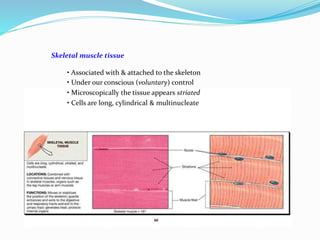
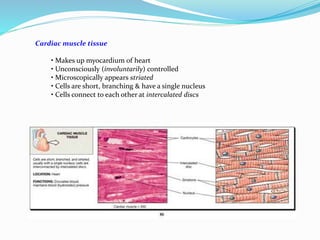
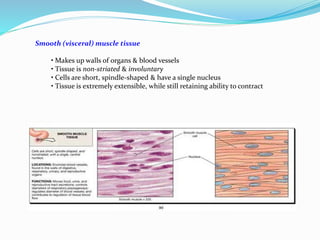
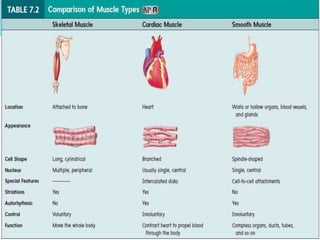
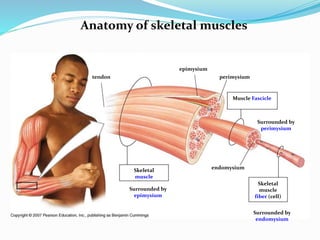
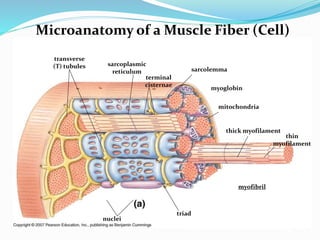
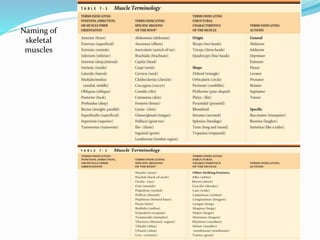
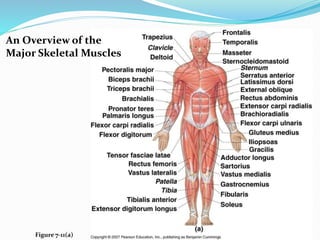
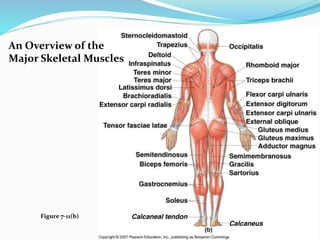
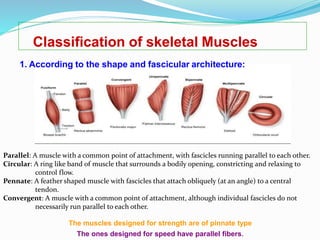
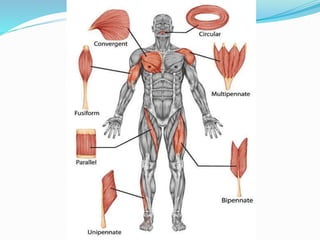
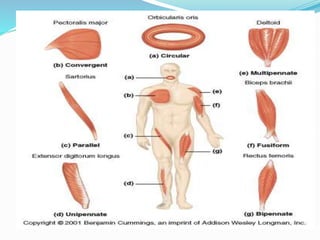
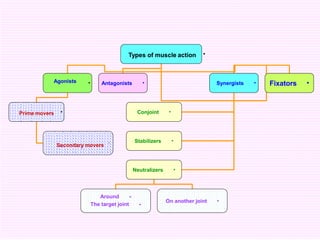
The document discusses the characteristics and types of muscle tissue. There are four main characteristics of muscle tissue: excitability, contractility, extensibility, and elasticity. These characteristics allow muscles to perform important functions like movement, posture, and temperature regulation. There are three main types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is voluntarily controlled and attached to bones. Cardiac muscle involuntarily controls the heart. Smooth muscle is involuntary and found in organs and blood vessels. The document then discusses the anatomy and functions of skeletal muscle in more detail.