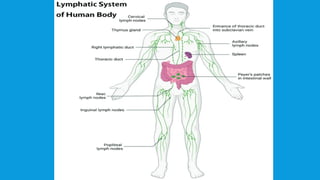
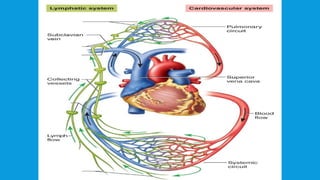
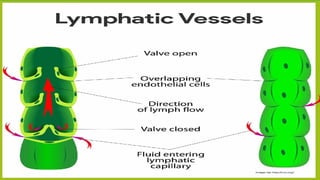
The lymphatic system is a crucial component of the circulatory and immune systems, consisting of lymphatic vessels that transport lymph, a fluid essential for fluid balance, fat absorption, and immune response. Key structures include lymph nodes, thymus, tonsils, and spleen, each performing specific functions such as filtering foreign substances, maturing T-cells, and producing antibodies. The system maintains body fluid levels and helps protect against infections by capturing and destroying pathogens.