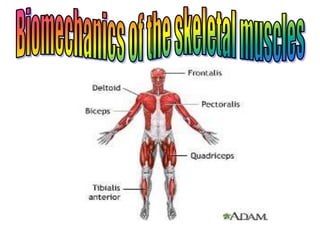
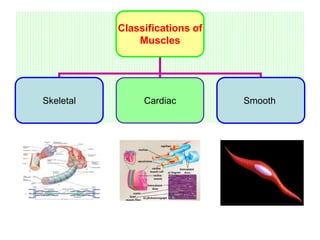
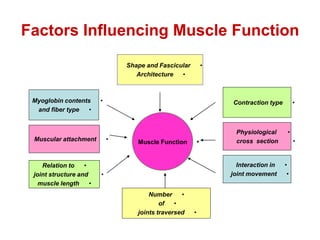
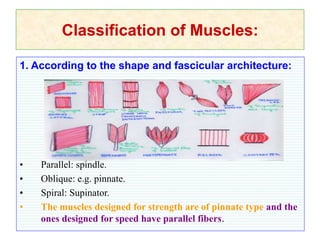
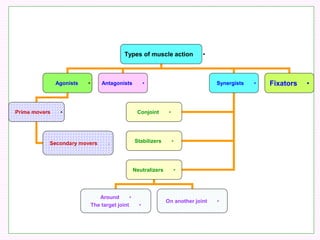
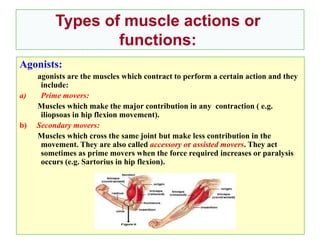
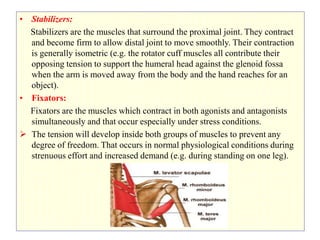
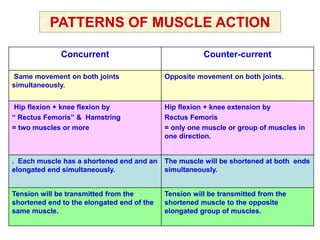
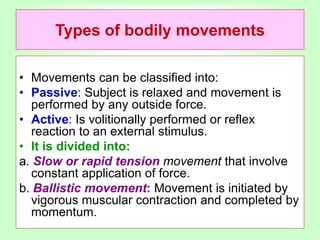
Skeletal muscles are classified according to their shape, fiber type, number of joints crossed, and action. They have properties of irritability, contractility, relaxation, distensibility, and elasticity. Factors like architecture, myoglobin content, length, and physiological cross-section influence muscle function. Skeletal muscles create movement, provide postural support, and give shape to the body through actions of agonists, antagonists, synergists, and fixators. Two-joint muscles have concurrent or countercurrent patterns of action.