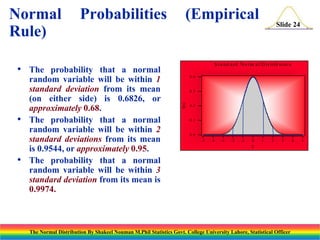
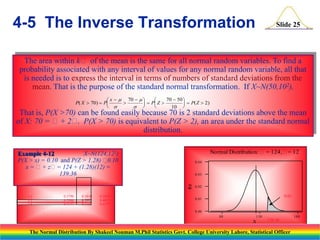
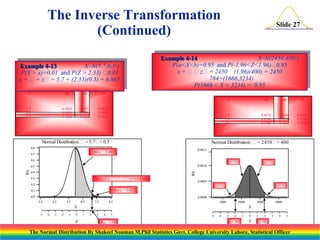
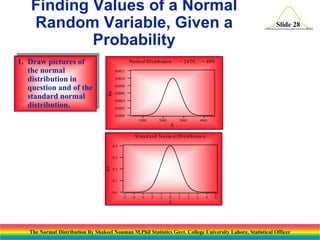
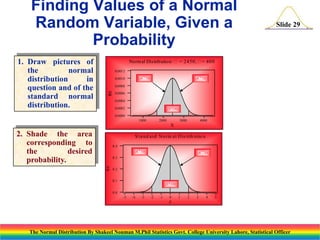
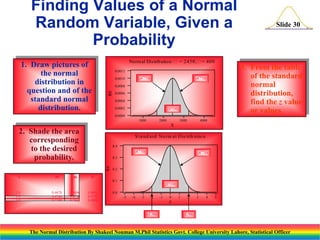
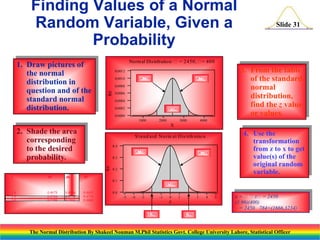
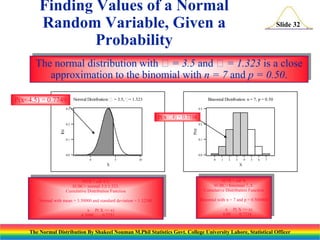
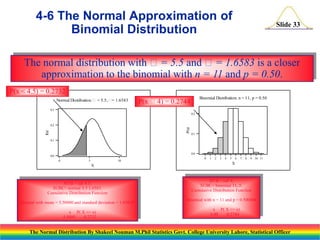
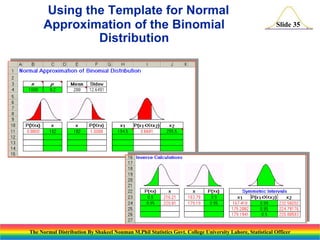
The document discusses the normal distribution and its key properties. It introduces the normal probability density function and how it is characterized by a mean and variance. Some key properties covered are that the sum of independent normally distributed variables is also normally distributed, with the mean being the sum of the individual means and the variance being the sum of the individual variances. It also discusses how to compute probabilities and find values for the standard normal distribution.


![Properties of the Normal
Probability Distribution
•
Slide 5
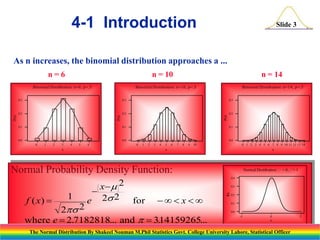
The normal is a family of
Bell-shaped and symmetric distributions. because the
distribution is symmetric, one-half (.50 or 50%) lies
on either side of the mean.
Each is characterized by a different pair of mean, ,
and variance, . That is: [X~N( )].
Each is asymptotic to the horizontal axis.
The area under any normal probability density
function within kof is the same for any normal
distribution, regardless of the mean and variance.
The Normal Distribution By Shakeel Nouman M.Phil Statistics Govt. College University Lahore, Statistical Officer](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/thenormaldistribution-140123035021-phpapp01/85/The-normal-distribution-5-320.jpg)