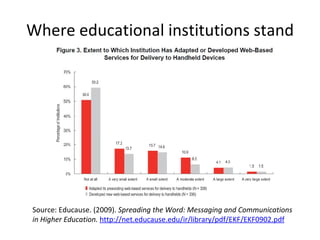
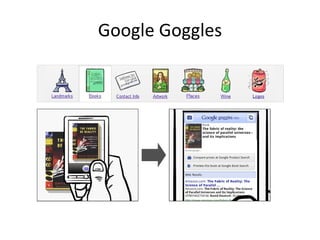
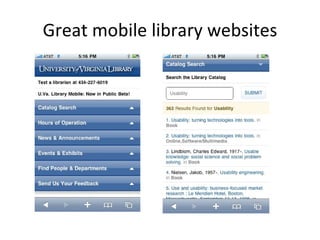
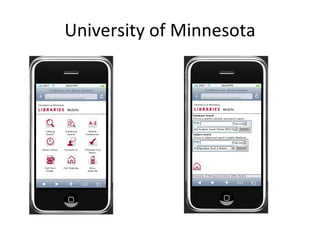
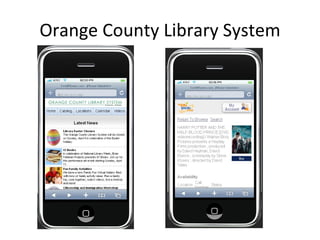
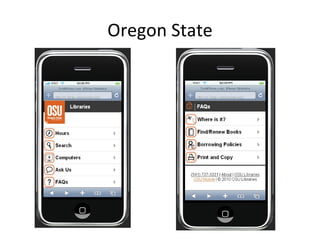
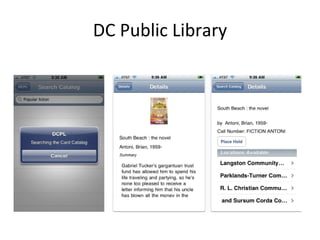
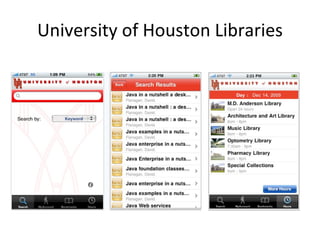
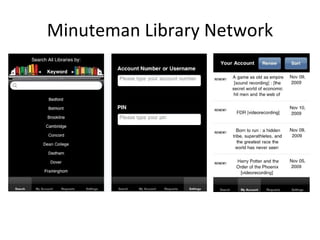
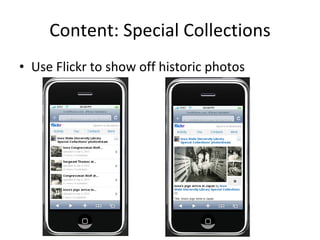
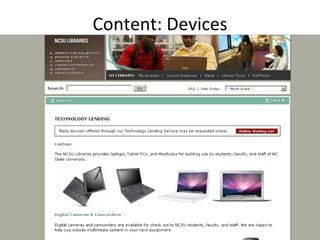
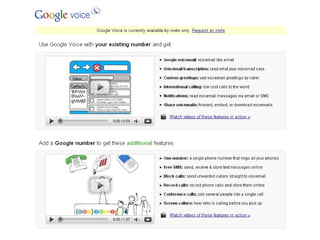
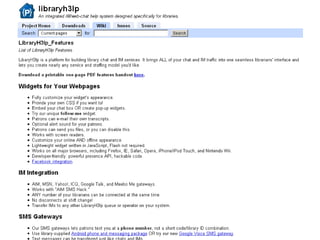
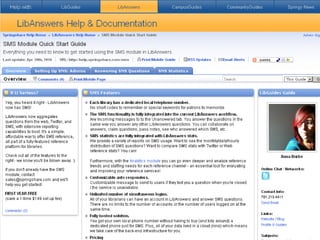
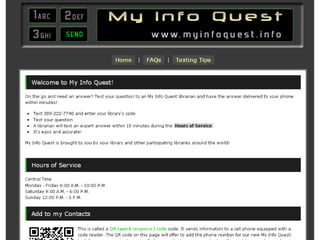
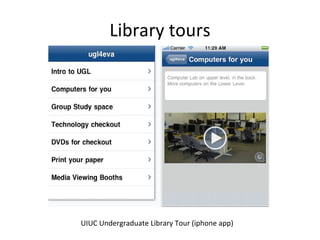
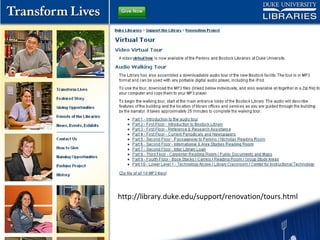
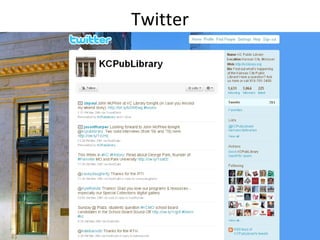
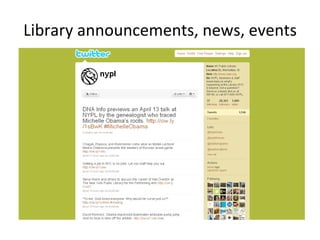
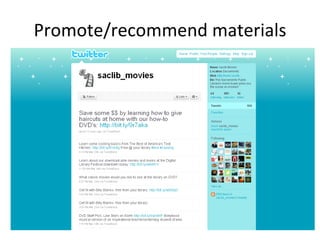
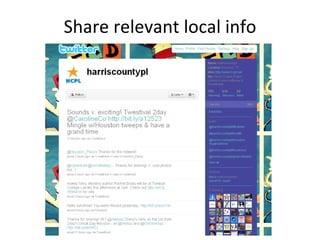
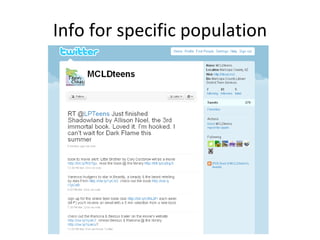
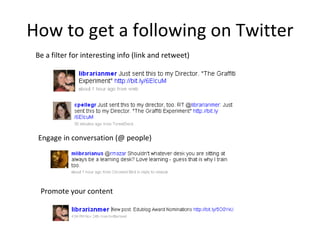
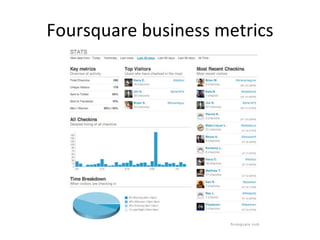
The document discusses the growing importance of mobile devices in libraries, highlighting various types of devices and their functionalities, trends in mobile applications, and social software. It emphasizes the need for libraries to adapt their services to meet mobile users' needs, including the development of mobile-friendly websites and apps. The piece also explores location-aware technologies, augmented reality, and innovative uses of mobile tools to enhance library services and user engagement.