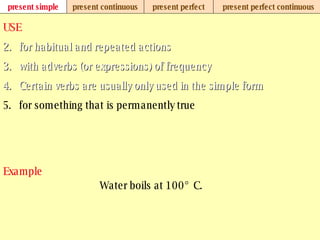
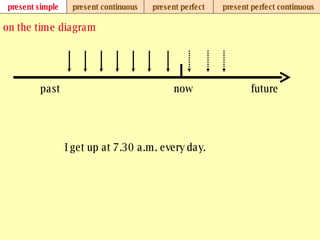
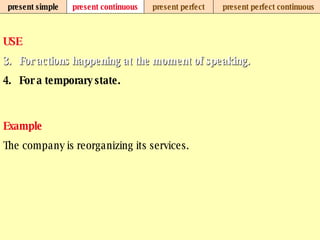
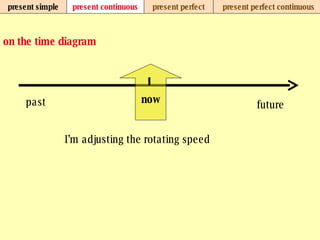
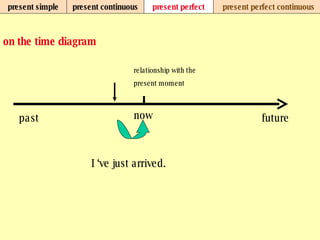
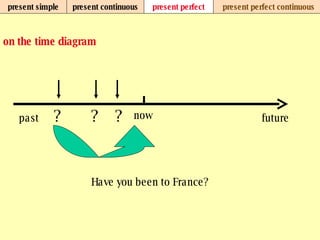
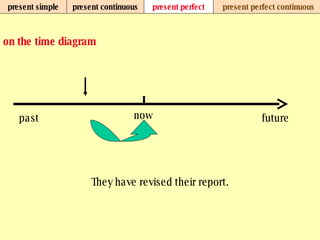
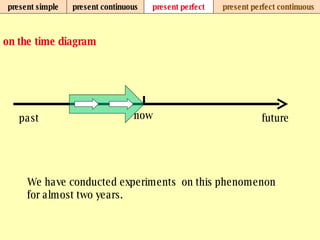
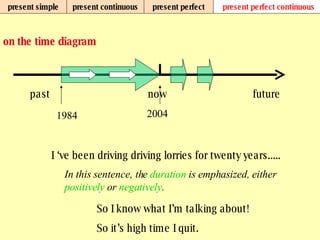
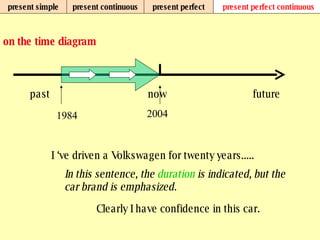
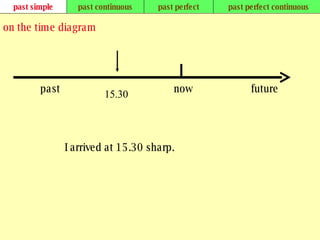
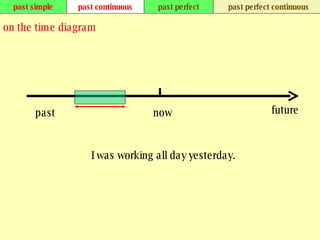
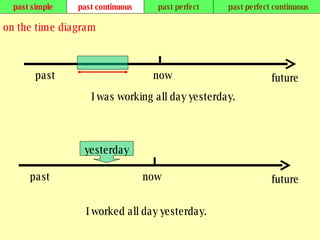
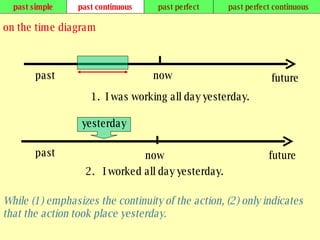
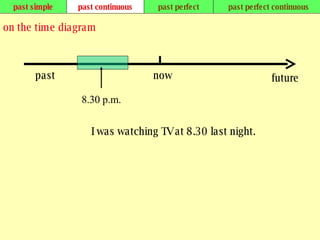
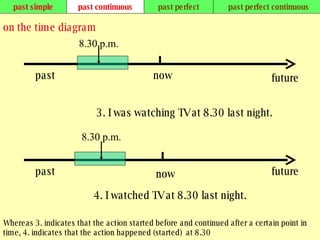
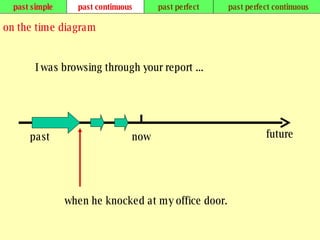
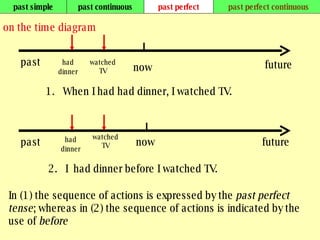
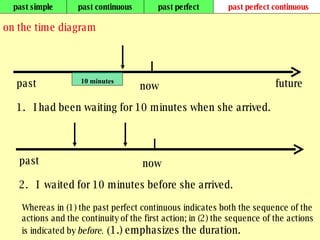
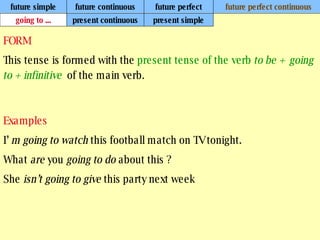
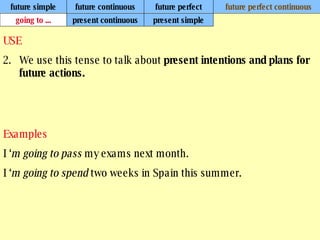
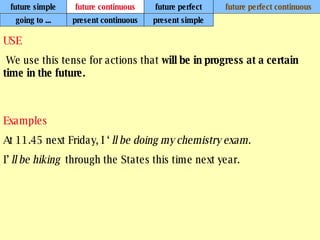
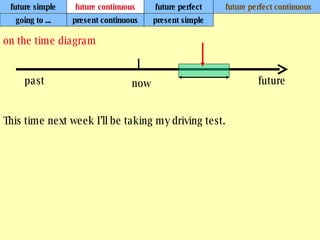
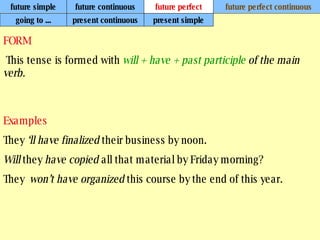
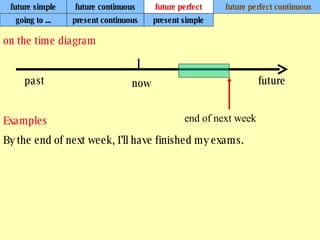
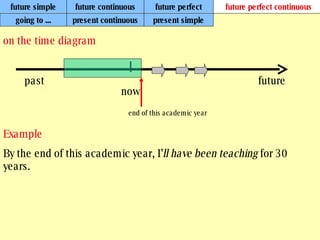
We use verb tenses to refer to actions or situations in the present, past, and future. There are four main types of tenses: simple, continuous, perfect, and perfect continuous. Each tense is formed differently and used to express different aspects of time such as completed actions, ongoing actions, or the sequence of past actions.